- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.7.11 Strength of Acids & Bases
Strong & Weak Acids & Bases
- Strong and weak acids can be distinguished from each other by their:
- pH value (using a pH meter or universal indicator)
- Electrical conductivity
- Reactivity
pH
- An acid dissociates into H+ in solution according to:
HA → H+ + A-
- The stronger the acid, the greater the concentration of H+ and therefore the lower the pH
pH value of a strong acid & base table

- The most accurate way to determine the pH is by reading it off a pH meter
- The pH meter is connected to the pH electrode which shows the pH value of the solution
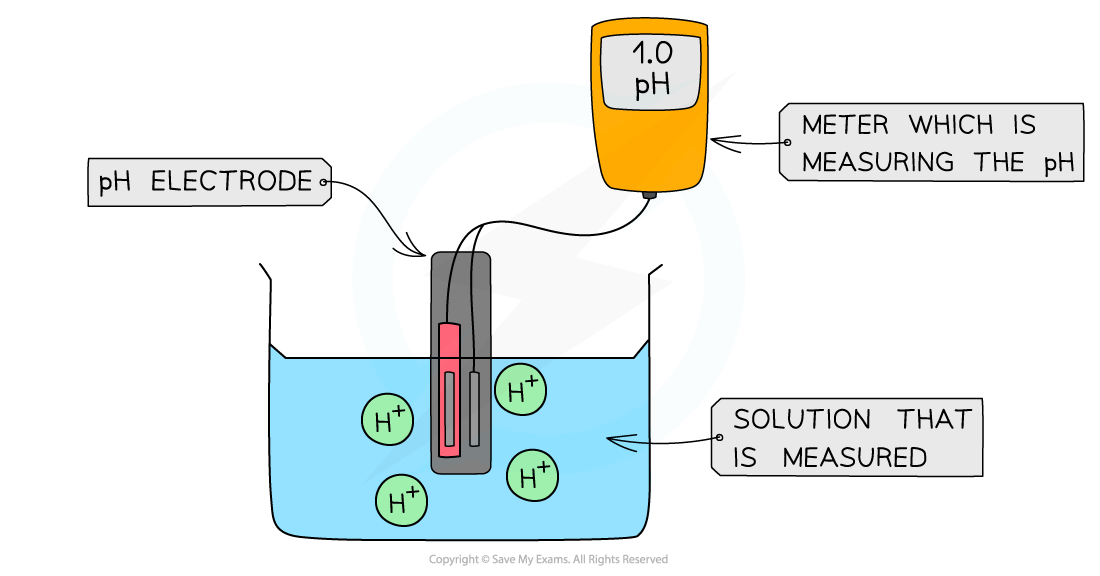
The diagram shows a digital pH meter that measures the pH of a solution using a pH electrode
- A less accurate method is to measure the pH using universal indicator paper
- The universal indicator paper is dipped into a solution of acid upon which the paper changes colour
- The colour is then compared to those on a chart which shows the colours corresponding to different pH values
