- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: SL复习笔记7.3.2 Quarks & Leptons
Quarks & Leptons
Quarks
- Quarks are fundamental particles that make up other subatomic particles such as protons and neutrons
- Protons and neutrons are in a category of particles called hadrons
Hadrons are defined as any particle made up of quarks
- Fundamental means that quarks are not made up of any other particles. Another example is electrons
- Quarks have never been observed on their own, they’re either in pairs or groups of three
- There are six flavours (types) of quarks that exist:
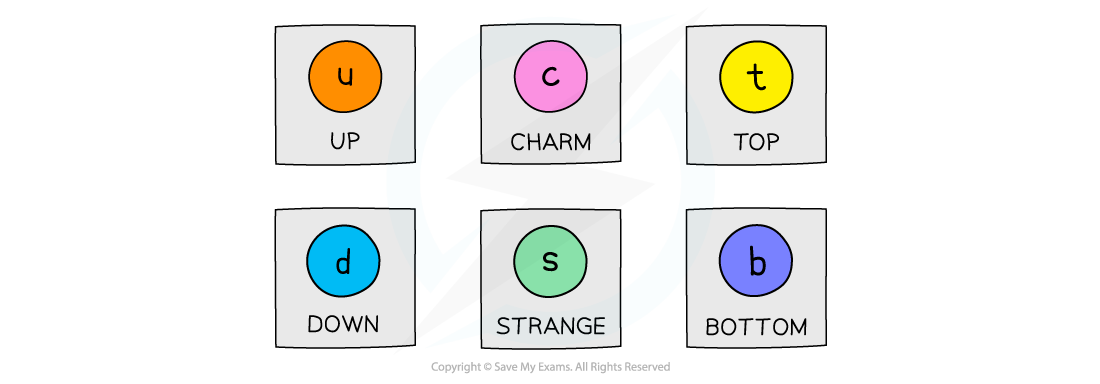
The six flavours of quarks
- The charge of a hadron is determined by the sum of the charges of its quarks
- Each flavour of quark has a certain relative charge:
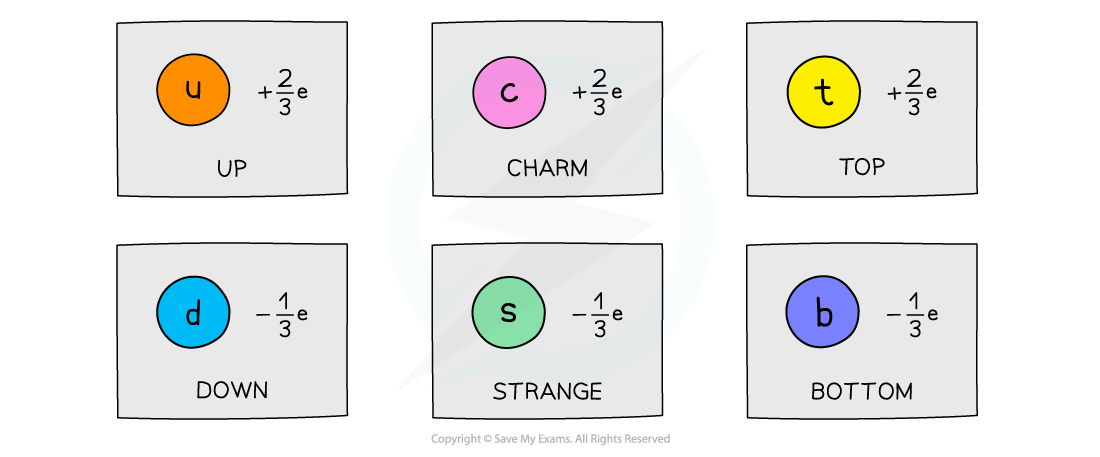 Each flavour of quark has a charge of either +⅔e or -⅓e
Each flavour of quark has a charge of either +⅔e or -⅓e
- For example, a proton is made up of two up quarks and a down quark. Adding up their charges gives the charge of a proton:
