- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Biology复习笔记14.1.5 Formation of Urine
Formation of Urine in the Nephron
- The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney – the nephrons are responsible for the formation of urine
- The process of urine formation in the kidneys occurs in two stages:
-
- Ultrafiltration
- Selective reabsorption
The Two Stages of Urine Production in the Kidneys Table
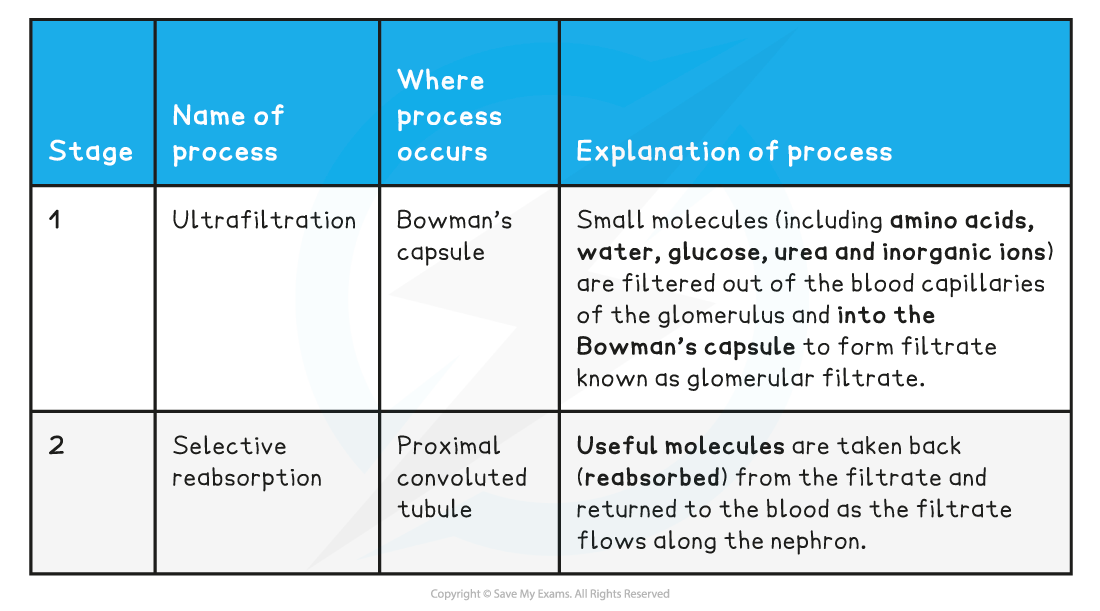
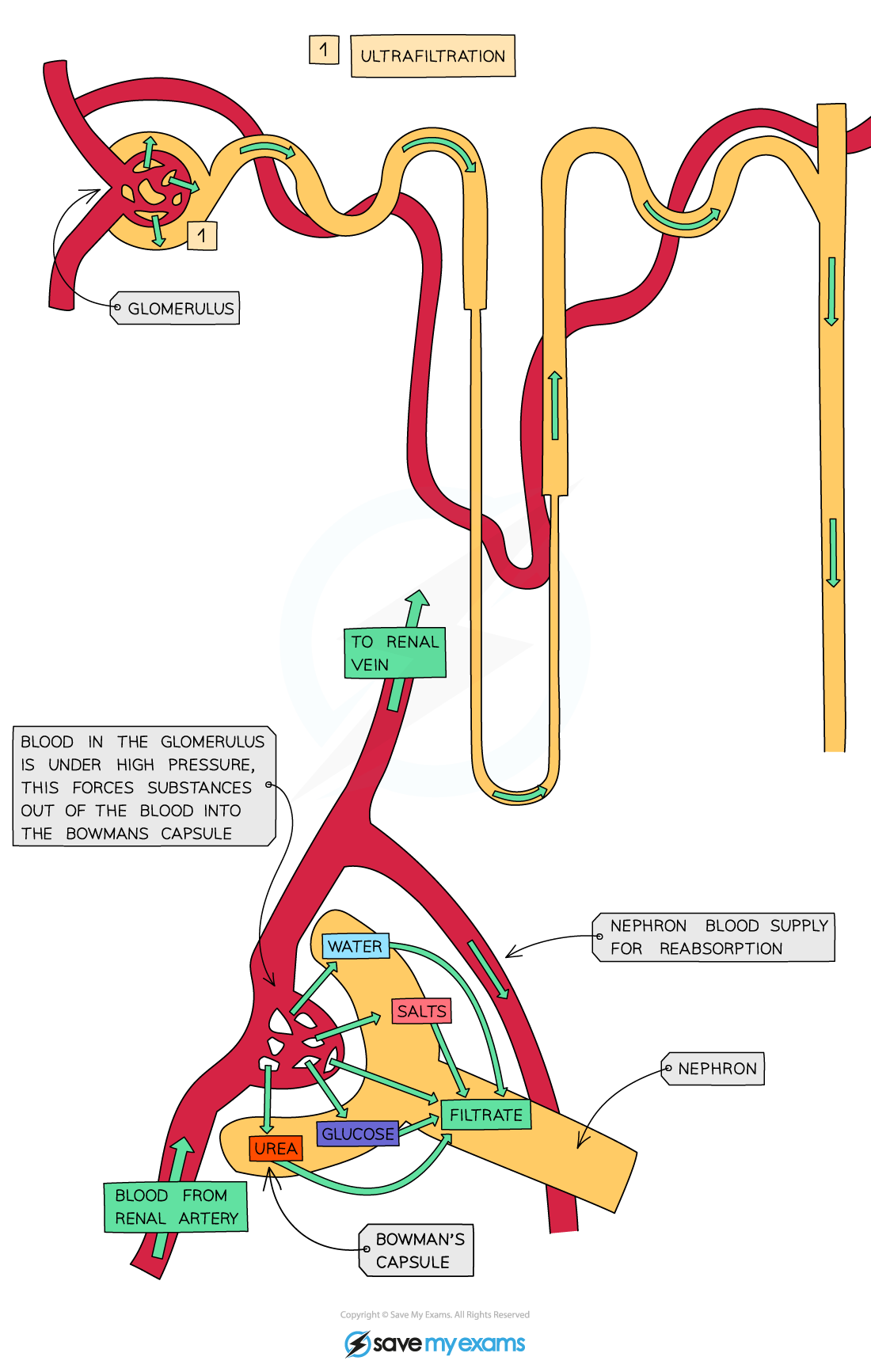
The processes of ultrafiltration and selective reabsorption
- After the necessary reabsorption of amino acids, water, glucose and inorganic ions is complete (even some urea is reabsorbed), the filtrate eventually leaves the nephron and is now referred to as urine
- This urine then flows out of the kidneys, along the ureters and into the bladder, where it is temporarily stored
Ultrafiltration
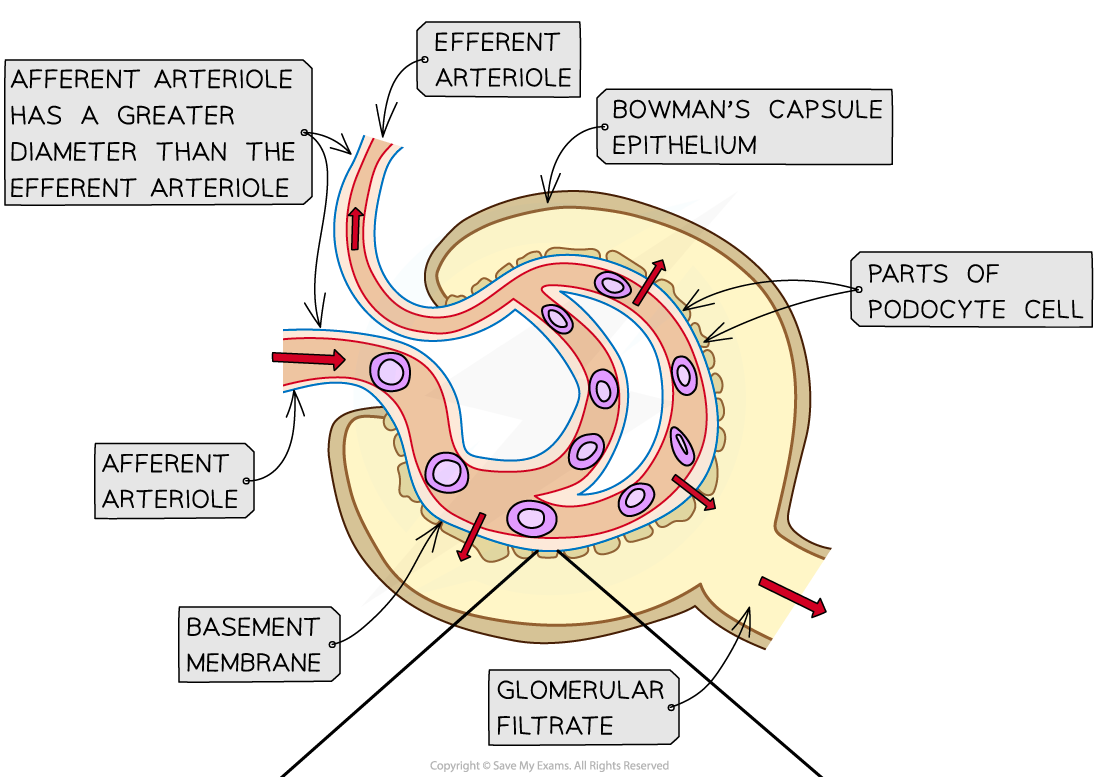
- Arterioles branch off the renal artery and lead to each nephron, where they form a knot of capillaries (the glomerulus) sitting inside the cup-shaped Bowman’s capsule
