- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: SL复习笔记5.2.5 Resistivity
Resistivity
Resistance, Length and Cross-Sectional Area
- The resistance of a sample depends on:
- The material it is made of
- The length of the sample
- The cross-sectional area of the sample
- The resistance of a conductor (e.g. a wire) is:
- Directly proportional to its length
- Inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area
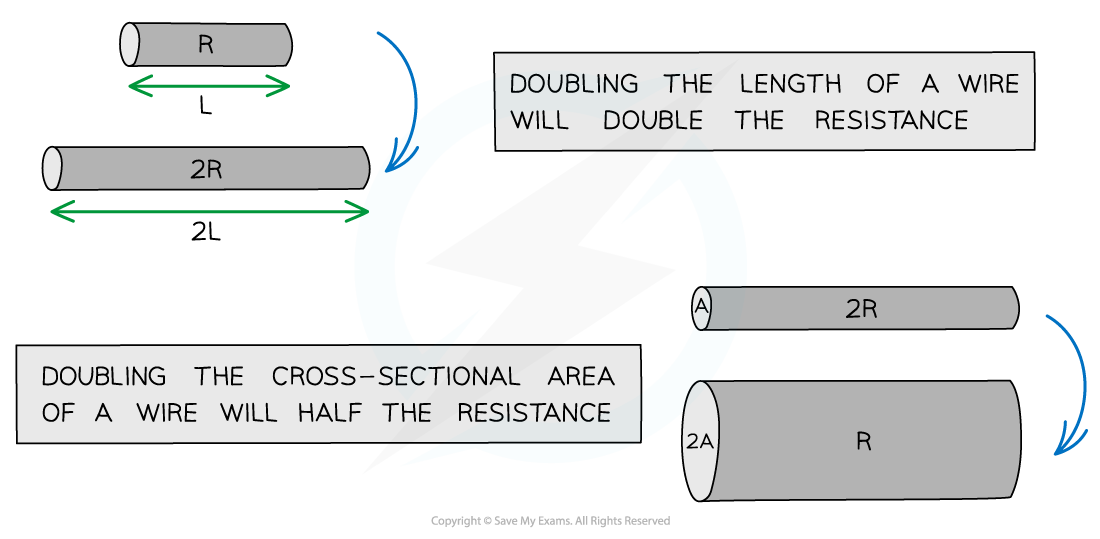 How the length and width of a wire affect its resistance
How the length and width of a wire affect its resistance
Defining Resistivity
- This leads to the definition of a new quantity, called resistivity
- Resistivity is a property describing the extent to which a material opposes the flow of electric current through it
- It is defined as follows:
The resistivity of a material is equal to the resistance per unit length of a material with unit cross-sectional area
- The equation for the resistivity is:
![]()
- Where:
- ρ = resistivity in ohm-metres (Ω m)
- R = resistance in ohms (Ω)
- A = cross sectional area of material in square metres (m2)
- L = length of material in meres (m)
Resistivity of Conductors and Insulators
- Resistivity is dependent on temperature
- In conductors, the resistivity increases with increasing temperature
- In insulators, the resistivity decreases with increasing temperature
- Since ρ ∝ R, when a wire or the filament inside a lamp heat up, their resistance increases
Resistivity of some materials at room temperature
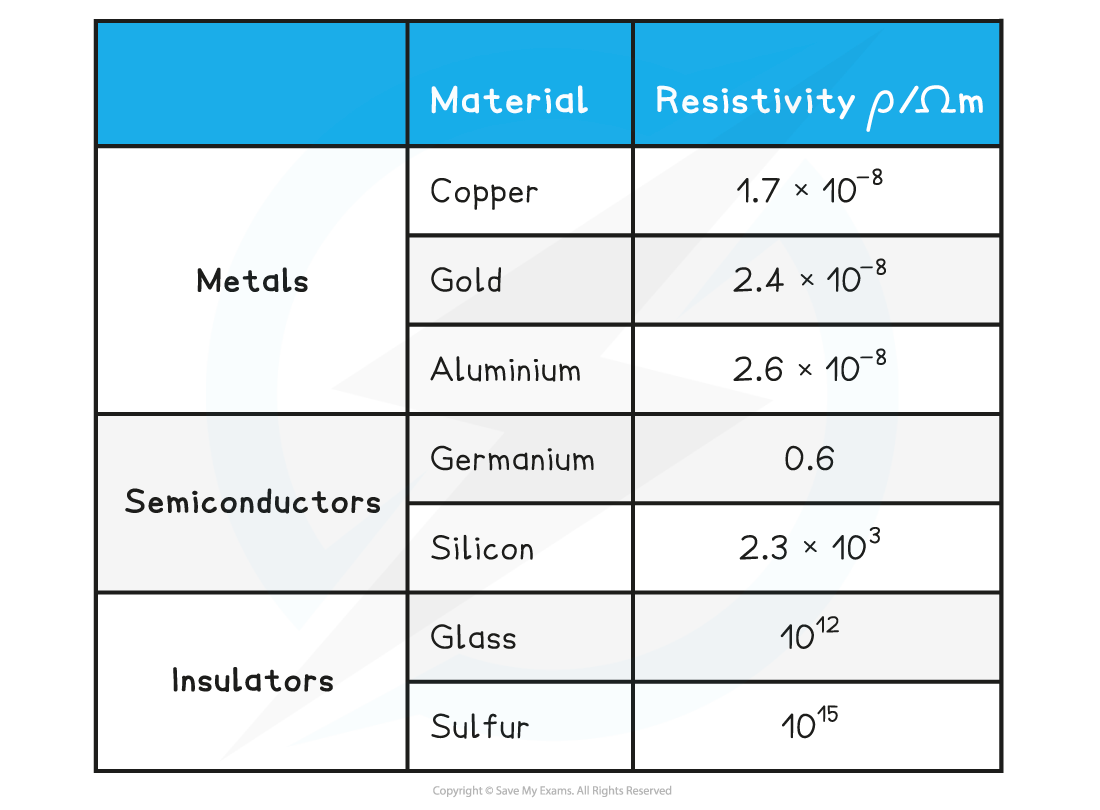
- Conductors have the lowest values of resistivity
- Wires are made from copper because of its relatively low resistivity at room temperature
- Insulators have such a high resistivity that virtually no current will flow through them
Worked Example
