- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.7.2 Le Chaterlier's Principle
Le Chatelier's Principle
Position of the equilibrium
- The position of the equilibrium refers to the relative amounts of products and reactants in an equilibrium mixture.
- When the position of equilibrium shifts to the left, it means the concentration of reactants increases
- When the position of equilibrium shifts to the right, it means the concentration of products increases
Le Chatelier’s principle
- Le Chatelier’s principle says that if a change is made to a system at dynamic equilibrium, the position of the equilibrium moves to minimise this change
- The principle is used to predict changes to the position of equilibrium when there are changes in temperature, pressure or concentration
Effects of concentration
Effects of concentration table

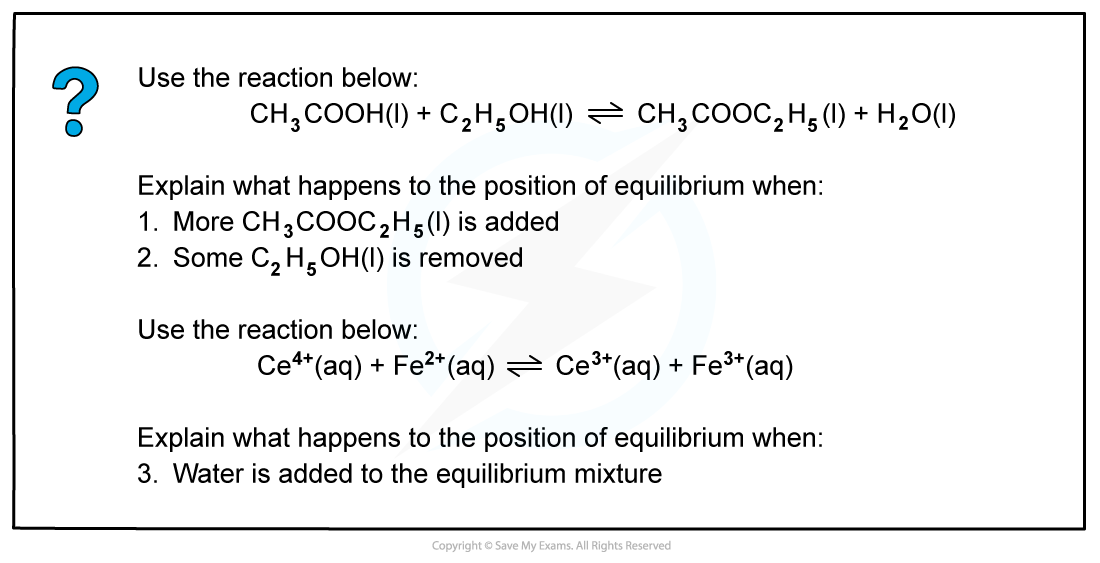
Worked example: Changes in equilibrium position
Answer
Answer 1:
The position of the equilibrium moves to the left and more ethanoic acid and ethanol are formed.The reaction moves in this direction to oppose the effect of added ethyl ethanoate, so the ethyl ethanoate decreases in concentration.
Answer 2:
The position of the equilibrium moves to the left and more ethanoic acid and ethanol are formed.
The reaction moves in this direction to oppose the removal of ethanol so more ethanol (and ethanoic acid) are formed from ethyl ethanoate and water.
Answer 3:
There is no effect as the water dilutes all the ions equally so there is no change in the ratio of reactants to products.
Effects of pressure
- Changes in pressure only affect reactions where the reactants or products are gases
Effects of pressure table

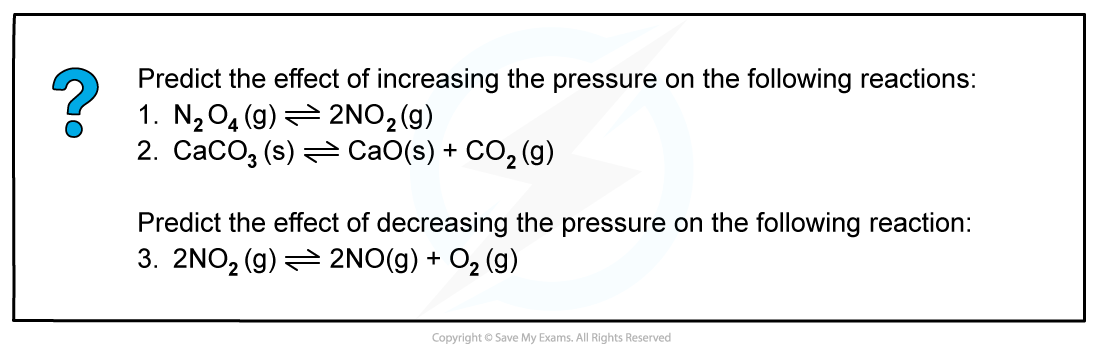
Worked example: Changes in pressure
Answer
Answer 1:
The equilibrium shifts to the left as there are fewer gas molecules on the left.This causes a decrease in pressure.