- The capillaries get narrower as they get further into the glomerulus which increases the pressure on the blood moving through them (which is already at high pressure because it is coming directly from the renal artery which is connected to the aorta)
- This eventually causes the smaller molecules being carried in the blood to be forced out of the capillaries and into the Bowman’s capsule, where they form what is known as the filtrate
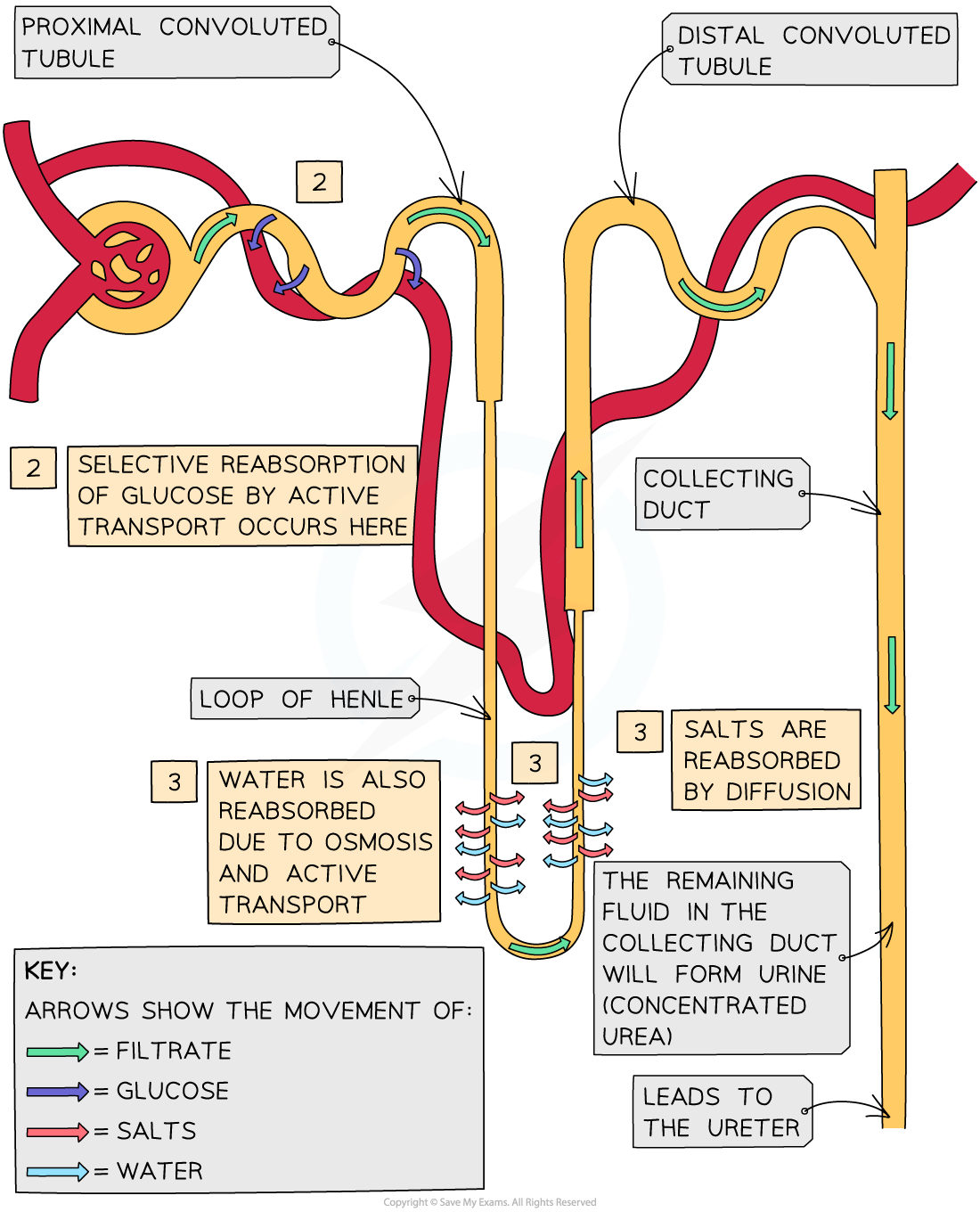
- The blood in the glomerular capillaries is separated from the lumen of the Bowman’s capsule by two cell layers with a basement membrane in between them:
- The first cell layer is the endothelium of the capillary – each capillary endothelial cell is perforated by thousands of tiny membrane-lined circular holes
- The next layer is the basement membrane – this is made up of a network of collagen and glycoproteins
- The second cell layer is the epithelium of the Bowman’s capsule – these epithelial cells have many tiny finger-like projections with gaps in between them and are known as podocytes