+⅔e + ⅔e - ⅓e = +1e
- The equivalent antiparticle of the quark is the anti-quark
- These are identical to quarks except with opposite relative charges
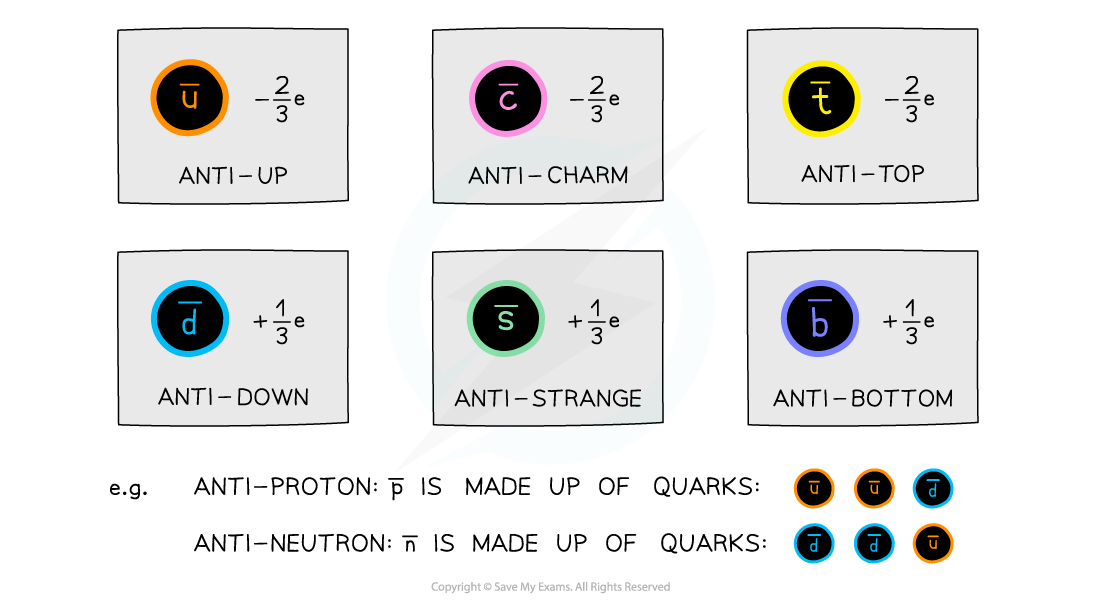
Each flavour of anti-quark has a charge of either -⅔e or +⅓e. The quark composition of anti-protons and anti-neutrons changes to anti-quarks
- Quarks have a baryon number of +1/3
- Anti-quarks having a baryon number of –1/3
- Strange quarks have a strangeness of –1
- Anti-strange quarks have a strangeness of +1
- This is unique to the strange quark
Worked Example
Particles are made up of a combination of three quarks or two quarks. Which quark combination would not give a particle a charge of -1 or 0?
A. up, strange, strange
B. charm, charm, down
C. top, anti-up
D. anti-up, anti-up, anti-strange
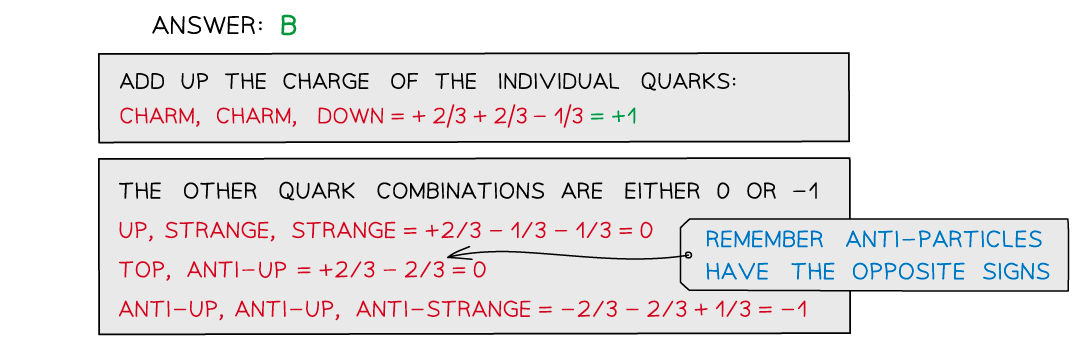
Worked Example
A K- particle has a strangeness of –1. Determine the quark structure of this particle.