Answer 2:
The equilibrium shifts to the left as there are no gas molecules on the left but there is CO2 on the right.
This causes a decrease in pressure.
Answer 3:
The equilibrium shifts to the right as there is a greater number of gas molecules on the right.This causes an increase in pressure.
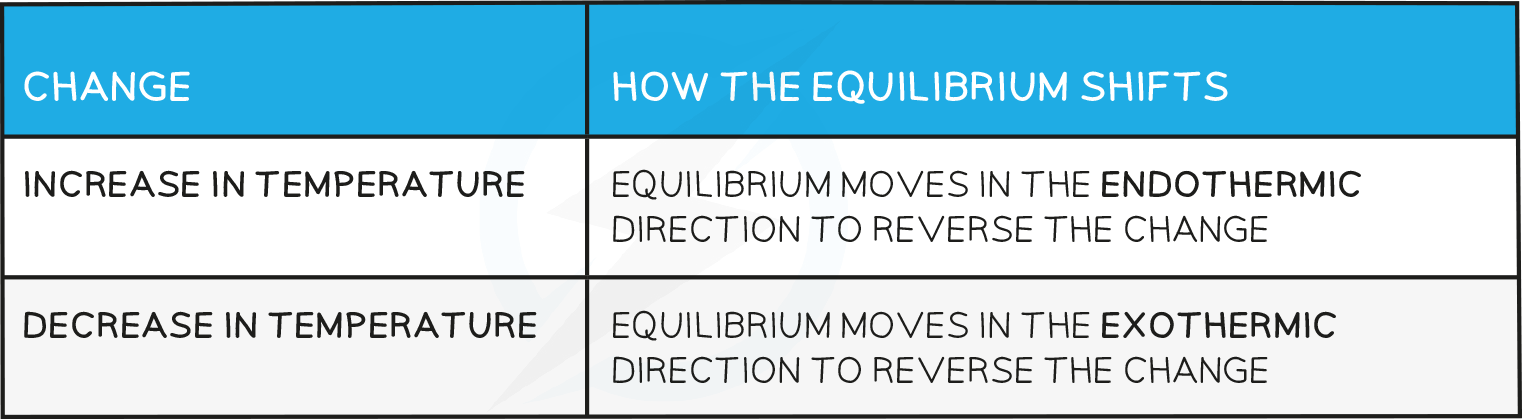
Effects of temperature
Effects of temperature table
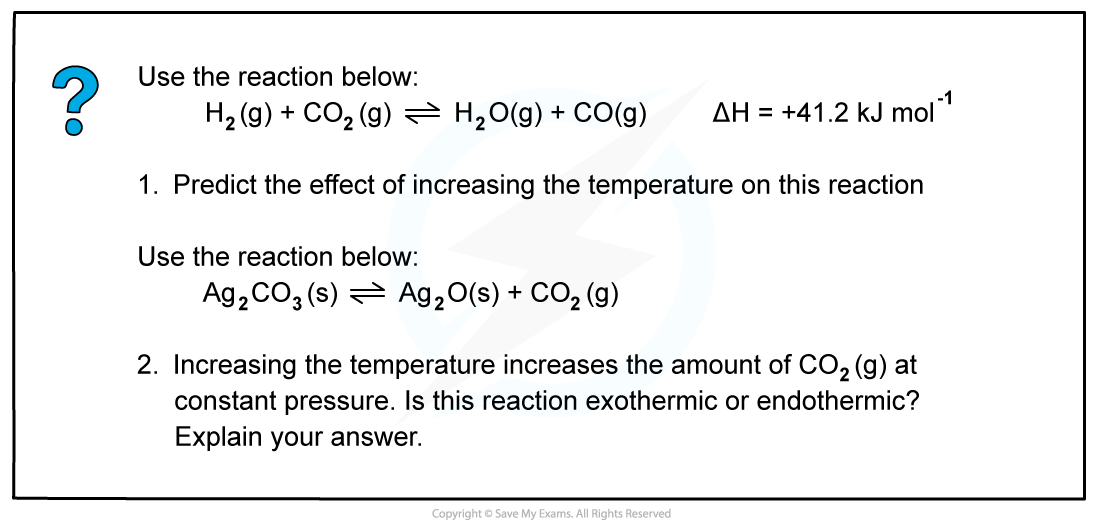
Worked example: Changes in temperature
Answer
Answer 1:
The reaction will absorb the excess energy and since the forward reaction is endothermic, the equilibrium will shift to the right.Answer 2:
The reaction will absorb the excess energy and since this causes a shift of the equilibrium towards the right (as more CO2(g) is formed) this means that the reaction is endothermic (because endothermic reactions favour the products).
Effects of catalysts
- A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction (they increase the rate of the forward and reverse reaction equally)
- Catalysts only cause a reaction to reach its equilibrium faster
- Catalysts therefore have no effect on the position of the equilibrium once this is reached
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1