- As blood passes through the glomerular capillaries, the holes in the capillary endothelial cells and the gaps between the podocytes allows substances dissolved in the blood plasma to pass into the Bowman’s capsule
- The fluid that filters through from the blood into the Bowman’s capsule is known as the glomerular filtrate
- The main substances that pass out of the capillaries and form the glomerular filtrate are: amino acids, water, glucose, urea and inorganic ions (mainly Na+, K+ and Cl-)
- Red and white blood cells and platelets remain in the blood as they are too large to pass through the holes in the capillary endothelial cells
- The basement membrane acts as a filter as it stops large protein molecules from getting through
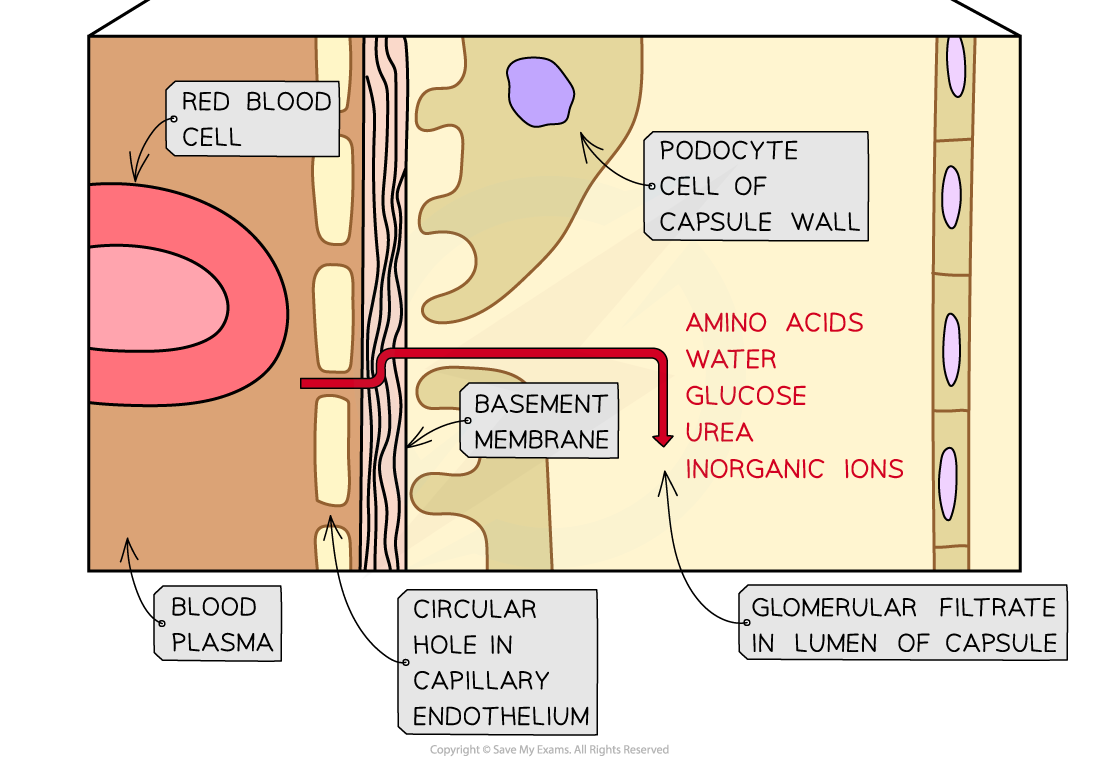
Ultrafiltration occurs when small molecules (such as amino acids, water, glucose, urea and inorganic ions) filter out of the blood and into the Bowman’s capsule to form glomerular filtrate. These molecules must pass through three layers during this process: the capillary endothelium, the basement membrane and the Bowman’s capsule epithelium
