- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry复习笔记1.3.1 Electronegativity
Electronegativity: Definition
- Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract a pair of electrons towards itself in a covalent bond
- This phenomenon arises from the positive nucleus’s ability to attract the negatively charged electrons, in the outer shells, towards itself
- The Pauling scale is used to assign a value of electronegativity for each atom
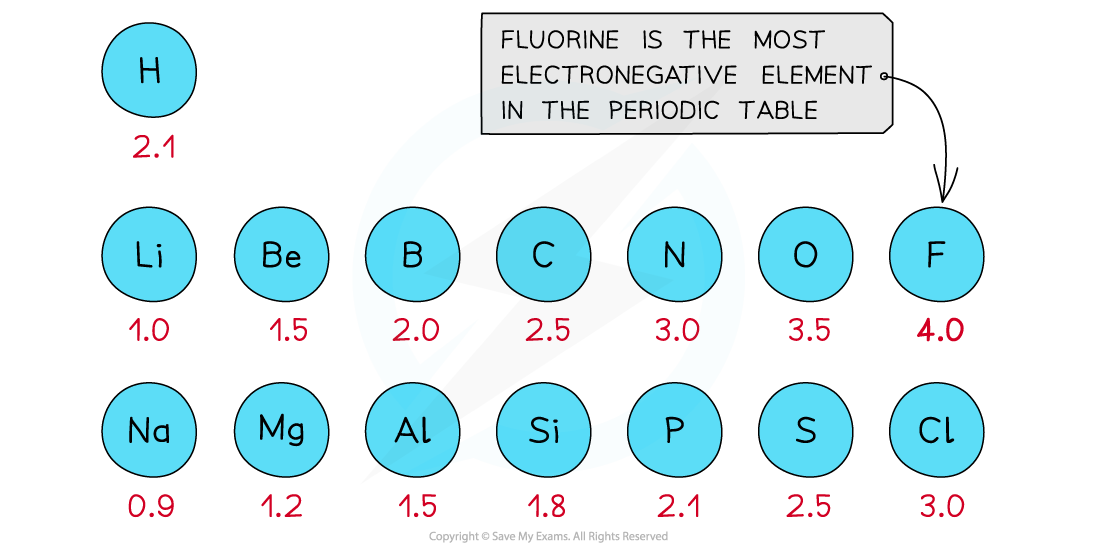
First three rows of the periodic table showing electronegativity values
- Fluorine is the most electronegative atom on the Periodic Table, with a value of 4.0 on the Pauling Scale
- It is best at attracting electron density towards itself when covalently bonded to another atom
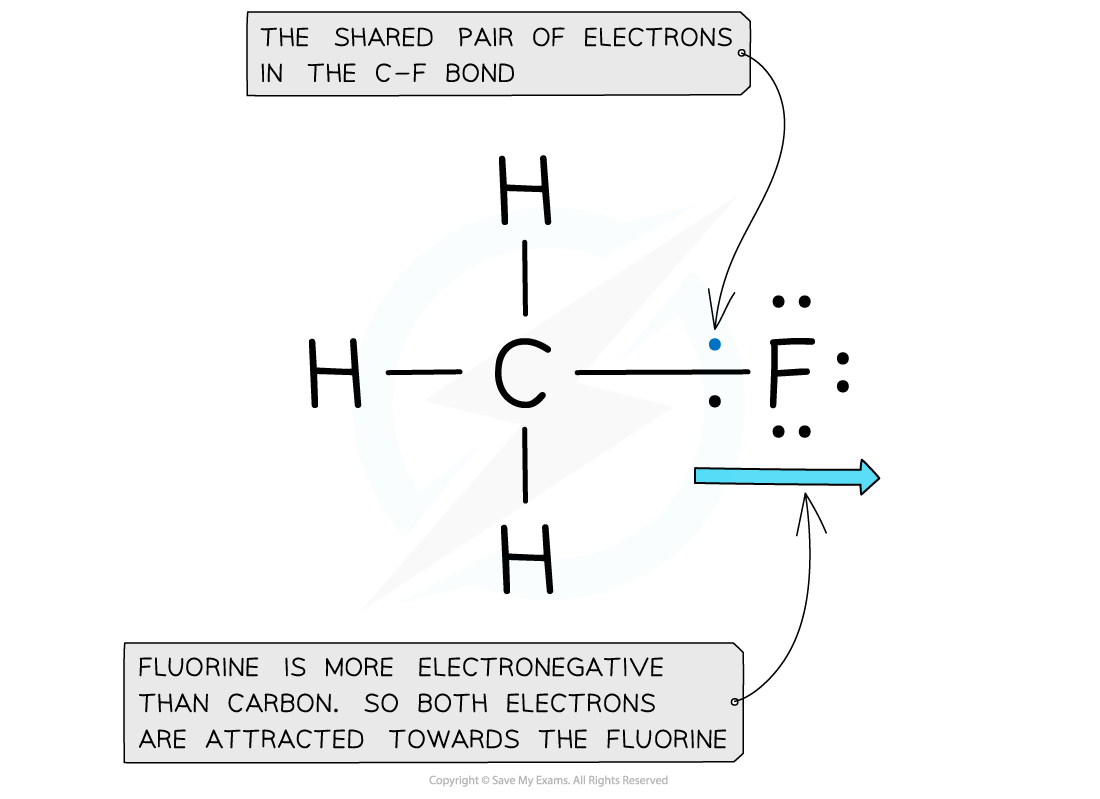
Electron distribution in the C-F bond of fluoromethane
Electronegativity: Affecting Factors
Nuclear charge
- Attraction exists between the positively charged protons in the nucleus and negatively charged electrons found in the energy levels of an atom
