- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: SL复习笔记5.2.6 Investigating Resistivity
Investigating Resistivity
Aims of the Experiment
- The aim of the experiment is to determine the resistivity of a 2 metre constantan wire
Variables:
- Independent variable = Length, L, of the wire (m)
- Dependent variable = The current, I, through the wire (A)
- Control variables:
- Voltage through the wire
- The material the wire is made from
Equipment List
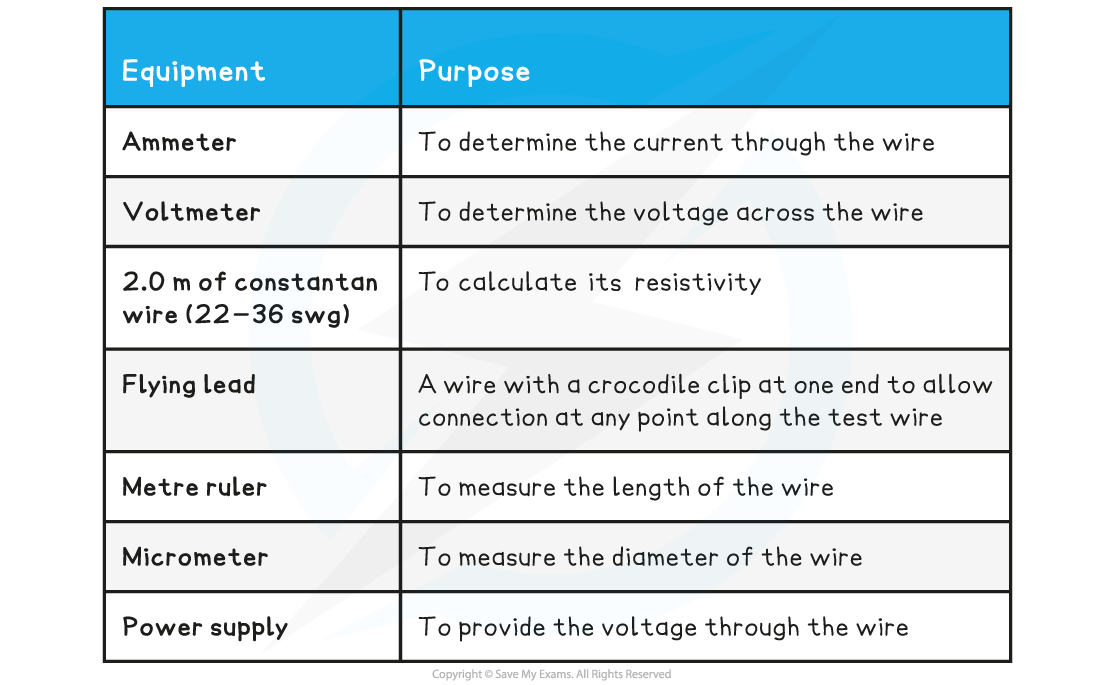
- Resolution of measuring equipment:
- Metre ruler = 1 mm
- Micrometer screw gauge = 0.01 mm
- Voltmeter = 0.1 V
- Ammeter = 0.01 A
Method
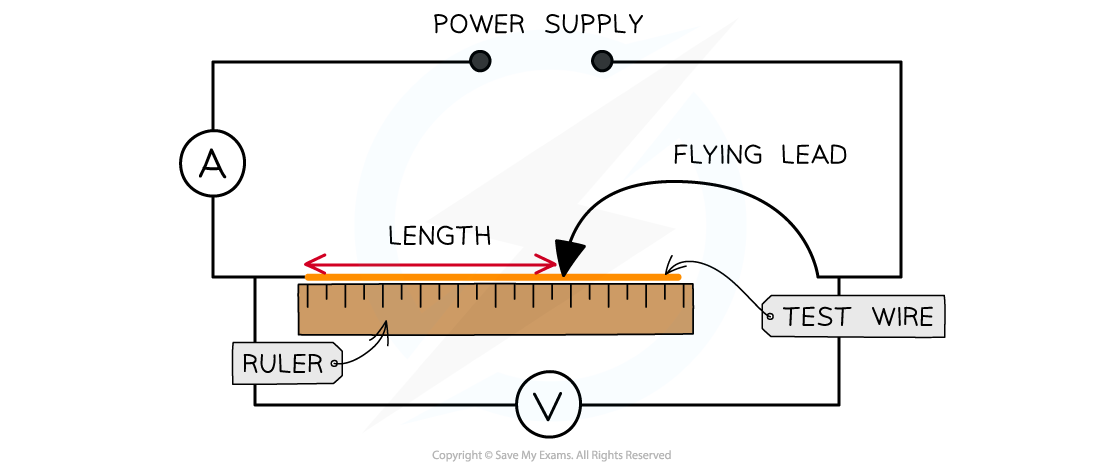
- Measure the diameter of the constantan wire using a micrometer. The measurement should be taken between 5-10 times randomly along the wire. Calculate the mean diameter from these values