How ultrafiltration occurs
- Ultrafiltration occurs due to the differences in water potential between the plasma in the glomerular capillaries and the filtrate in the Bowman’s capsule
- Remember – water moves down a water potential gradient, from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential. Water potential is increased by high pressure and decreased by the presence of solutes
Factors Affecting Water Potential Table

- Overall, the effect of the pressure gradient outweighs the effect of solute gradient
- Therefore, the water potential of the blood plasma in the glomerulus is higher than the water potential of the filtrate in the Bowman’s capsule
- This means that as blood flows through the glomerulus, there is an overall movement of water down the water potential gradient from the blood into the Bowman’s capsule
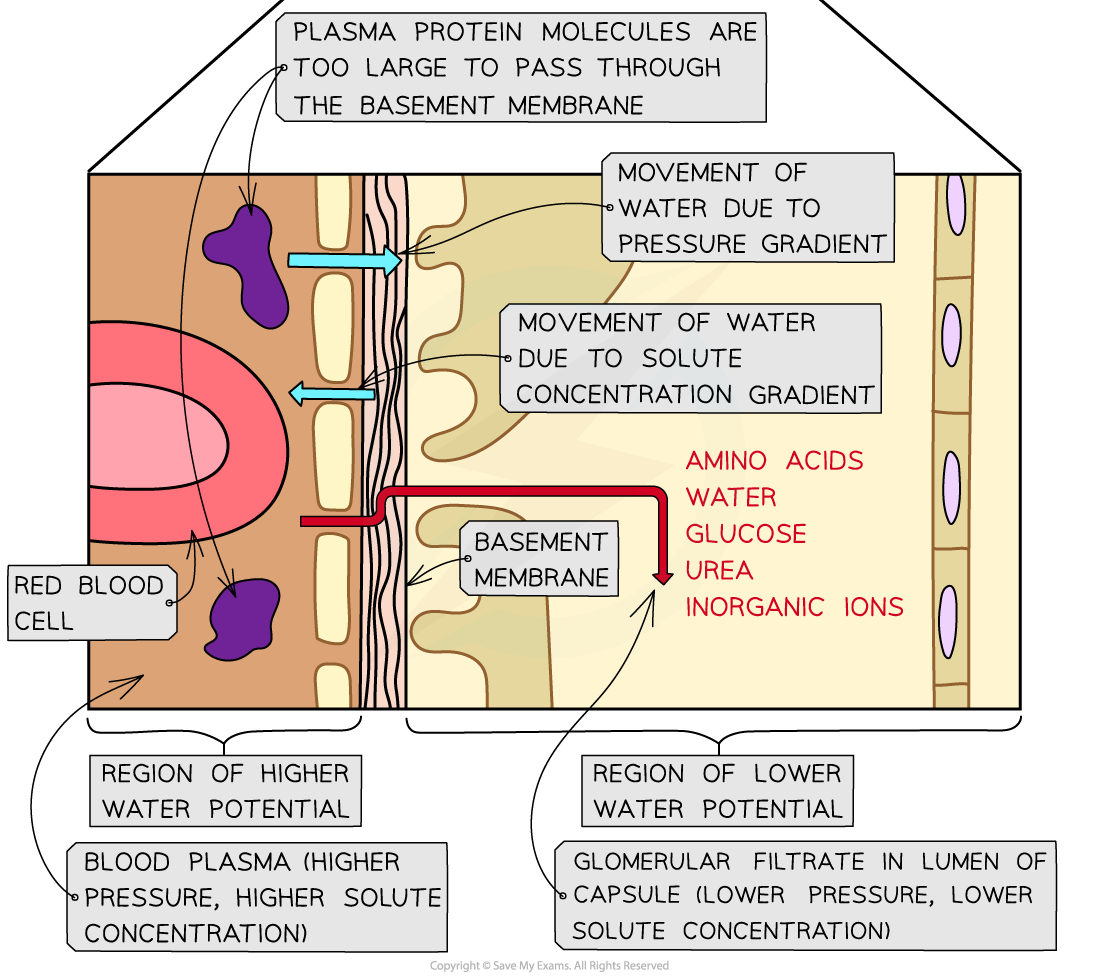