Leptons
- Leptons are a group of fundamental (elementary) particles
- This means they are not made up of any other particles (no quarks)
- There are six leptons altogether:
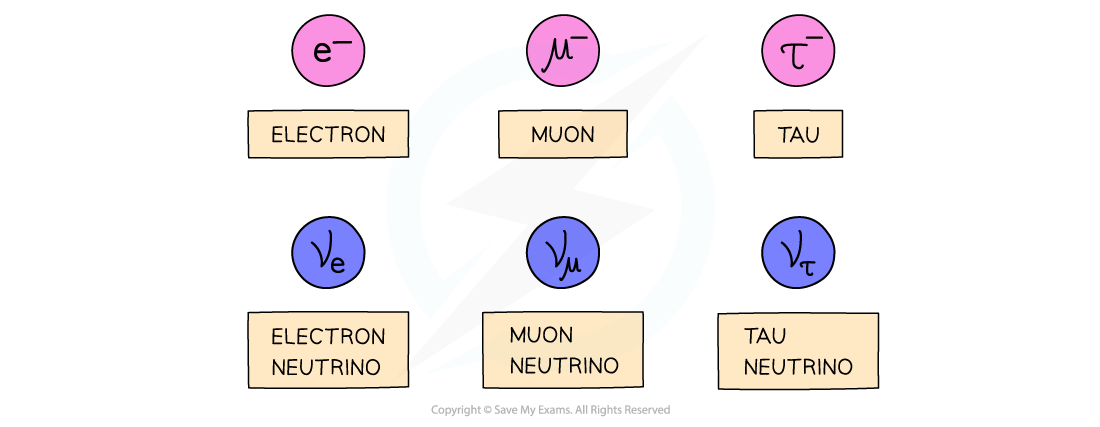 The six leptons are all fundamental particles
The six leptons are all fundamental particles
- The muon and tau particle are very similar to the electron but with slightly larger mass
- Electrons, muon, and tau particles all have a charge of -1e and a mass of 0.0005u
- There are three flavours (types) of neutrinos (electron, muon, tau)
- Neutrinos are the most abundant leptons in the universe
- They have no charge and negligible mass (almost 0)
- Leptons interact with the weak interaction, electromagnetic and gravitational forces
- However, they do not interact with the strong force
- Although quarks are fundamental particles too, they are not classed as leptons
- Leptons do not interact with the strong force, whilst quarks do
Worked Example
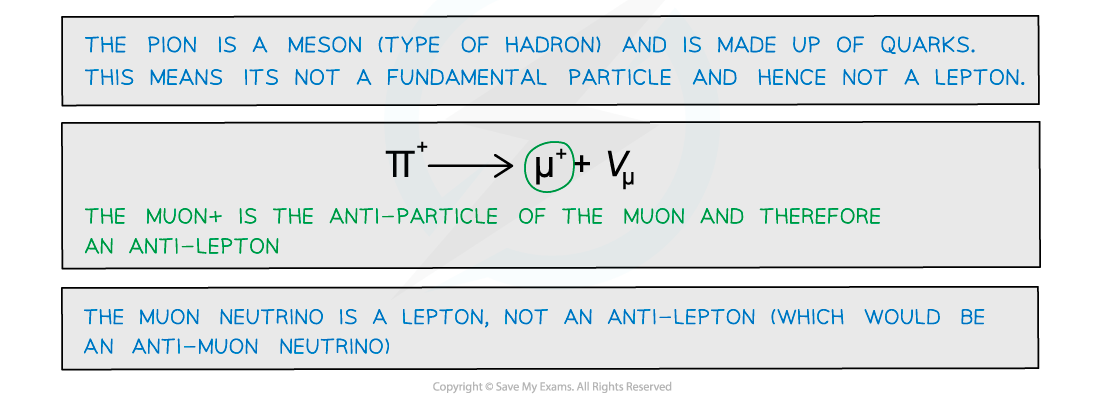
Circle all the anti-leptons in the following decay equation.