- Set up the equipment so the wire is taped or clamped to the ruler with one end of the circuit attached to the wire where the ruler reads 0. The ammeter is connected in series and the voltmeter in parallel to the wire
- Attach the flying lead to the test wire at 0.25 m and set the power supply at a voltage of 6.0 V. Check that this is the voltage through the wire on the voltmeter
- Read and record the current from the ammeter, then switch off the current immediately after the reading (the short wire will get very hot)
- Vary the distance between the fixed end of the wire and the flying lead in 0.25 m intervals (0.25 m, 0.50 m, 0.75 etc.) until the full length of the 2.0 m wire. The original length and the intervals can be changed (e.g. start at 0.1 m and increase in 0.1 m intervals), as long as there are 8-10 readings
- Record the current for each length at least 3 times and calculate an average current, I
- For each length, calculate the average resistance of the length of the wire using the equation
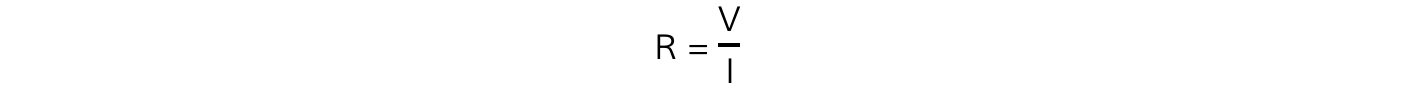
where V is the voltage and I is the average current through the wire for that length
- An example of a table of results might look like this:

Analysis of Results
- The resistivity, ρ, of the wire is equal to
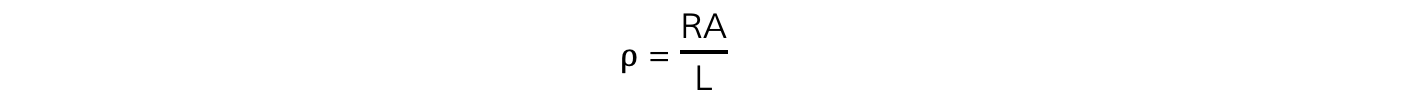
- Where:
- ρ = resistivity (Ω m)
- R = resistance (Ω)
- A = cross-sectional area of the wire (m2)
- L = length of wire (m)
- Rearranging for the resistance, R:
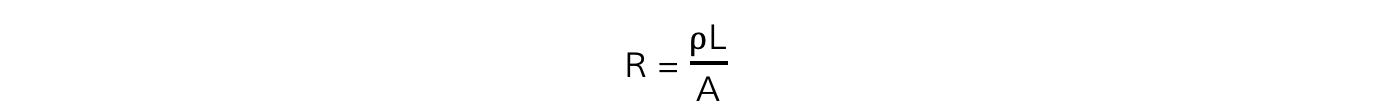
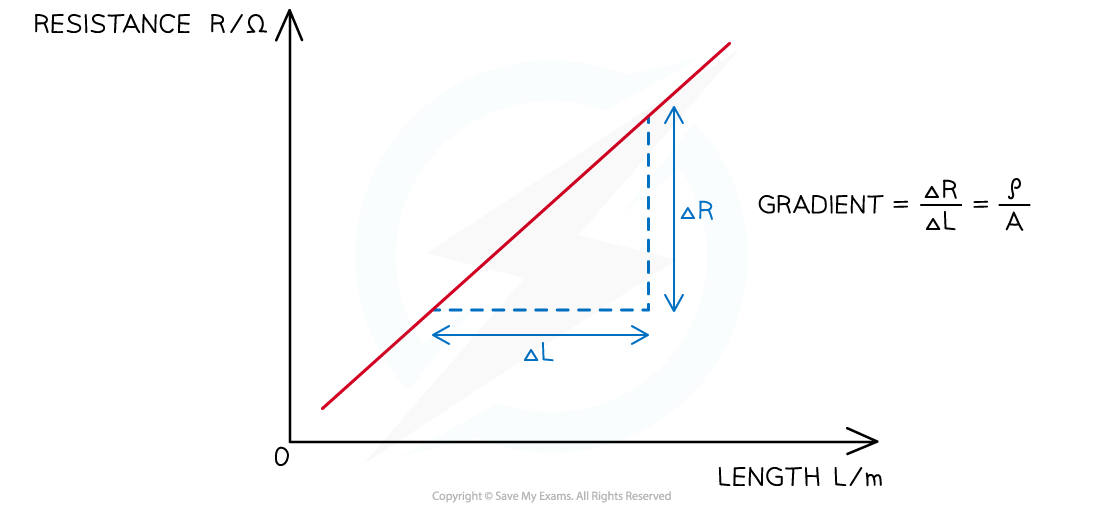
- Comparing this to the equation of a straight line: y = mx
- y = R
- x = L
- Gradient = ρ / A
- The resistivity can therefore be calculated from the gradient of the resistance against length graph, multiplied by the cross-sectional area of the wire
1. Calculate the cross-sectional area, A, of the wire 2. Plot a graph of the length of the wire, L, against the average resistance of the wire, R3. Draw a line of best fit and calculate the gradient of this graph4. Calculate the resistivity ρ by multiplying the gradient by the cross-sectional area A