As blood flows through the glomerulus, there is an overall movement of water down the water potential gradient from the blood plasma (region of higher water potential) into the Bowman’s capsule (region of lower water potential)
Selective Reabsorption
- Many of the substances that end up in the glomerular filtrate actually need to be kept by the body
- These substances are reabsorbed into the blood as the filtrate passes along the nephron
- This process is knowns as selective reabsorption as only certain substances are reabsorbed
- Glucose reabsorption occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule
- The lining of the proximal convoluted tubule is composed of a single layer of epithelial cells, which are adapted to carry out reabsorption in several ways:
- Microvilli
- Co-transporter proteins
- A high number of mitochondria
- Tightly packed cells
- Water and salts are reabsorbed via the Loop of Henle and collecting duct
Adaptations for Selective Reabsorption Table
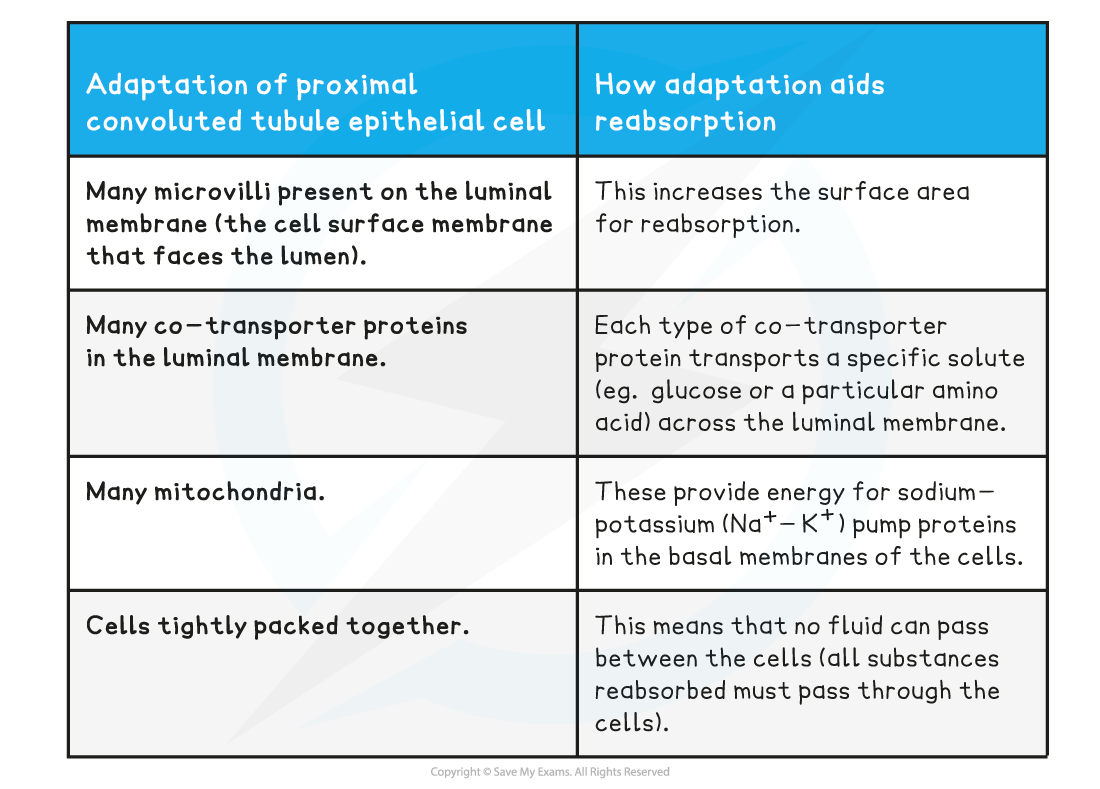
How the selective reabsorption of solutes occurs
