- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.7.9 Acid & Base Dissociation
Acid & Base Dissociation
Strong acids
- A strong acid is an acid that dissociates almost completely in aqueous solutions
- HCl (hydrochloric acid), HNO3 (nitric acid) and H2SO4 (sulfuric acid)
- The position of the equilibrium is so far over to the right that you can represent the reaction as an irreversible reaction
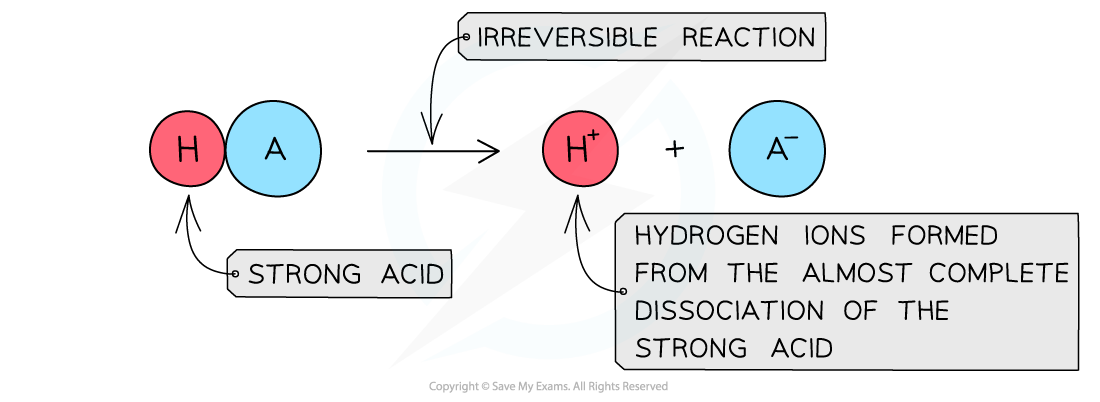
The diagram shows the almost complete dissociation of a strong acid in aqueous solution
- The solution formed is highly acidic due to the high concentration of the H+/H3O+ ions
- Since the pH depends on the concentration of H+/H3O+ ions, the pH can be calculated if the concentration of the strong acid is known
 pH is the negative log of the concentration of H+/H3O+ ions and can be calculated if the concentration of the strong acid is known using the stoichiometry of the reaction
pH is the negative log of the concentration of H+/H3O+ ions and can be calculated if the concentration of the strong acid is known using the stoichiometry of the reaction
Weak acids
- A weak acid is an acid that partially (or incompletely) dissociates in aqueous solutions
- Eg. most organic acids (ethanoic acid), HCN (hydrocyanic acid), H2S (hydrogen sulfide) and H2CO3 (carbonic acid)