- An increase in the number of protons leads to an increase in nuclear attraction for the electrons in the outer shells
- Therefore, an increased nuclear charge results in an increased electronegativity
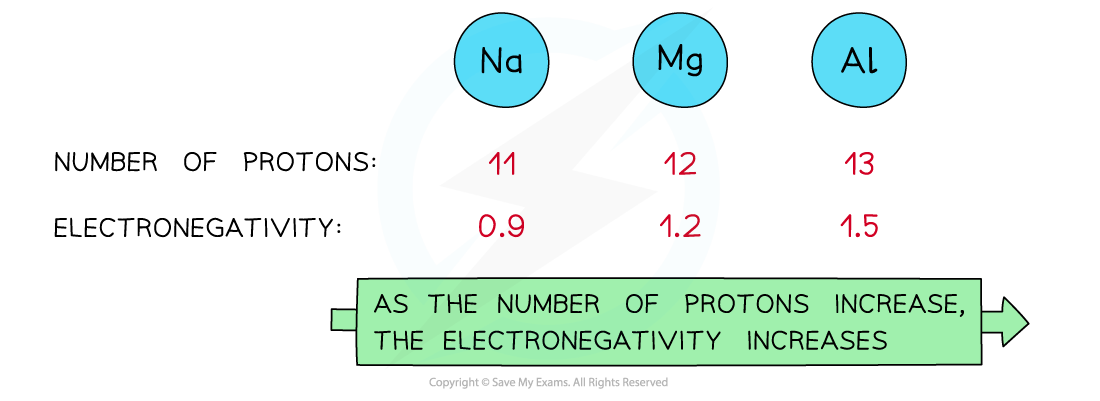
As the nuclear charge increases, the electronegativity of an element increases as well
Atomic radius
- The atomic radius is the distance between the nucleus and electrons in the outermost shell
- Electrons closer to the nucleus are more strongly attracted towards its positive nucleus
- Those electrons further away from the nucleus are less strongly attracted towards the nucleus
- Therefore, an increased atomic radius results in a decreased electronegativity
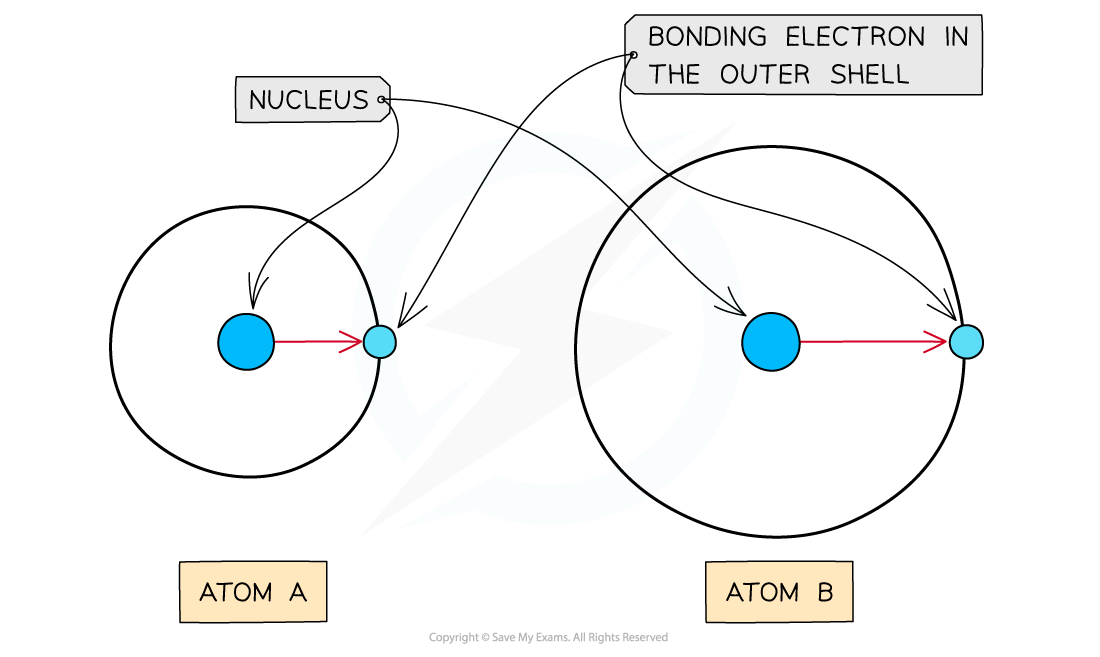
As the atomic radius increases, the nucleus has less of an attraction for the bonding electrons causing atom A to have a higher electronegativity than atom B
Shielding