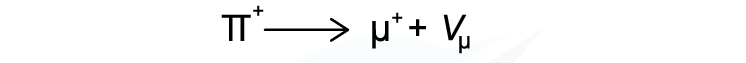
Lepton Number
- Similar to baryon number, the lepton number, L is the number of leptons in an interaction
- L depends on whether the particle is a lepton, anti-lepton or neither
- Leptons have a lepton number L = +1
- Anti-leptons have a lepton number L = –1
- Particles that are not leptons have a lepton number L = 0
- Lepton number is a quantum number and is conserved in all interactions
- This is helpful for knowing whether an interaction is able to happen
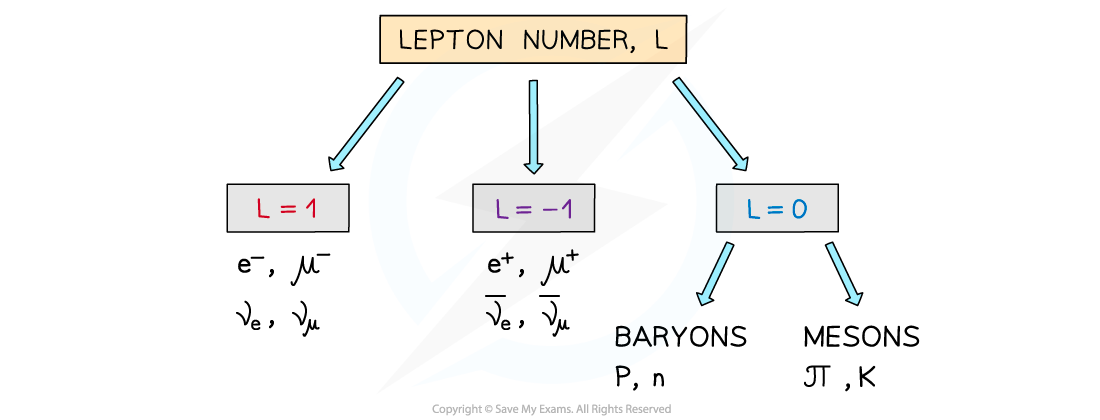
The lepton number depends if the particle is a lepton, anti-lepton or neither
Worked Example
If the lepton number is conserved in the following decay, identify whether particle X should be a neutrino or anti-neutrino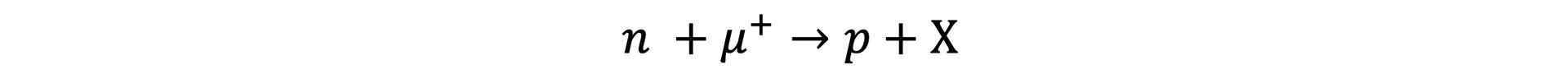
Step 1: Determine the lepton number of all the particles on both sides of the equation
-
- 0 + (–1) = 0 + X
Step 2: Identify the lepton number of X
-
- If the lepton number must be conserved, X must also have a lepton number of –1
Step 3: State the particle X
-
- Particle X is an anti-neutrino
Protons & Neutrons
Protons and Neutrons
- Protons and neutrons are not fundamental particles. They are each made up of three quarks
