- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Biology复习笔记3.1.2 Enzyme Action
Mode of Enzyme Action
- Enzymes have an active site where specific substrates bind forming an enzyme-substrate complex
- The active site of an enzyme has a specific shape to fit a specific substrate
- Extremes of heat or pH can change the shape of the active site, preventing substrate binding – this is called denaturation
- Substrates collide with the enzymes active site and this must happen at the correct orientation and speed in order for a reaction to occur
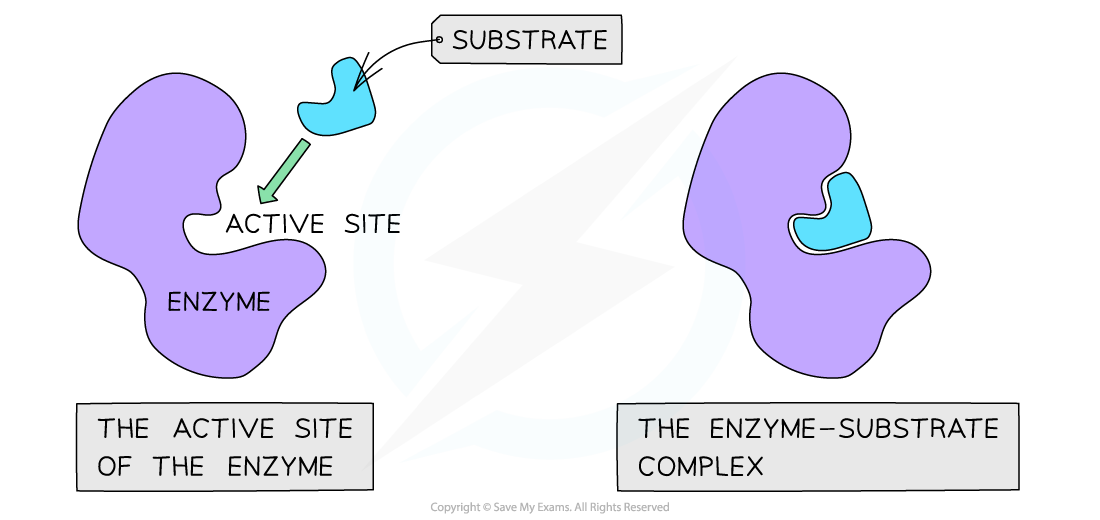
The active site of an enzyme has a specific shape to fit a specific substrate (when the substrate binds an enzyme-substrate complex is formed)
- The specificity of an enzyme is a result of the complementary nature between the shape of the active site on the enzyme and its substrate(s)