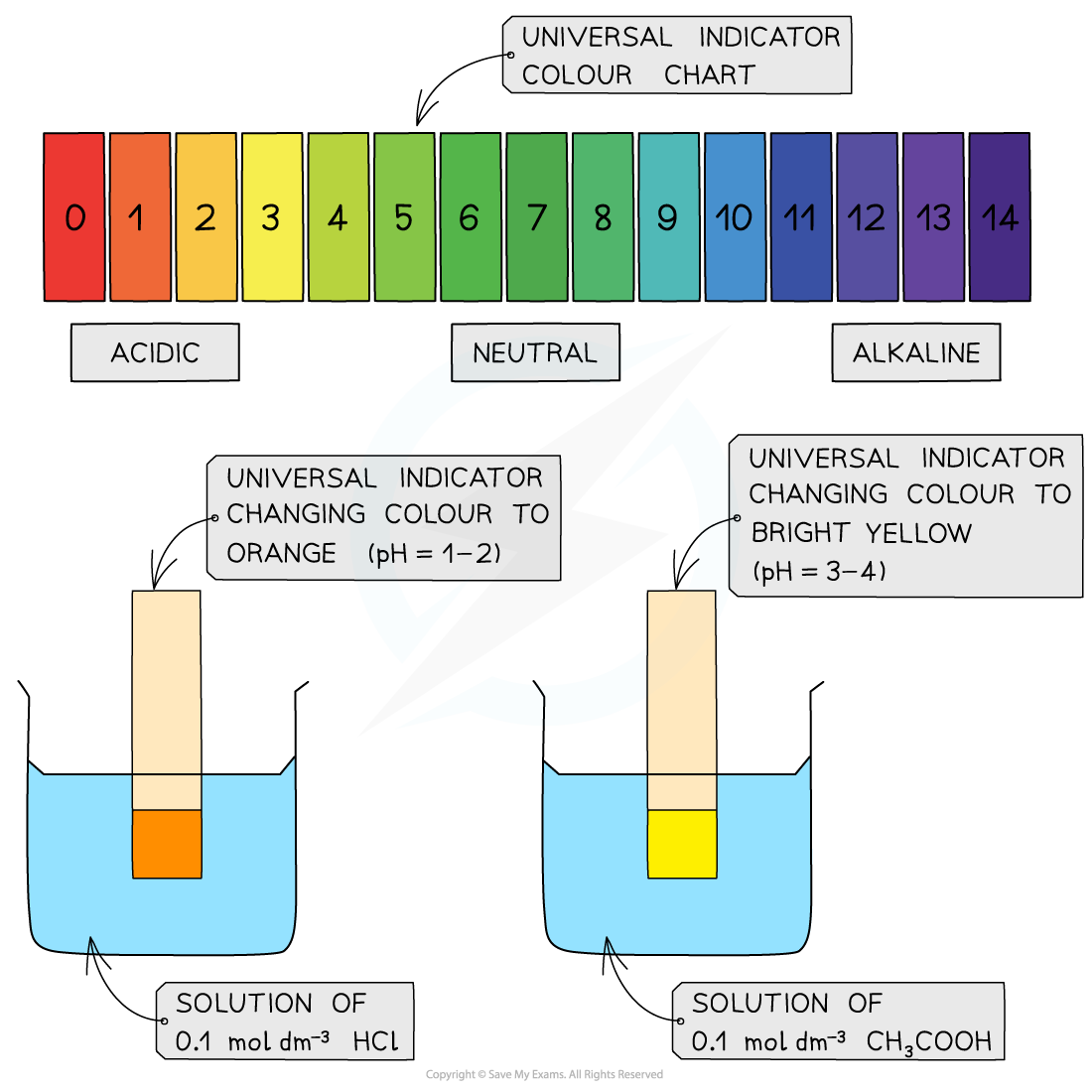
The diagram shows the change in colour of the universal indicator paper when dipped in a strong (HCl) and weak (CH3COOH) acid. The colour chart is used to read off the corresponding pH values which are between 1-2 for HCl and 3-4 for CH3COOH
Electrical conductivity
- Since a stronger acid has a higher concentration of H+ it conducts electricity better
- Stronger acids therefore have a greater electrical conductivity
- The electrical conductivity can be determined by using a conductivity meter
- Like the pH meter, the conductivity meter is connected to an electrode
- The conductivity of the solution can be read off the meter
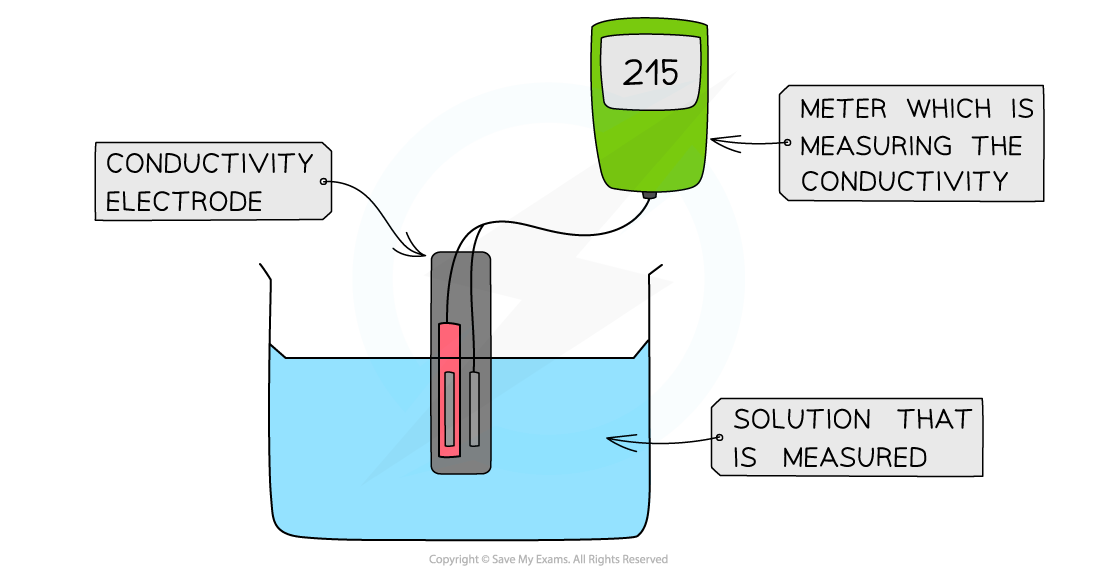 The diagram shows a digital conductivity meter that measures the electrical conductivity of a solution using an electrode
The diagram shows a digital conductivity meter that measures the electrical conductivity of a solution using an electrode
Reactivity