2. Plot a graph of the length of the wire, L, against the average resistance of the wire, R3. Draw a line of best fit and calculate the gradient of this graph4. Calculate the resistivity ρ by multiplying the gradient by the cross-sectional area A
Evaluating the Experiment
Systematic Errors:
- The end of the wire that is attached to the circuit (not the flying lead) must start at 0 on the ruler
- Otherwise, this could cause a zero error in your measurements of the length
Random Errors:
- Only allow small currents to flow through the wire
- The resistivity of a material depends on its temperature. The current flowing through the wire will cause its temperature to increase and affect its resistance and resistivity. Therefore the temperature is kept constant and low by small currents
- The current should be switched off between readings so its temperature doesn't change its resistance
- Make at least 5-10 measurements of the diameter of the wire with the micrometer screw gauge and calculate an average diameter to reduce random errors in the reading
Safety Considerations
- When there is a high current, and a thin wire, the wire will become very hot. Make sure never to touch the wire directly when the circuit is switched on
- Switch off the power supply right away if you smell burning
- Make sure there are no liquids close to the equipment, as this could damage the electrical equipment
Worked Example
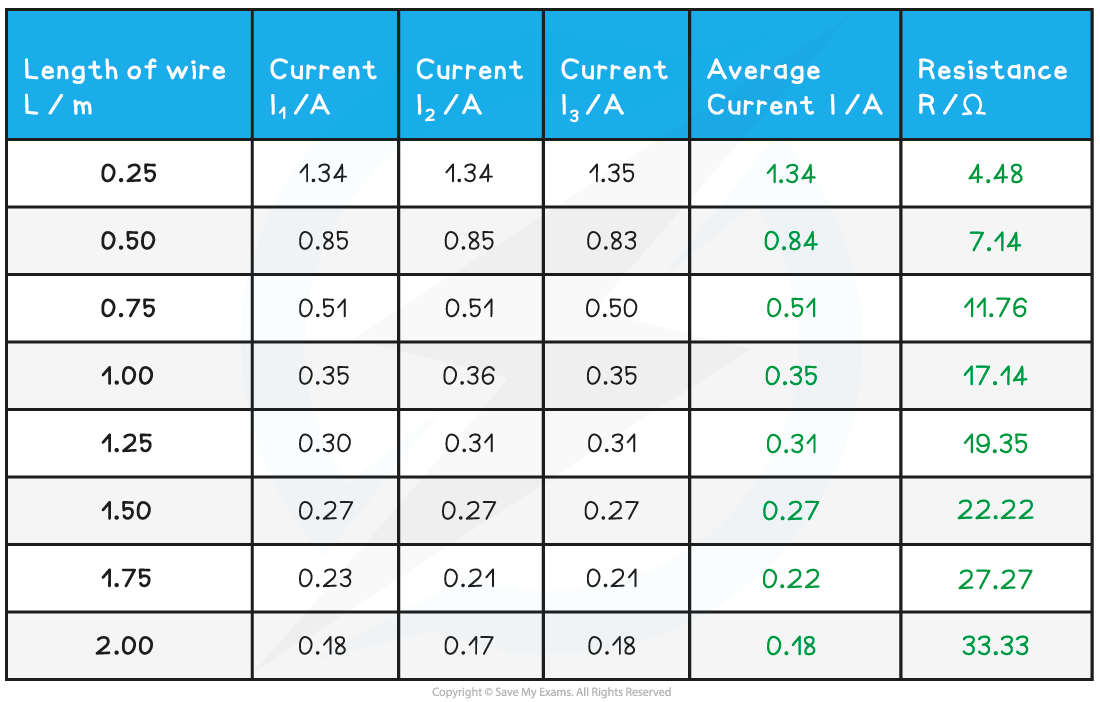
A student wants to find the resistivity of a constantan wire. They set up the experiment by attaching one end of the wire to a circuit with a 6.0 V battery and the other with a flying lead and measure the length with a ruler. Attaching the flying lead onto the wire at different lengths, they obtain the following table of results.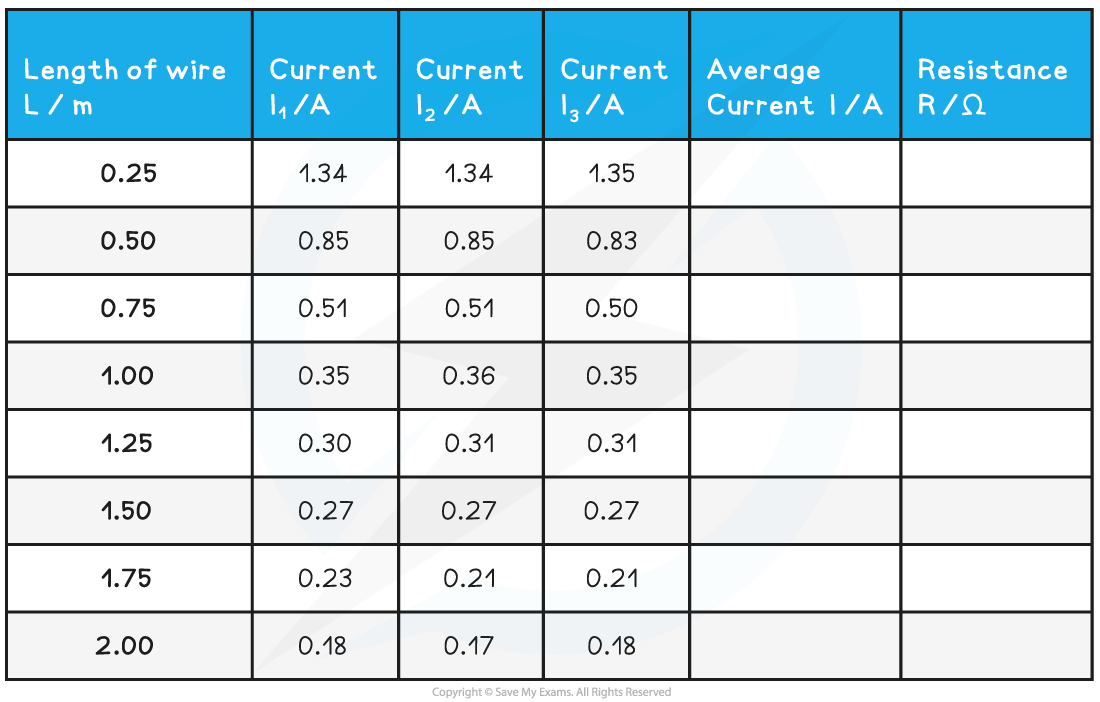