- The position of the equilibrium is more over to the left and an equilibrium is established
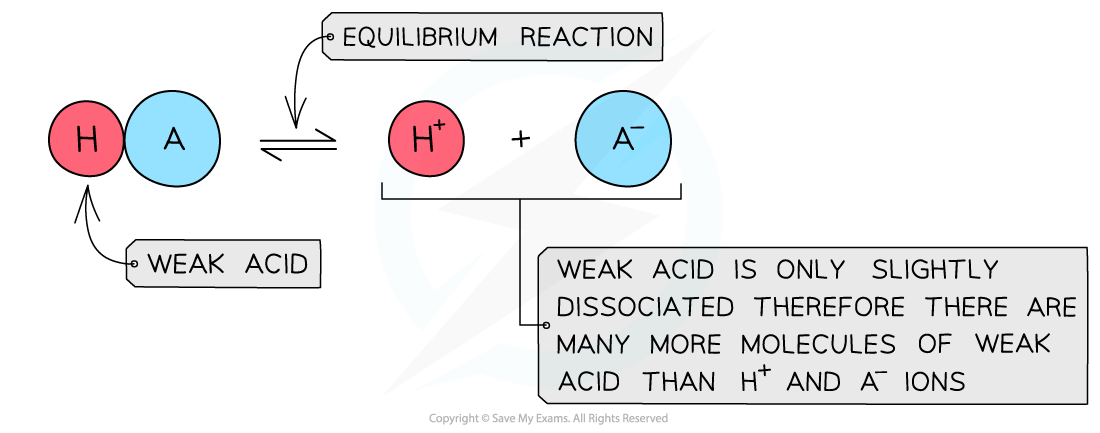
The diagram shows the almost complete dissociation of a weak acid in aqueous solution
- The solution is less acidic due to the lower concentration of H+/H3O+ ions
- Finding the pH of a weak acid is a bit more complicated as now the concentration of H+ ions is not equal to the concentration of acid
- To find the concentration of H+ ions, the acid dissociation constant (Ka) should be used
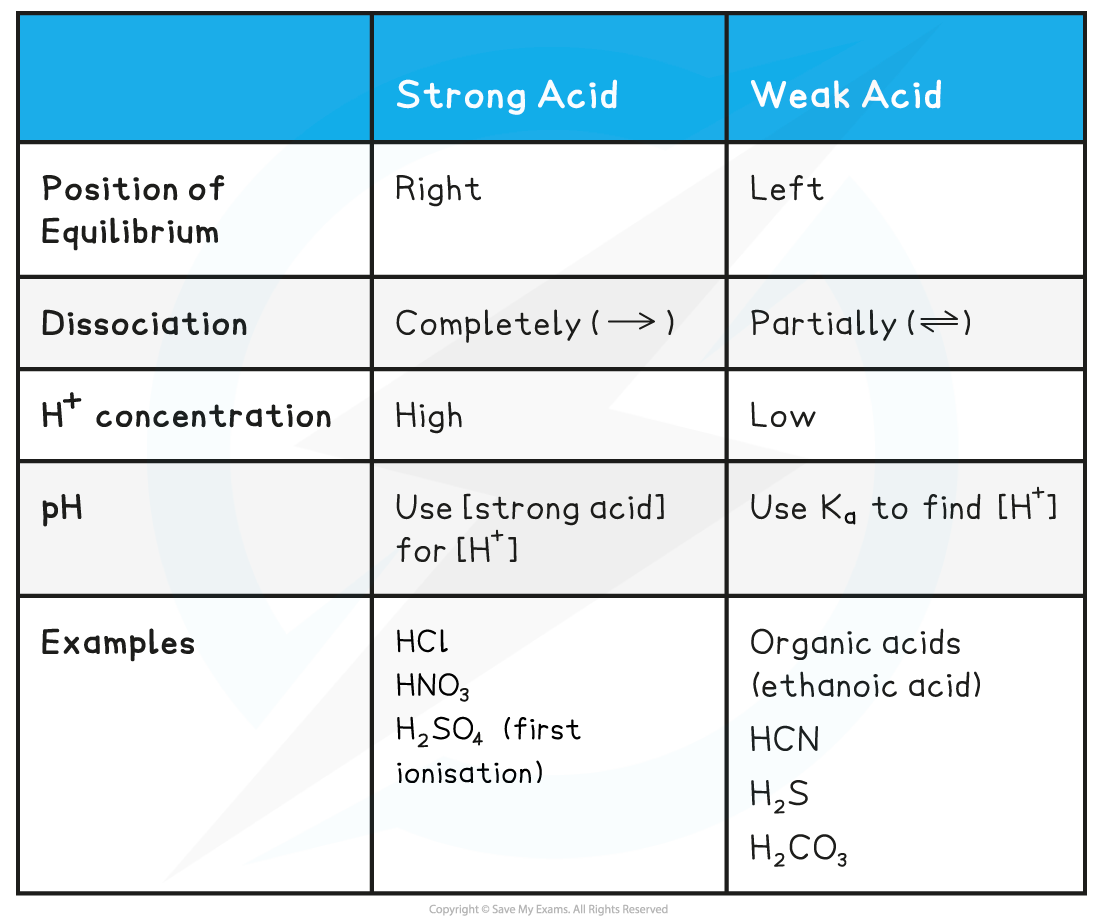
Acid & equilibrium position table
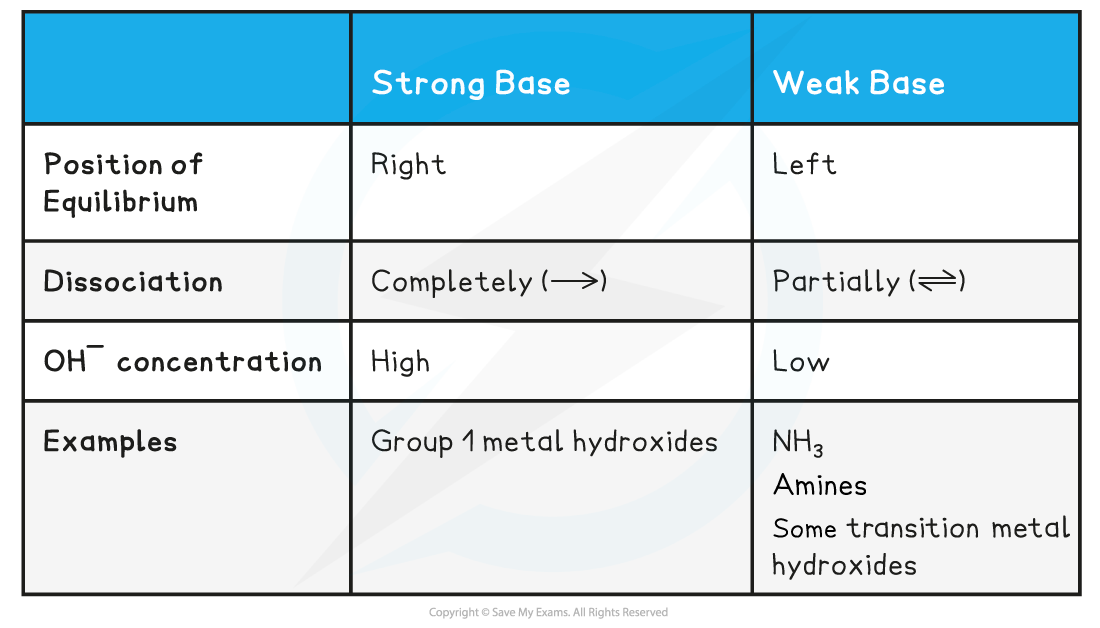
Strong bases
- A strong base is a base that dissociates almost completely in aqueous solutionsE.g. group 1 metal hydroxides such as NaOH (sodium hydroxide)
The position of the equilibrium is so far over to the right that you can represent the reaction as an irreversible reaction
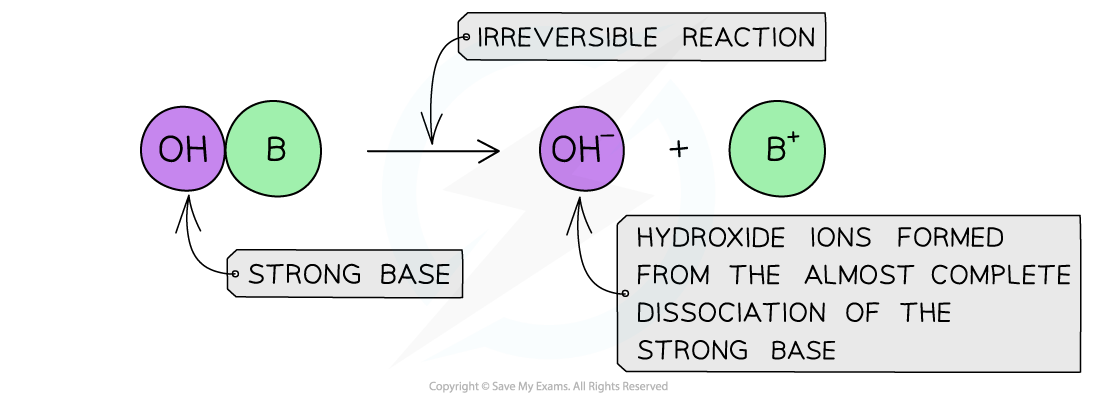 The diagram shows the almost complete dissociation of a strong base in aqueous solution
The diagram shows the almost complete dissociation of a strong base in aqueous solution
- The solution formed is highly basic due to the high concentration of the OH- ions
