- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Biology复习笔记18.3.2 Reasons for Maintaining Biodiversity
Reasons for Maintaining Biodiversity
- Biodiversity is the range and variety of genes, species and habitats within a particular region
- It is made up of three components:
- Genetic diversity
- Species diversity
- Ecosystem diversity
- Global biodiversity has a major impact on humans and all other species on the planet
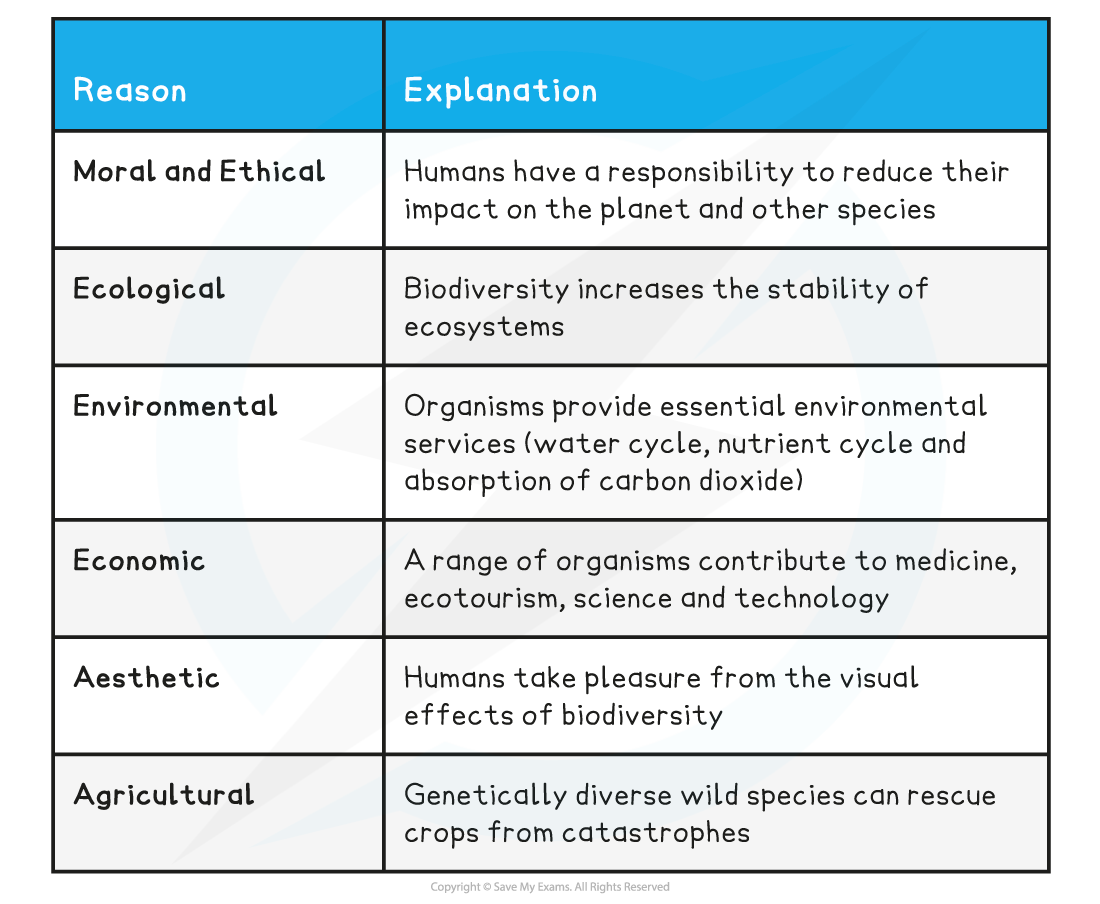
- There are many reasons for maintaining biodiversity:
- Moral and ethical
- Ecological
- Environmental
- Economic
- Aesthetic
- Agricultural
Moral & ethical reasons
- Many people believe that humans have a moral obligation to prevent the manmade loss of biodiversity
- Humans share the planet with millions of others species and they have no right to cause the extinction of other species
- As humans are the most intelligent species on the planet the responsibility falls upon their shoulders to protect and value all of the organisms on the planet
Ecological reasons
- Biodiversity has a major effect on the stability of an ecosystem
- A more diverse ecosystem is better able to survive and adapt to environmental changes or threats
- For example, if the temperature of a species-rich lake rises due to global warming:
- Some species of fish in the ecosystem are unable to cope with the change while others can
- The fish that are able to cope will survive, reproduce and keep contributing to the ecosystem
- Within communities there are keystone species that have a larger impact on the ecosystem than others
- When these species are lost there are several knock-on effects
- Bush elephants in the African savannah are a keystone species
- They graze in a very extreme way, knocking over and eating several species of tree
- This destruction of vegetation actually helps to maintain the ecosystem
- Elephant dung also provides a habitat for many important fungi and insect species
- When elephants were legally hunted for their ivory, their numbers reduced and scientists observed a major negative impact on the savannah
Environmental reasons
- Humans need diverse ecosystems because of the essential environmental services they provide
- Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and help to reduce the greenhouse effect and climate change
- Microorganisms digest and break down the masses of organic waste that are produced by larger organisms
- Humans have irrigation and drinking water thanks to the transpiration of plants and their contribution to the water cycle
- Different fungi and bacteria species are a major part of the nutrient cycle that allows for nutrients to reenter the soil for further plant growth
- Plants are producers in food webs. They are both a direct and indirect energy source for humans through fruit, vegetables and meat
Economic reasons
- Ecosystems have a lot of economic value
- Many of the medicines used today have originated from plants, fungi and bacteria
- For example the cancer-fighting drug paclitaxel is sourced from Pacific and Himalayan Yew Trees
- The Himalayan Yew has declined in numbers due to over-harvesting for fuel and medicine
- Due to the large number of drugs that have already been sourced from nature it is reasonable to assume that there are other drugs, yet to be found in nature, that could be used in the future
- Ecotourism a major source of income for many countries
- Many tourists travel to and spend money in National parks so they can see wildlife
- Increased tourism in a country contributes to the economy and provides jobs
- Ecosystems have also made major contributions to the field of science and technology
- The specific enzyme used in DNA sequencing was first discovered in thermophilic bacterium found in a hot spring in Yellowstone National Park, USA
Aesthetic reasons
- Humans find great joy and pleasure in the beauty of nature
- It provides inspiration for creatives such as photographers, poets, musicians and artists
- There is a strong argument for preserving biodiversity because of its aesthetic benefits
Agricultural reasons
- Most of the crops that humans grow are very uniform with low genetic diversity
- The wild relatives of crops can provide a source of genetic diversity to rescue crops that are affected by disease or other disasters
- Many of the wild relative species are under threat due to habitat destruction and climate change
- All of the world's potato crop comes from a single species
- This lack of species diversity makes the crop highly susceptible to disease
- There are over 100 species of wild potatoes that grow in the Andes
- These Andean species act as a source of alleles for disease resistance
- These alleles have been introduced to the potato crop through gene technology and interbreeding
Summary of reasons for maintaining biodiversity table
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