The following additional data for the wire is: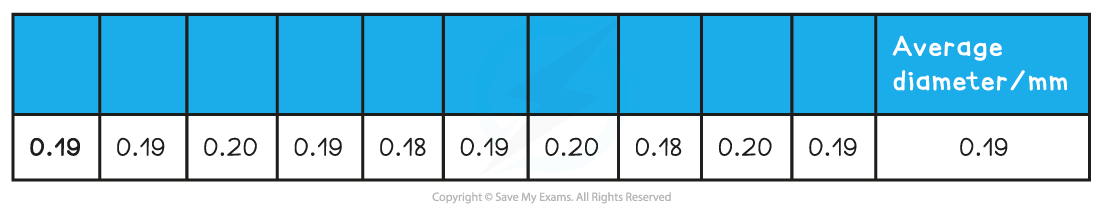
Calculate the resistivity of the wire
Step 1: Complete the average current and resistance columns in the table
The resistance is calculated using the equation
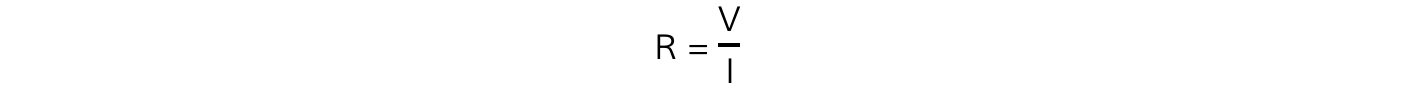
Step 2: Calculate the cross-sectional area of the wire from the diameter
-
- The average diameter is 0.191 mm = 0.191 × 10–3 m
- The cross-sectional area is equal to
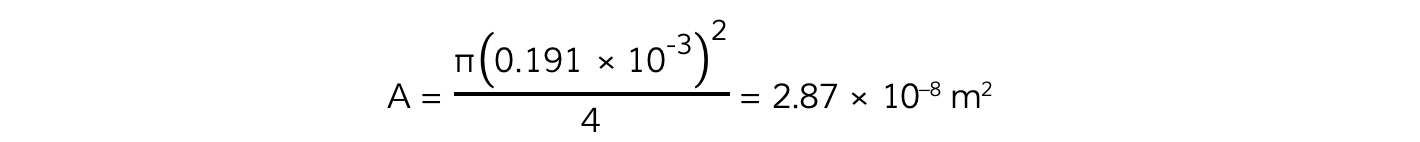 Step 3: Plot a graph of the length L against the resistance R
Step 3: Plot a graph of the length L against the resistance R
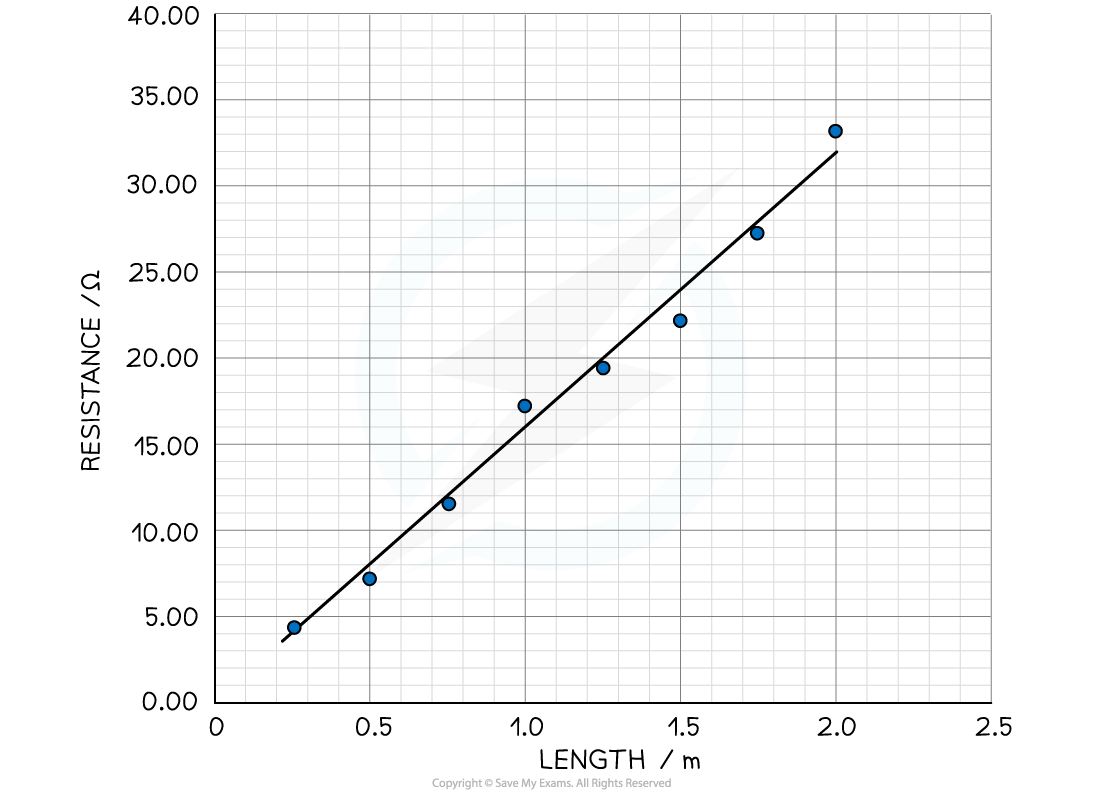
Step 4: Calculate the gradient of the graph
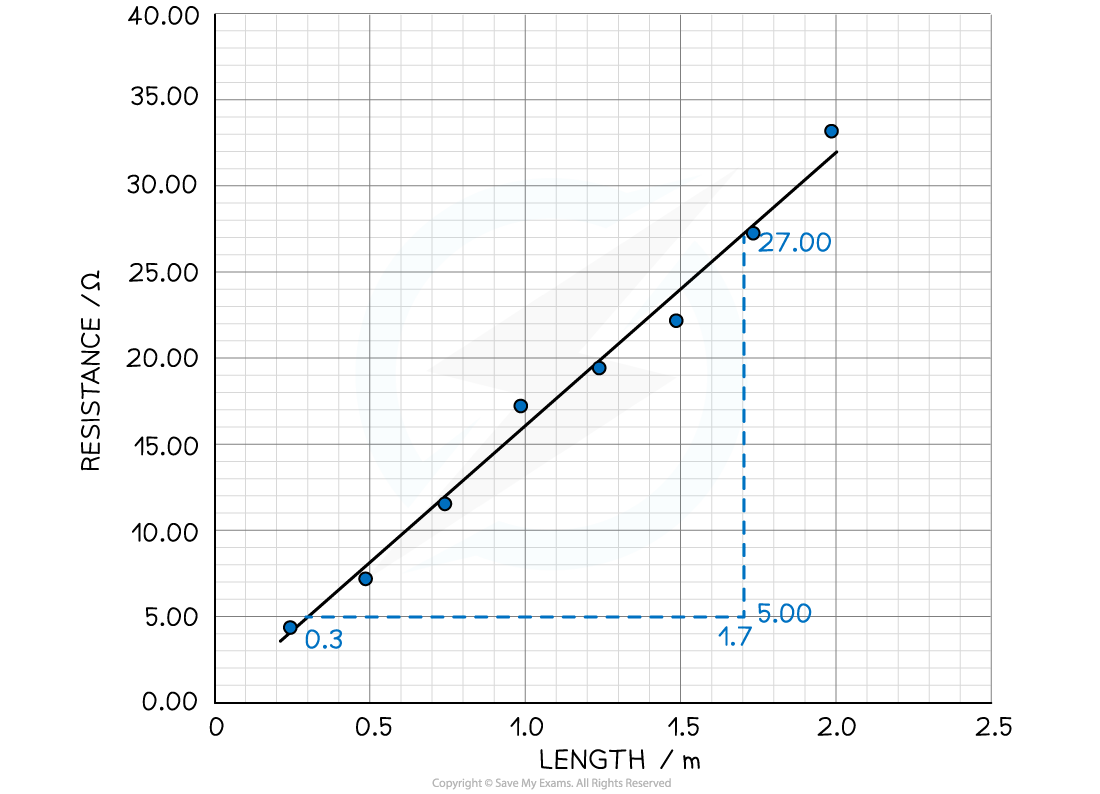

Step 5: Calculate the resistivity of the wire
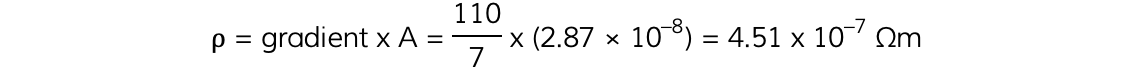
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









