- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: SL复习笔记5.1.3 Potential Difference & DC
Potential Difference
- Potential difference is a measure of the electrical potential energy transferred from an electron as it moves between two points in a conductor
Potential difference is work done per unit charge
- It is also known as voltage
- Potential difference (pd) is calculated as follows:
![]()
- Where:
- V = potential difference in volts (V)
- W = work done in joules (J)
- q = charge in coulombs (C)
- From the above equation, one volt is equal to one joule per unit coulomb
- 1 V = 1 J C–1
The Electronvolt
- The energy values associated to electrons and other microscopic particles are very small when expressed in SI units
- For this reason, it is often more convenient to use another unit for energy - the electronvolt (eV)
- The electronvolt is defined as follows:
The amount of energy needed to move an electron through a potential difference of one volt
Worked Example
Determine the value of 1 eV in joules (J).
Step 1: Recall the definition of electronvolt
-
- One electronvolt is the work W associated to an electron of charge e moving through a potential difference V = 1V
W = eV
Step 2: Look up the charge e of the electron in the data booklet
-
- e = 1.6 × 10–19 C
Step 3: Substitute this and the value of the voltage into the above equation for W
W = (1.6 × 10–19 C) × 1 V
W = 1.6 × 10–19 J
One electronvolt is equal to 1.6 × 10–19 joules
Direct Current
- The potential difference in a circuit is provided by cells or batteries
- Each cell has a positive terminal (high potential location) and a negative terminal (low potential location)
- A battery is a collection of cells arranged positive terminal to negative terminal

A cell and a battery made of three cells
- When a cell or a battery is connected to a loop of copper wire, a circuit is formed
- The battery is the source of the potential difference V needed for the electrons to flow
- Electrons gain electrical potential energy as they move through the battery
- They then leave the battery and move through the wire
- A little amount of their energy is transferred to the metal atoms of the wire
- The flow of electrons is from the negative terminal to the positive one
- Direct current (dc) flows through the circuit in one direction
- The direction of conventional current is from the positive terminal to the negative one
- This is opposite to the electrons flow
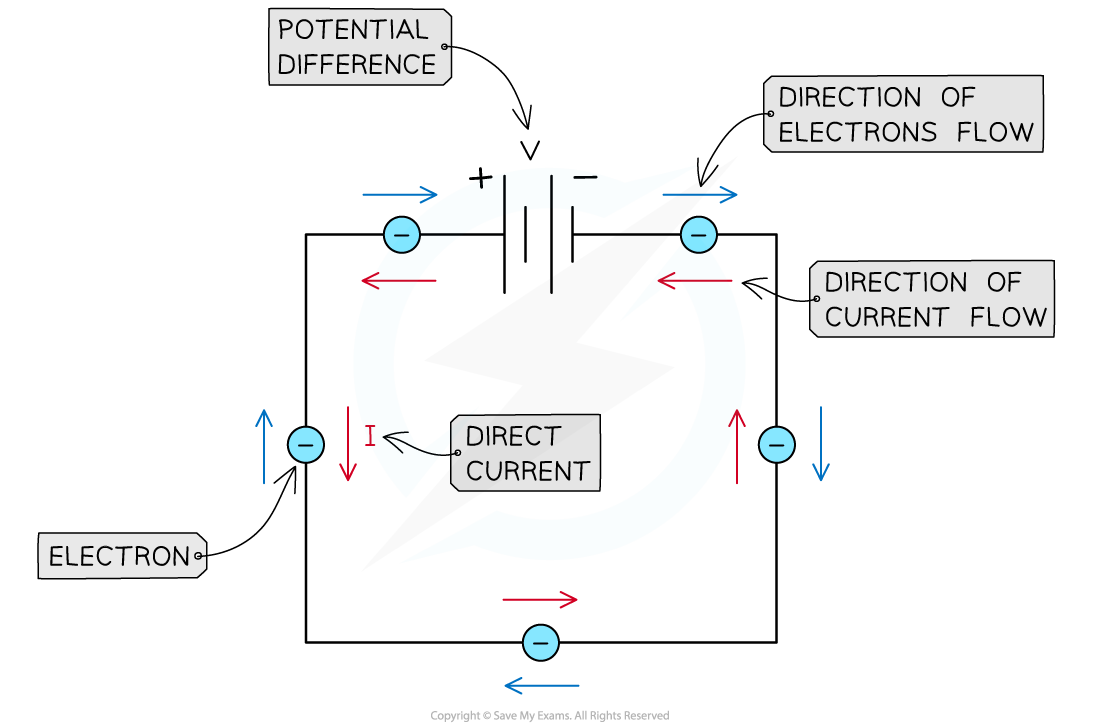
Direct current flows from the positive to the negative terminal of the battery in a circuit. Electrons flow in the opposite direction
Alternating Current
- Alternating current (ac) is used instead of dc in high voltage devices (i.e. those typically used in homes and industries)
- Alternating current flows one way around the circuit and then reverses its flow
- ac direction usually changes every 0.01 s
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