- Blood capillaries are located very close to the outer surface of the proximal convoluted tubule
- As the blood in these capillaries comes straight from the glomerulus, it has very little plasma and has lost much of its water, inorganic ions and other small solutes
- The basal membranes (of the proximal convoluted tubule epithelial cells) are the sections of the cell membrane that are closest to the blood capillaries
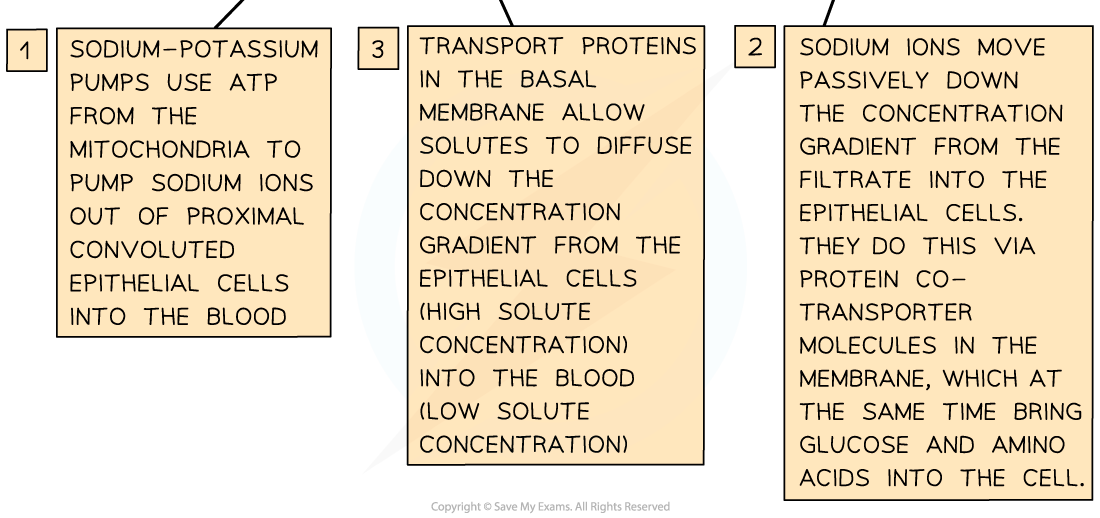
- Sodium-potassium pumps in these basal membranes move sodium ions out of the epithelial cells and into the blood, where they are carried away
- This lowers the concentration of sodium ions inside the epithelial cells, causing sodium ions in the filtrate to diffuse down their concentration gradient through the luminal membranes (of the epithelial cells)
- These sodium ions do not diffuse freely through the luminal membranes – they must pass through co-transporter proteins in the membrane
- There are several types of these co-transporter proteins – each type transports a sodium ion and another solute from the filtrate (eg. glucose or a particular amino acid)