- Strong and weak acids of the same concentrations react differently with reactive metals
- This is because the concentration of H+ is greater in strong acids compared to weak acids
- The greater H+ concentration means that more H2 gas is produced
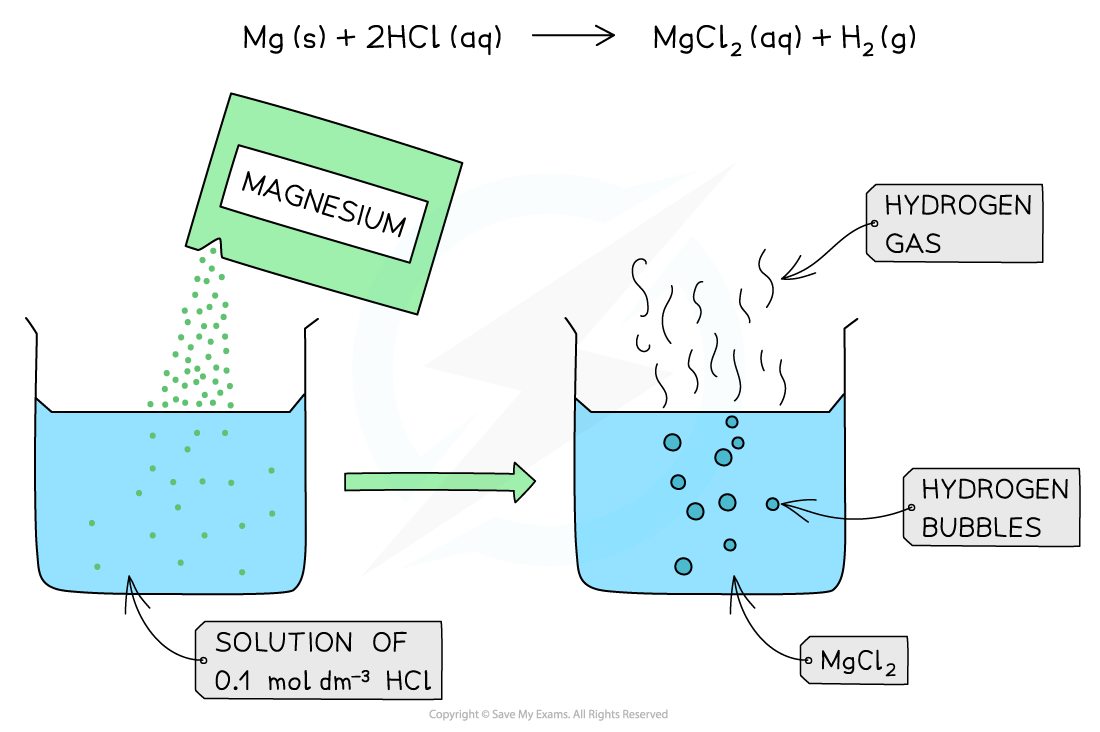 The diagram shows the reaction of 0.1 mol dm-3 of a strong acid (HCl) with Mg. The reaction produces a lot of bubbles and hydrogen gas due to the high concentration of H+ present in solution
The diagram shows the reaction of 0.1 mol dm-3 of a strong acid (HCl) with Mg. The reaction produces a lot of bubbles and hydrogen gas due to the high concentration of H+ present in solution
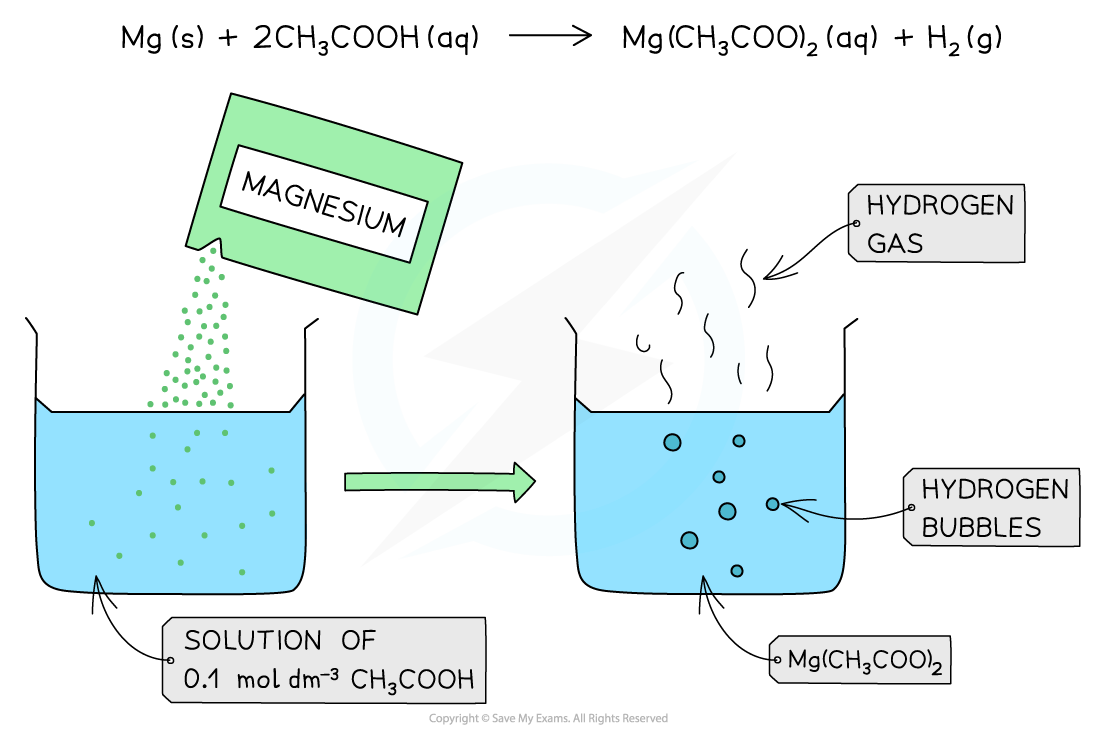
The diagram shows the reaction of 0.1 mol dm-3 of a weak acid (CH3COOH) with Mg. The reaction produces less bubbles and hydrogen gas due to the lower concentration of H+ present in solution
Exam Tip