- Protons are made up of two up quarks and a down quark
- Neutrons are made up of two down quarks and an up quark
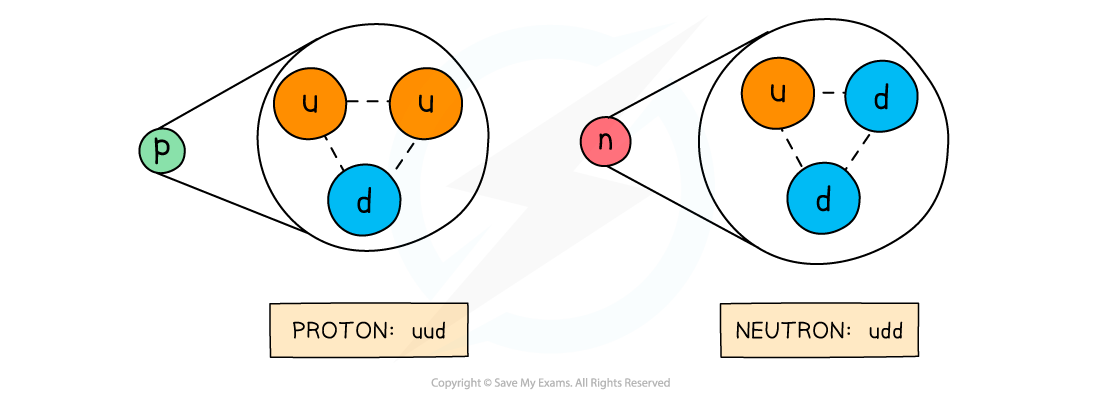
Protons and neutrons are made up of three quarks
- You will be expected to remember these quark combinations for exam questions
Protons as Baryons
- The proton is the most stable baryon
- This means it has the longest half-life of any baryon and is the particle which other baryons eventually decay to
- It is the most stable baryon because it is also the lightest baryon
- Radioactive decay occurs when heavier particles decay into lighter particles
- A decay of the proton would therefore violate the conservation of baryon number
- It is theorized that the proton has a half-life of around 1032 years and research experiments are still underway that are designed to detect proton decay
Worked Example

Step 1: Calculate number of protons:
-
- The number of protons is from the proton number = 26 protons
Step 2: Calculate number of neutrons:
-
- The number of neutrons = nucleon number - proton number = 56 - 26 = 30 neutrons
Step 3: Up quarks in a proton:
-
- Protons are made up of uud quarks = 2 up quarks
Step 4: Up quarks in a neutron:
-
- Neutrons are made up of udd quarks = 1 up quark