- Once inside the epithelial cells these solutes diffuse down their concentration gradients, passing through transport proteins in the basal membranes (of the epithelial cells) into the blood
Molecules reabsorbed from the proximal convoluted tubule during selective reabsorption
- All glucose in the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed into the blood
- This means no glucose should be present in the urine
- Amino acids, vitamins and inorganic ions are reabsorbed
- The movement of all these solutes from the proximal convoluted tubule into the capillaries increases the water potential of the filtrate and decreases the water potential of the blood in the capillaries
- This creates a steep water potential gradient and causes water to move into the blood by osmosis
- A significant amount of urea is reabsorbed too
- The concentration of urea in the filtrate is higher than in the capillaries, causing urea to diffuse from the filtrate back into the blood
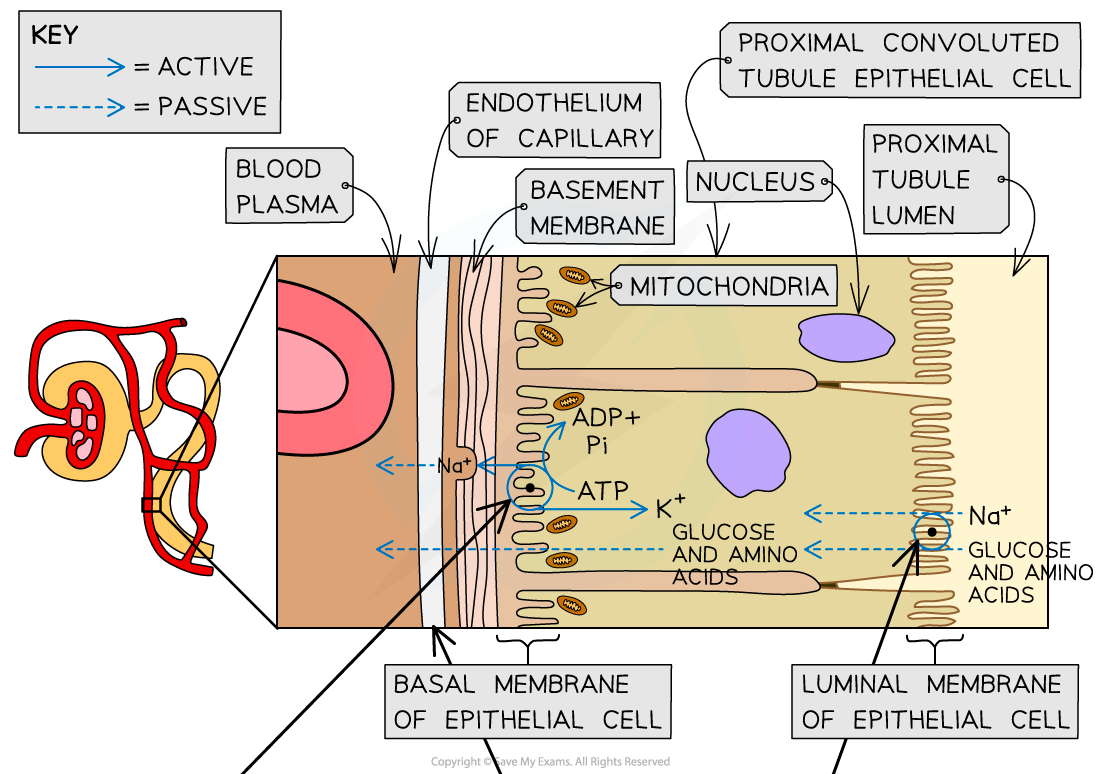
Selective reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule
Reabsorption of water and salts
- As the filtrate drips through the Loop of Henle necessary salts are reabsorbed back into the blood by diffusion
- As salts are reabsorbed back into the blood, water follows by osmosis
- Water is also reabsorbed from the collecting duct in different amounts depending on how much water the body needs at that time
Exam Tip
Selective reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule uses the same method of membrane transport that moves sucrose into companion cells in phloem tissue!As sodium ions move passively down their concentration gradient into the epithelial cells of the proximal convoluted tubule, this provides the energy needed to reabsorb solute molecules (eg. glucose and amino acids) into the epithelial cells, even against their concentration gradients.This is known as indirect or secondary active transport, as the energy (ATP) is used to pump sodium ions, not the solutes themselves.
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








