- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: SL复习笔记6.1.3 Centripetal Acceleration
Centripetal Acceleration
- For an object moving in a circle:
- The acceleration is towards the centre of the circle
- The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration a is:
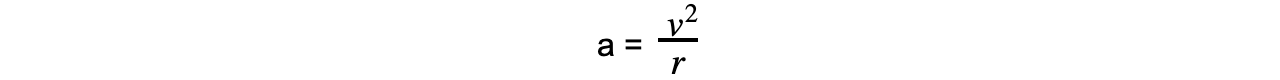
- Where:
- a = centripetal acceleration (m s–2)
- v = linear speed (m s–1)
- r = radius of orbit (m)
- Uniform circular motion is continuously changing direction, and therefore is constantly changing velocity
- The object must therefore be accelerating
- This is called the centripetal acceleration
Direction of the Centripetal Acceleration
- The centripetal acceleration is perpendicular to the direction of the linear velocity
- Centripetal means it acts towards the centre of the circular path
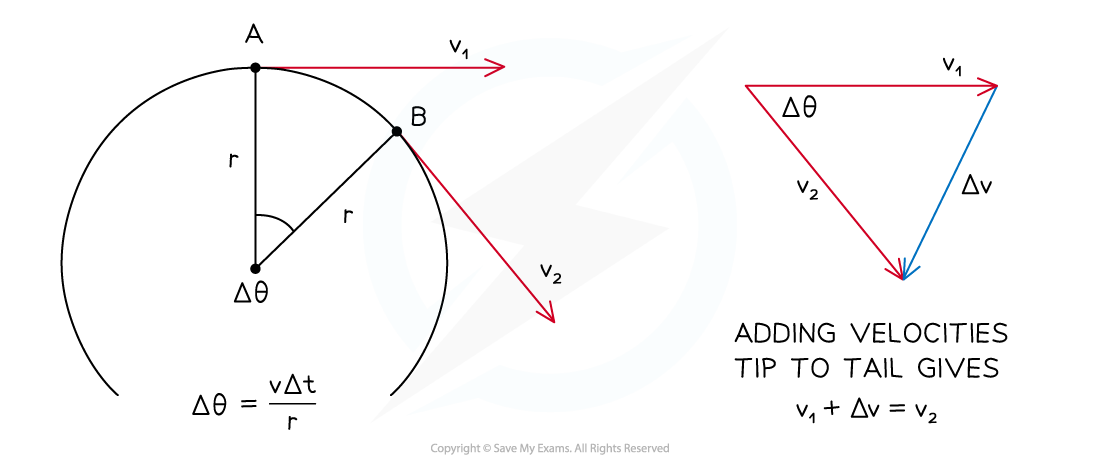
Slide a ruler parallel to Δv towards the circle. Midway between A and B, Δv points towards the centre of the circle. This is the same direction as the centripetal acceleration
- If an object moves through a section of a circle during some time Δt
- The change in velocity during this time is Δv
- The centripetal acceleration is Δv (a vector) divided by Δt (a scalar)
- The centripetal acceleration points in the same direction as the change in velocity Δv
- The centripetal acceleration is caused by a centripetal force of constant magnitude that also acts perpendicular to the direction of motion (towards the centre)
- There is no component of the centripetal force in the direction of the velocity