- The shape of the active site (and therefore the specificity of the enzyme) is determined by the complex tertiary structure of the protein that makes up the enzyme:
- Proteins are formed from chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds
- The order of amino acids determines the shape of an enzyme
- If the order is altered, the resulting three-dimensional shape changes
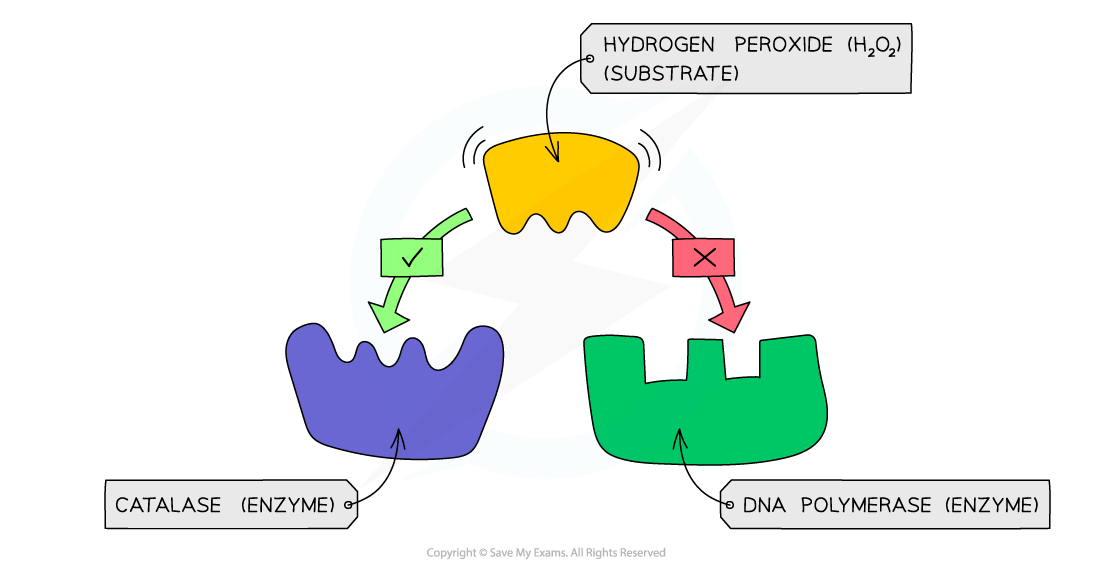
An example of enzyme specificity – the enzyme catalase can bind to its substrate hydrogen peroxide as they are complementary in shape, whereas DNA polymerase is not
- An enzyme-substrate complex forms when an enzyme and its substrate join together
- The enzyme-substrate complex is only formed temporarily, before the enzyme catalyses the reaction and the product(s) are released
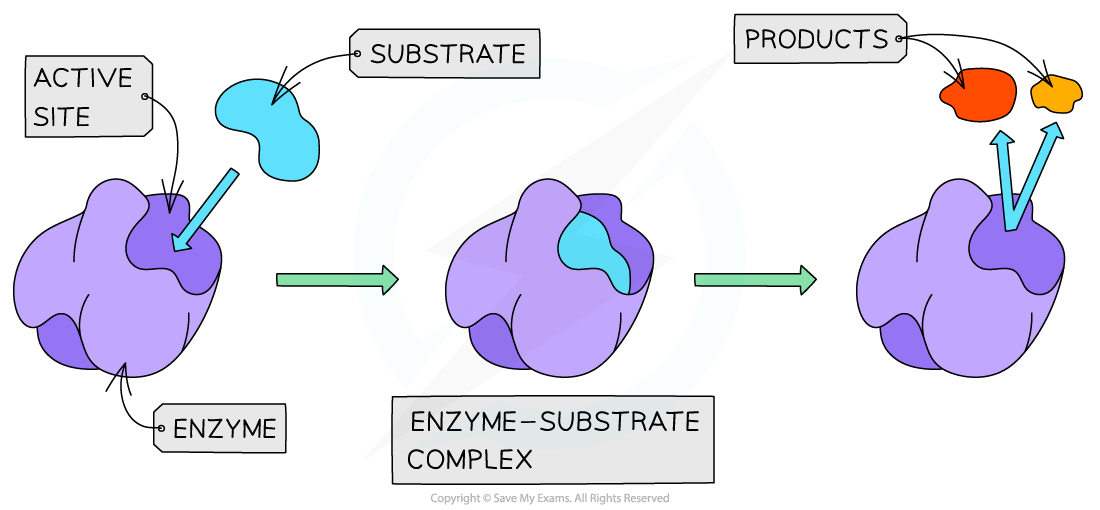
The temporary formation of an enzyme-substrate complex