The above-mentioned properties of strong and weak acids depend on their ability to dissociate and form H+ ions.Stronger acids dissociate more, producing a greater concentration of H+ ions and therefore showing lower pH values, greater electrical conductivity and more vigorous reactions with reactive metals.
Neutralisation Reactions
- A neutralisation reaction is one in which an acid (pH <7) and a base/alkali (pH >7) react together to form water (pH = 7) and a salt

- The proton of the acid reacts with the hydroxide of the base to form water

- The spectator ions which are not involved in the formation of water, form the salt
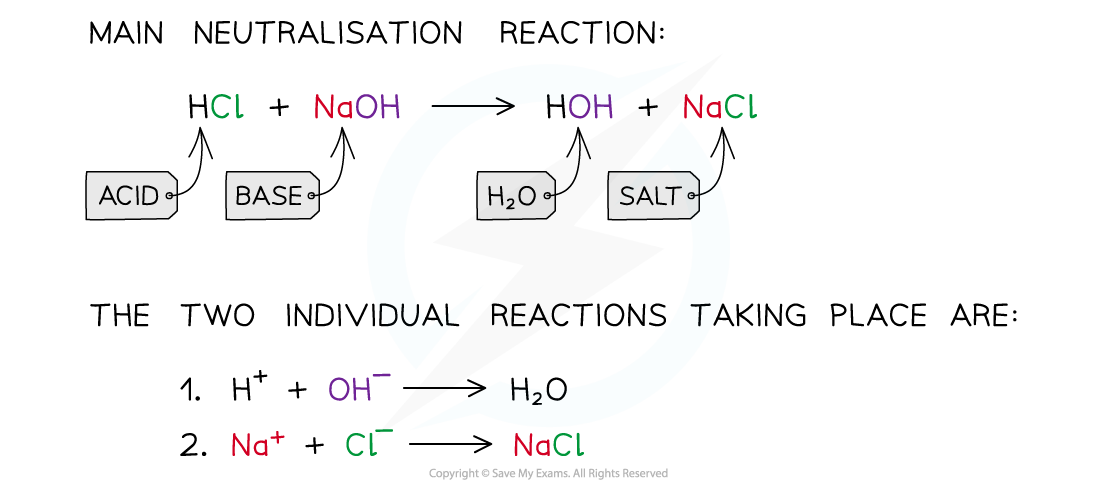
The diagram shows a neutralisation reaction of HCl and NaOH and the two individual reactions that take place to form the water and salt
- The name of the salt produced can be predicted from the acid that has reacted
Acid reacted & salt table

Exam Tip
Note that the reaction of an acid and metal carbonate also forms carbon dioxide:
acid + metal carbonate → salt + water + carbon dioxide
转载自savemyexams


最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