- Therefore, there is no acceleration in the direction of the velocity
- Hence, there is uniform motion at constant speed
- Therefore, the centripetal acceleration and force act in the same direction
Magnitude of the Centripetal Acceleration
- In the diagram above notice how the angle Δθ is defined in terms of the arc length vΔt and the radius r
- v is the magnitude of v1 and v2
- Notes for deriving the equation for centripetal acceleration:
- The vector triangle should be formed so that Δv is horizontal
- The velocity vectors v should be of the same length
- Hence, the vertical line bisects the angle Δθ and the vector Δv
- Use trigonometry for one of the small triangles
- The small-angle approximation requires that the angles are in radians
- The two equations for Δθ lead to the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration
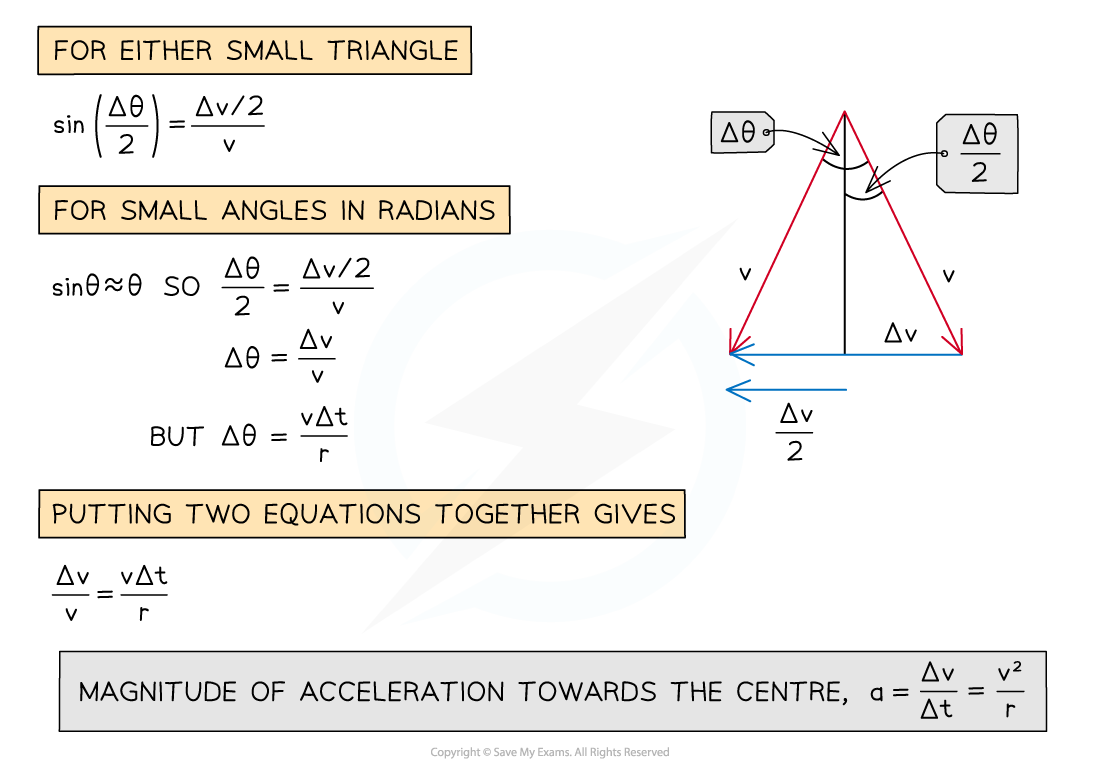
Deriving the equation for the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration
- This leads to the equation for centripetal acceleration:
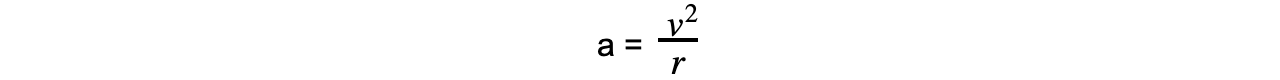
- Using the equation relating angular speed ω and linear speed v:
v = r⍵
- These equations can be combined to give another form of the centripetal acceleration equation:
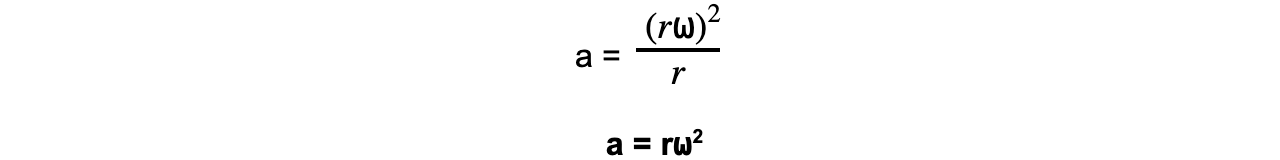
- Where:
- a = centripetal acceleration (m s−2)
- v = linear speed (m s−1)
- ⍵ = angular speed (rad s−1)
- r = radius of the orbit (m)
- Uniform centripetal acceleration is defined as:
The acceleration of an object towards the centre of a circle when an object is in motion (rotating) around a circle at a constant speed
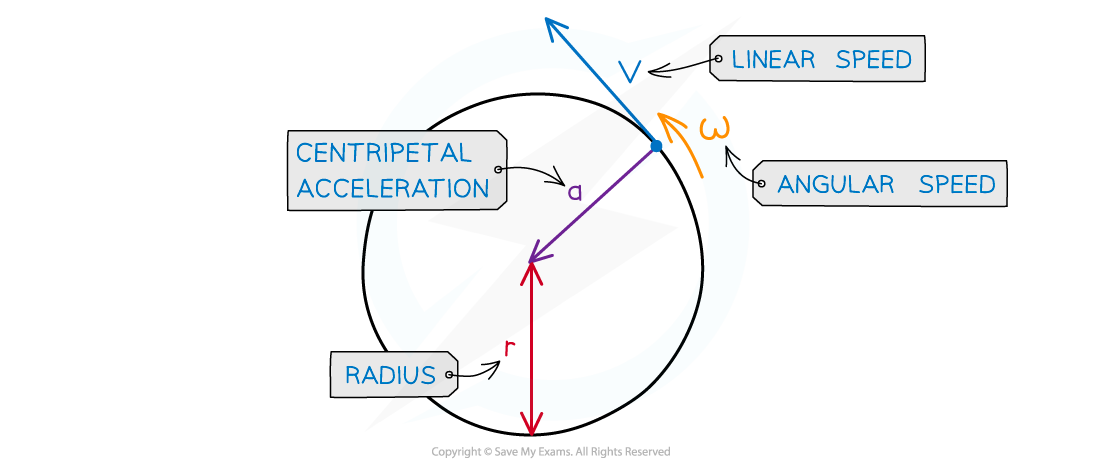
Centripetal acceleration is always directed toward the centre of the circle and is perpendicular to the object’s velocity
Worked Example
A domestic washing machine has a spin cycle of 1200 rpm (revolutions per minute) and a diameter of 50 cm.
Calculate the centripetal acceleration experienced by the washing during the spin cycle.
Step 1: List the known quantities
-
- Radius of the drum, r = ½ × 50 cm = 25 cm
Step 2: Convert the revolutions per minute to revolutions per second
1200 ÷ 60 = 20 rev s−1
Step 3: Convert revolutions per second to angular speed in radians per second
1 rev s–1 = 2π rad s–1
20 rev s–1 = 40π rad s–1 = ω
Step 4: Write the equation linking centripetal acceleration and angular speed
a = rω2
Step 5: Calculate the centripetal acceleration
a = (25 × 10−2) × (40π)2
Step 6: State the final answer
a = 3900 m s−2 (2 s.f.)
Worked Example
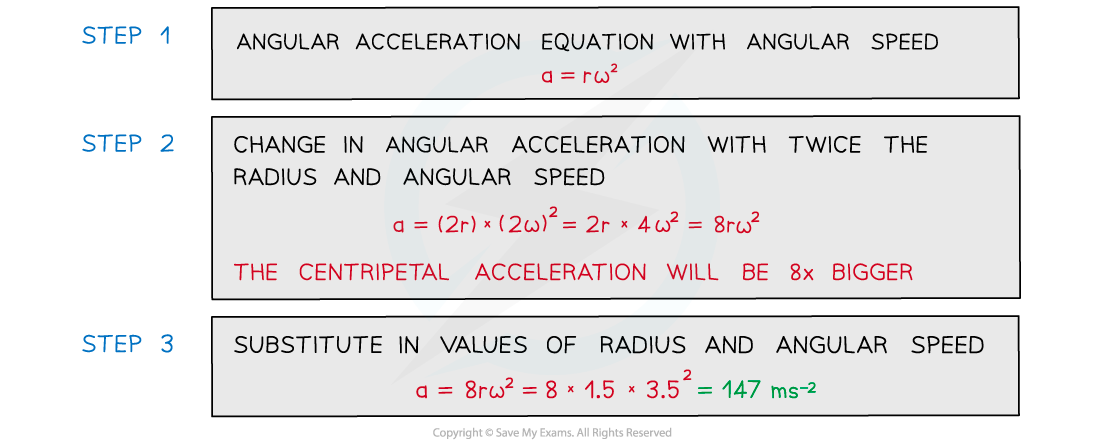
A ball tied to a string is rotating in a horizontal circle with a radius of 1.5 m and an angular speed of 3.5 rad s−1.
Calculate its centripetal acceleration if the radius was twice as large and angular speed was twice as fast.
Exam Tip
The key takeaways for an object moving in a circle are:
- The magnitude of the velocity vector does not change
- The direction of the velocity vector does change
- Therefore, there is an acceleration despite the speed not changing
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