- Enzyme reactions can either be catabolic or anabolic
- Catabolic reactions involve the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler products, which happens when a single substrate is drawn into the active site and broken apart into two or more distinct molecules
- Examples of catabolic reactions include cellular respiration and hydrolysis reactions
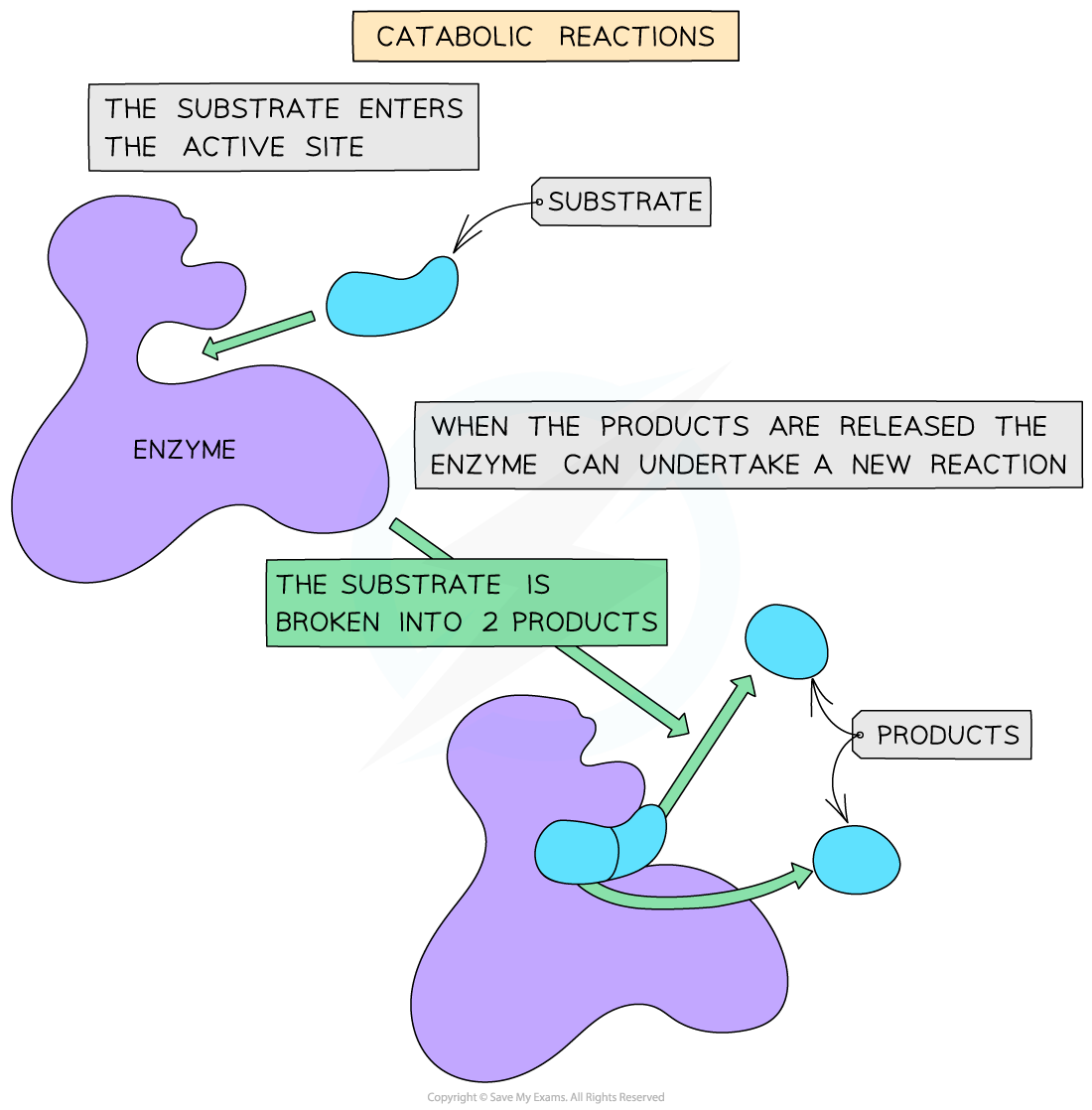
A catabolic reaction
- Anabolic reactions involve the building of more complex molecules from simpler ones by drawing two or more substrates into the active site, forming bonds between them and releasing a single product
- Examples of anabolic reactions include protein synthesis and photosynthesis
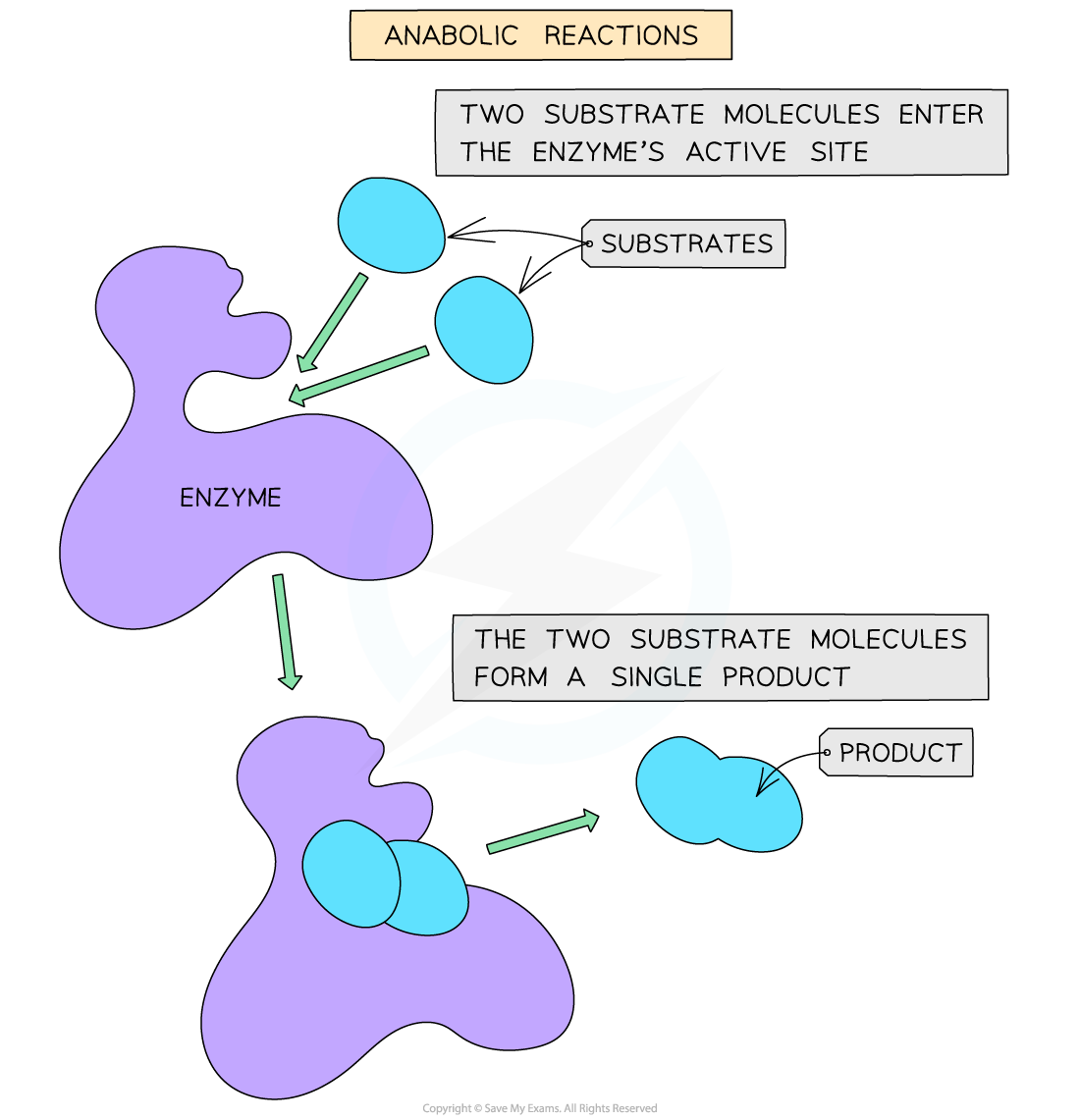
An anabolic reaction
Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy of a reaction
- All chemical reactions are associated with energy changes
