- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Biology复习笔记11.1.4 Memory Cells & Immunity
Memory Cells & Long-Term Immunity
- During an immune response, B-lymphocytes form two types of cell: plasma cells and memory cells
- Memory cells form the basis of immunological memory – the cells can last for many years and often a lifetime
- There are two types of immune response:
- Primary immune response (responding to a newly encountered antigen)
- Secondary immune response (responding to a previously encountered antigen)
Primary immune response
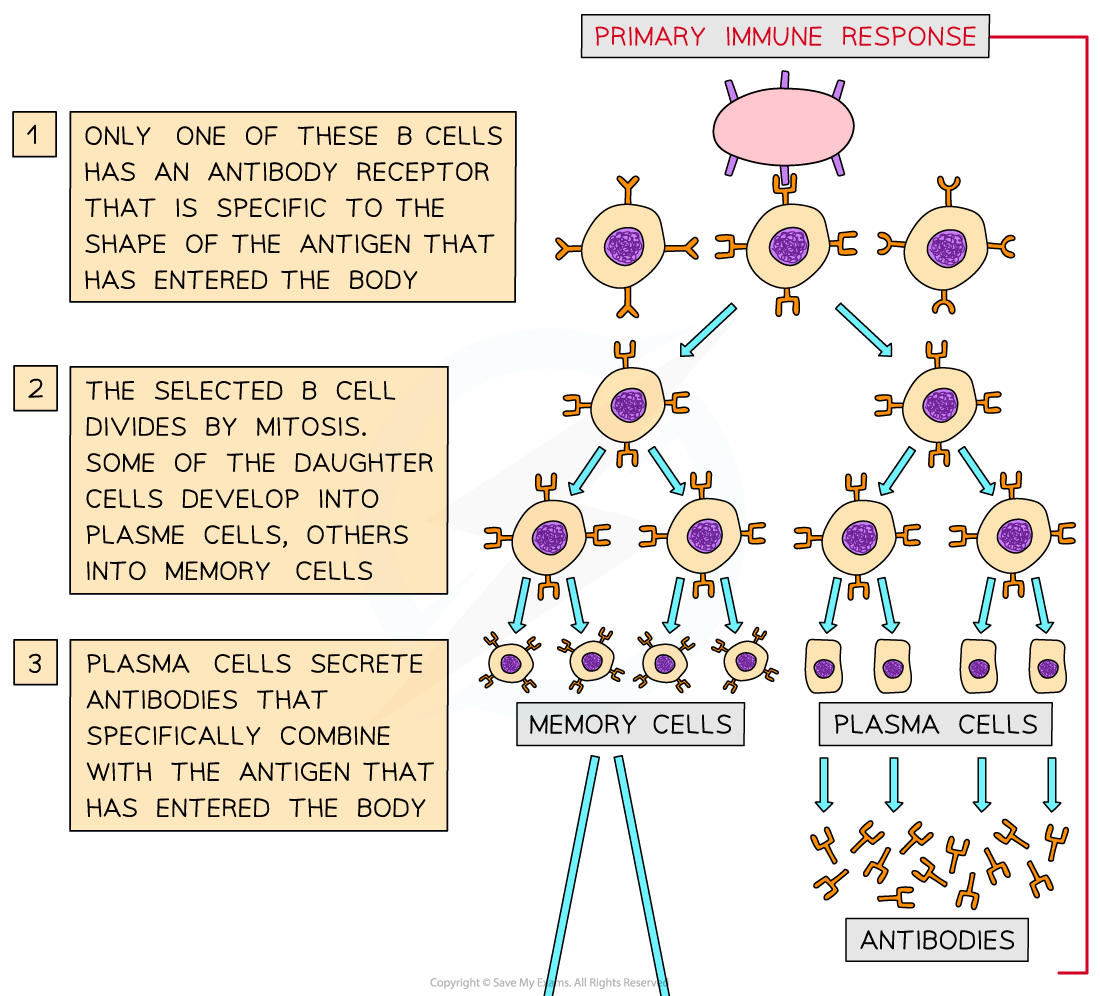
- When an antigen enters the body for the first time, the small numbers of B-lymphocytes with receptors complementary to that antigen are stimulated to divide by mitosis
- This is known as clonal selection
- As these clones divide repeatedly by mitosis (the clonal expansion stage) the result is large numbers of identical B-lymphocytes being produced over a few weeks
- Some of these B-lymphocytes become plasma cells that secrete lots of antibody molecules (specific to the antigen) into the blood, lymph or linings of the lungs and the gut
- These plasma cells are short-lived (their numbers drop off after several weeks) but the antibodies they have secreted stay in the blood for a longer time
- The other B-lymphocytes become memory cells that remain circulating in the blood for a long time
- This response to a newly encountered pathogen is relatively slow
Secondary immune response
- If the same antigen is found in the body a second time, the memory cells recognise the antigen, divide very quickly and differentiate into plasma cells (to produce antibodies) and more memory cells