Step 5: Total number of up quarks:
-
- 26 protons x 2 up quarks = 52 up quarks
- 30 neutrons x 1 up quark = 30 up quarks
- 52 + 30 = 82 up quarks
β– and β+ decay
- Beta decay happens via the weak interaction
- This is one of the four fundamental forces and it’s responsible for radioactive decays
Quark Composition: β- decay
- Recall that β- decay is when a neutron turns into a proton emitting an electron and anti-electron neutrino
- More specifically, a neutron turns into a proton because a down quark turns into an up quark
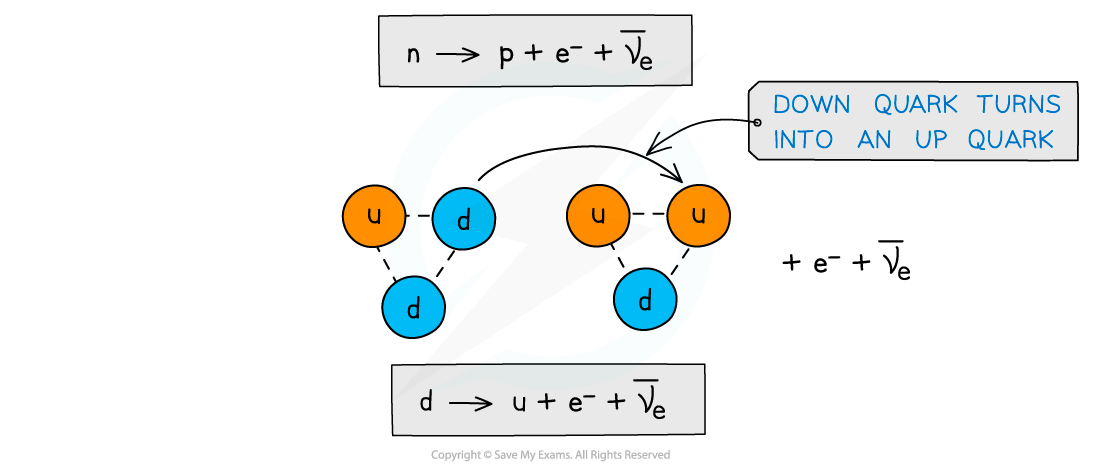
Beta minus decay is when a down quark turns into an up quark
Quark Composition: β+ decay
- Recall that β+ decay is when a proton turns into a neutron emitting a positron and an electron neutrino
- More specifically, a proton turns into a neutron because an up quark turns into a down quark
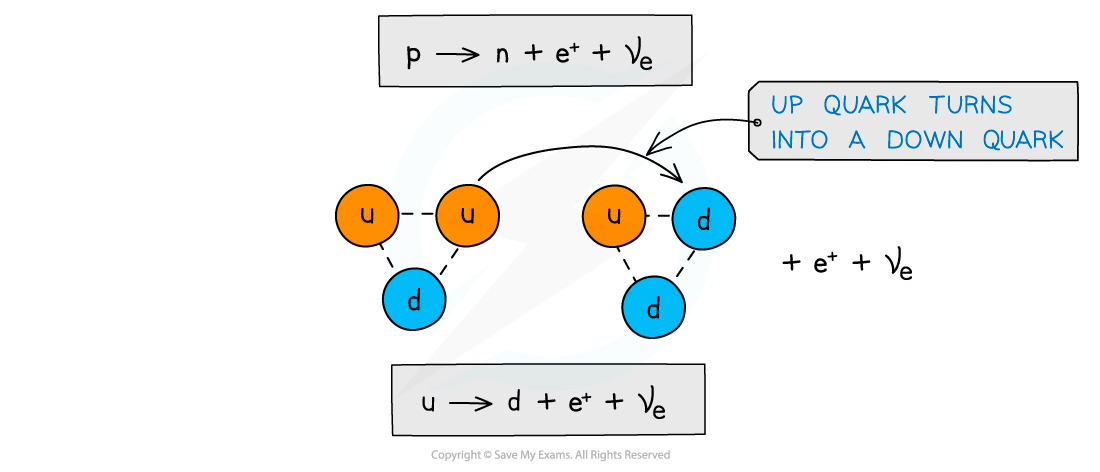
Beta plus decay is when an up quark turns into a down quark
Worked Example
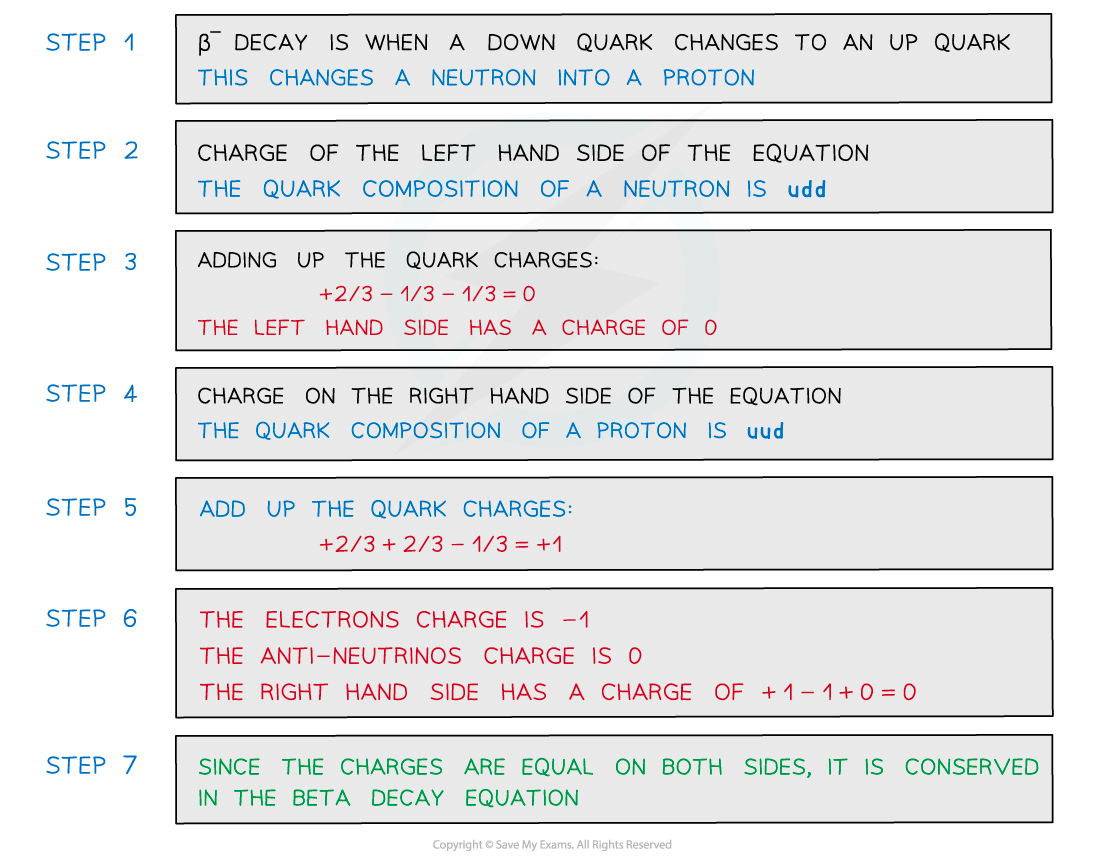
The equation for β– decay is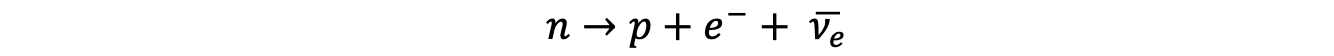
Using the quark model of beta decay, prove that the charge is conserved in this equation.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