- For a reaction to proceed there must be enough activation energy
- Activation energy is the amount of energy needed by the substrate to become just unstable enough for a reaction to occur and for products to be formed
- Enzymes speed up chemical reactions because they influence the stability of bonds in the reactants
- The destabilisation of bonds in the substrate makes it more reactive
- Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy of a reaction and in doing so they provide an alternative energy pathway
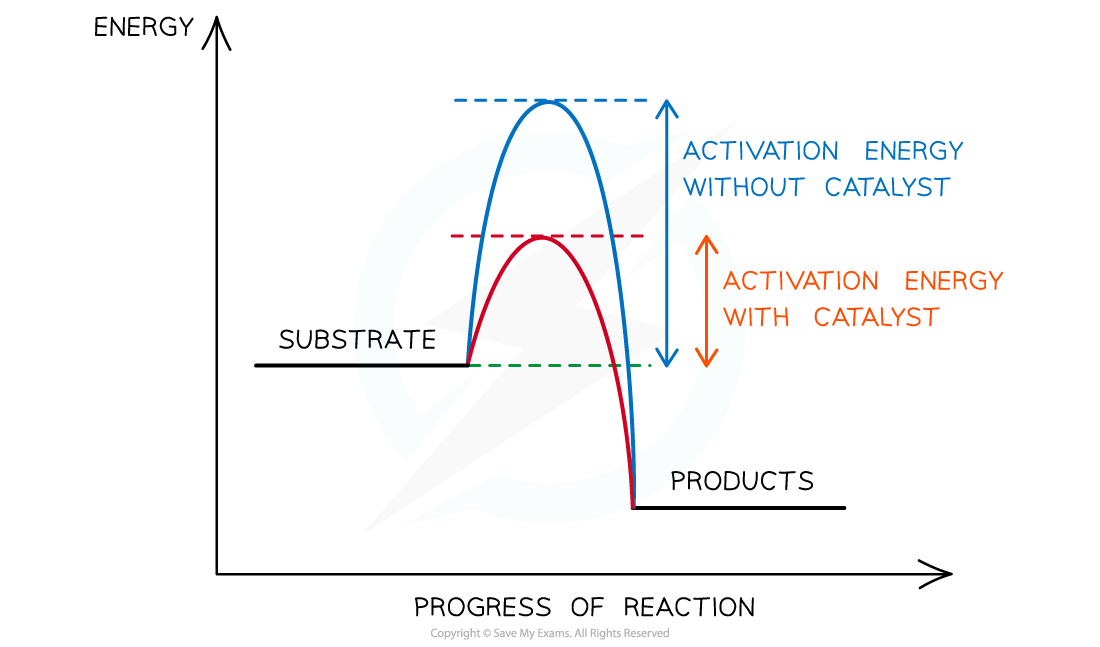
The activation energy of a chemical reaction is lowered by the presence of a catalyst (ie. an enzyme)
Exam Tip
Don't forget that both enzymes and their substrates are highly specific to each other – this is known as enzyme-substrate specificity.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