Weak bases
- A weak base is a base that partially (or incompletely) dissociates in aqueous solutions
- NH3 (ammonia), amines and some hydroxides of transition metals
- The position of the equilibrium is more to the left and an equilibrium is established
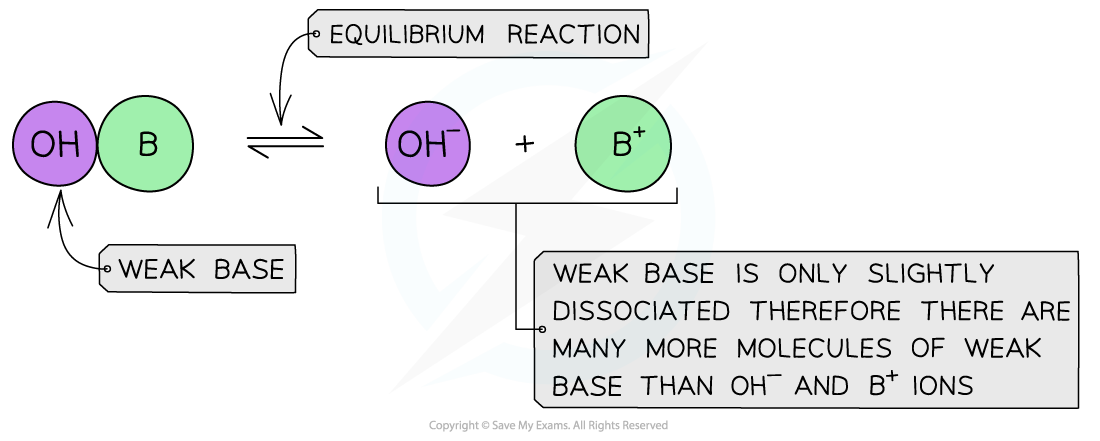
The diagram shows the almost complete dissociation of a weak base in aqueous solution
- The solution is less basic due to the lower concentration of OH- ions
Base & equilibrium position table
Exam Tip
Hydrogen ions in aqueous solutions can be written as either as H3O+ or as H+ however, if H3O+ is used, H2O should be included in the chemical equation:HCl(g) → H+(aq) + Cl-(aq)orHCl(g) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Remember that some acids are both strong and weak acids – for example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) has two hydrogen ions that can ionise.H2SO4 acts as a strong acid: H2SO4 → H+ + SO4-HSO4- acts as a weak acid: HSO4-⇌ H+ + SO42- Also, don't forget that the terms strong and weak acids and bases are related to the degree of dissociation and not the concentration.The appropriate terms to use when describing concentration are dilute and concentrated.
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