Two electrically-conducting cylinders made from copper and aluminium respectively.
Their dimensions are shown below.

Copper resistivity = 1.7 × 10–8 Ω m
Aluminium resistivity = 2.6 × 10–8 Ω mDetermine which cylinder is a better conductor.
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
-
- Copper (Cu):
- Diameter, dCu = 5 mm = 5 × 10–3 m
- Length, LCu = 8 mm = 8 × 10–3 m
- Resistivity, ρCu = 1.7 × 10–8 Ω m
- Copper (Cu):
-
- Aluminium (Al):
- Diameter, dAl = 10 mm = 10 × 10–3 m
- Length, LAl = 16 mm = 16 × 10–3 m
- Resistivity, ρAl = 2.6 × 10–8 Ω m
- Aluminium (Al):
Step 2: A conductor is better if it has a lower resistance
Step 3: Write down the equation for resistivity
![]()
Step 4: Rearrange the above equation to calculate the resistance R
![]()
Step 5: Substitute the numbers into the above equation to calculate the resistance of copper RCu and the resistance of aluminium RAl
-
- The cross-sectional area A is calculated from the diameter d as follows:
- A = π(d/2)2
- The cross-sectional area A is calculated from the diameter d as follows:
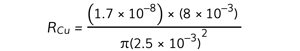
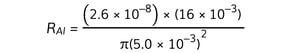
Step 6: Compare the two values of the resistance
-
- The cylinder with the lower resistance is the better conductor
RCu = 6.9 × 10–6 Ω
RAl = 5.3 × 10–6 Ω
RAl < RCu
The aluminium cylinder is the better conductor.
Exam Tip
You won’t need to memorise the value of the resistivity of any material, these will be given in the exam question. The equation for resistivity is given in the data booklet.Remember, if the cross-sectional area is a circle (e.g. in a wire), it is proportional to the diameter squared. This means if the diameter doubles, the area quadruples causing the resistance to drop by a quarter.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