- This response is very quick, meaning that the infection can be destroyed and removed before the pathogen population increases too much and symptoms of the disease develop
- This response to a previously encountered pathogen is, relative to the primary immune response, extremely fast
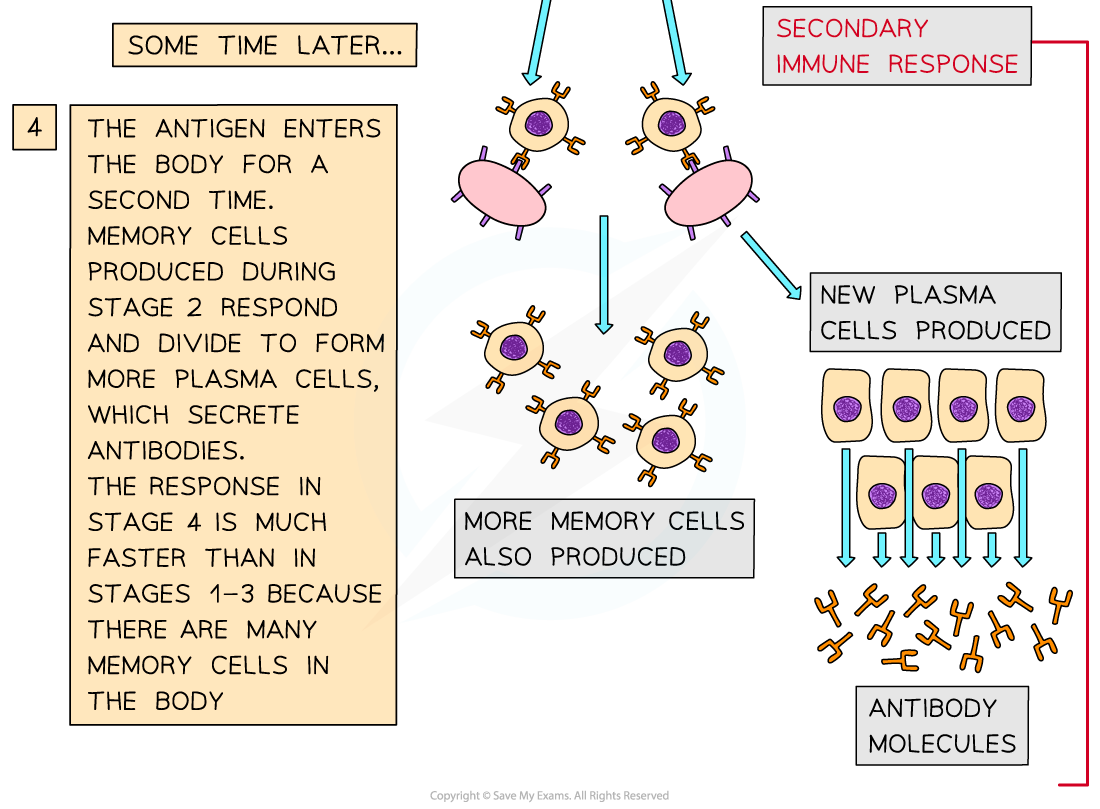
During a secondary immune response, memory cells that remained in the blood divide very quickly into plasma cells (to produce antibodies) and more memory cells
- T-lymphocytes also play a part in the secondary immune response
- They differentiate into memory cells, producing two main types:
- Memory helper T cells
- Memory killer T cells
- Just like the memory cells formed from B-lymphocytes, these memory T cells remain in the body for a long time
- If the same antigen is found in the body a second time, these memory T cells become active very quickly
Exam Tip
Immunological memory (made possible by memory cells) is the reason why catching certain diseases twice is so unlikely. For example, there is only one strain of the virus that causes measles, and each time someone is re-infected with this virus, there is a very fast secondary immune response so they do not get ill.However, some infections such as the common cold and influenza are caused by viruses that are constantly developing into new strains. As each strain has different antigens, the primary immune response (during which we often become ill) must be carried out each time before immunity can be achieved.
转载自savemyexams

在线登记
最新发布
翰林课程体验,退费流程快速投诉邮箱: yuxi@linstitute.net 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