- Filled energy levels can shield (mask) the effect of the nuclear charge causing the outer electrons to be less attracted to the nucleus
- Therefore, the addition of extra shells and subshells in an atom will cause the outer electrons to experience less of the attractive force of the nucleus
- Sodium (Period 3, Group 1) has higher electronegativity than caesium (Period 6, Group 1) as it has fewer shells and therefore the outer electrons experience less shielding than in caesium
- Thus, an increased number of inner shells and subshells will result in a decreased electronegativity
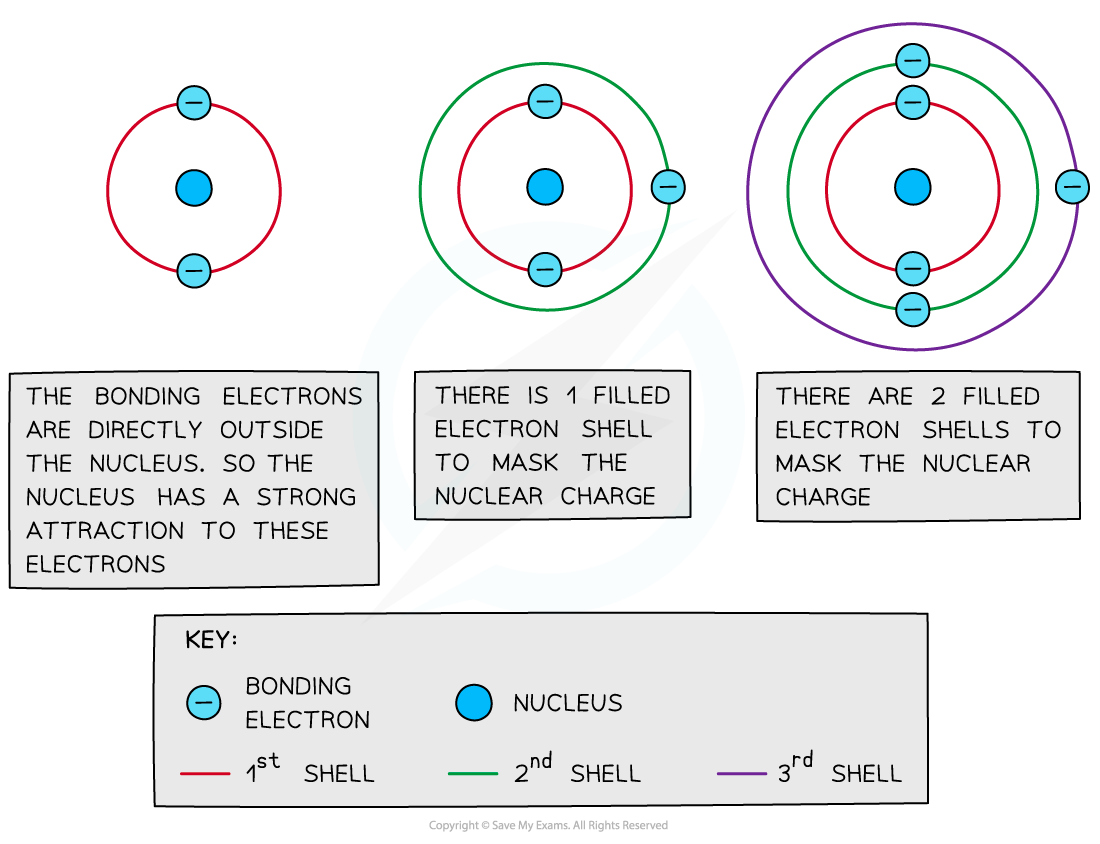
Filled inner energy levels mask the nuclear attraction from the outer bonding electrons
Exam Tip
The nuclear charge, atomic radius and shielding are all linked to each other.As nuclear charge increases, the nucleus has a greater attractive force on the electrons in shells given that the shielding doesn’t increase.As a result of this, the atomic radius decreases.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









