- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: SL复习笔记4.4.2 Reflection
Reflection
- When light hits a smooth plane surface, most of it gets reflected
- Very smooth reflective surfaces (e.g. mirrors) are known as specular plane reflectors
- For these surfaces, the law of reflection applies:
The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence
i = r
- Where:
- The angle of incidence (i) is the angle between the incident ray and the normal
- The angle of reflection (r) is the angle between the reflected ray and the normal
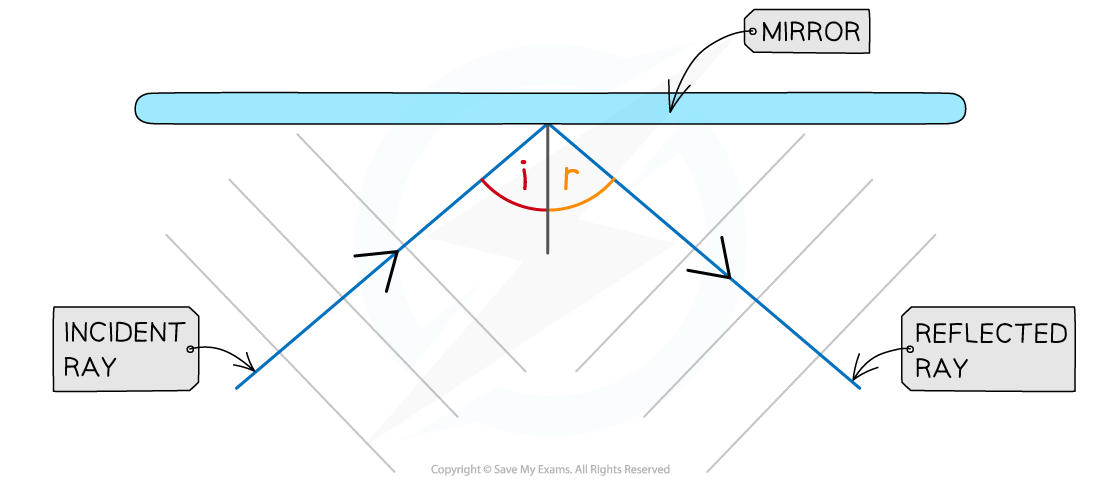
A light ray being reflected by a mirror
- The wavelength of the reflected ray is the same as that of the incident ray
Worked Example
A light ray is reflected by a mirror as shown in the diagram below.
a) State the angle of reflection
b) Add the incident and reflected wavefronts to the diagram
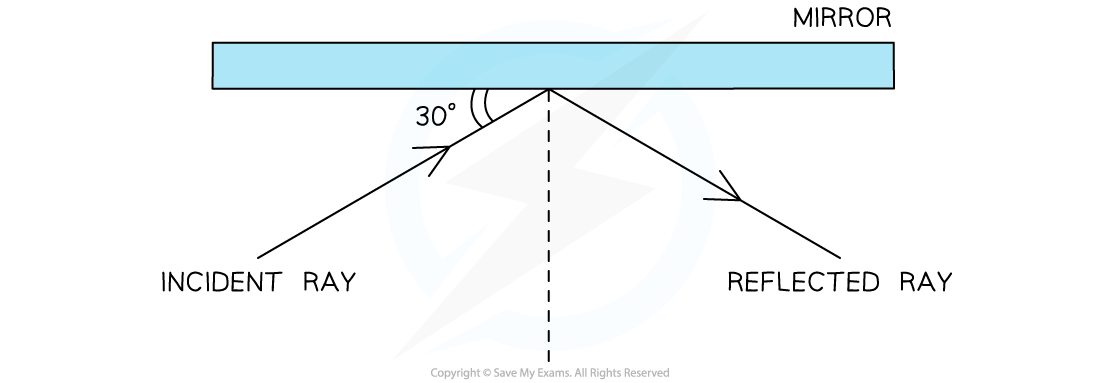
a) State the angle of reflection
Step 1: Recall the definition of the angle of incidence (i)
-
- The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the normal
- This is not the 30° angle marked in the diagram
i = 90° – 30°
i = 60°
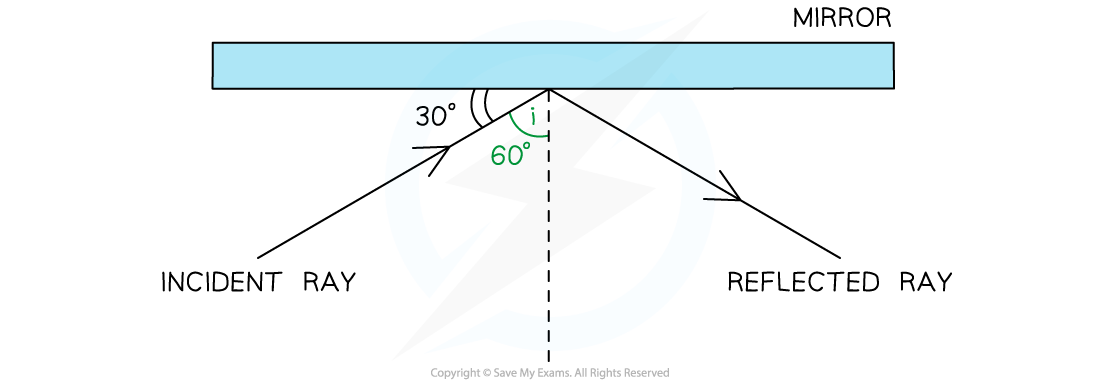
Step 2: Recall the law of reflection
The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence
Step 3: State the angle of reflection (r)
r = 60°
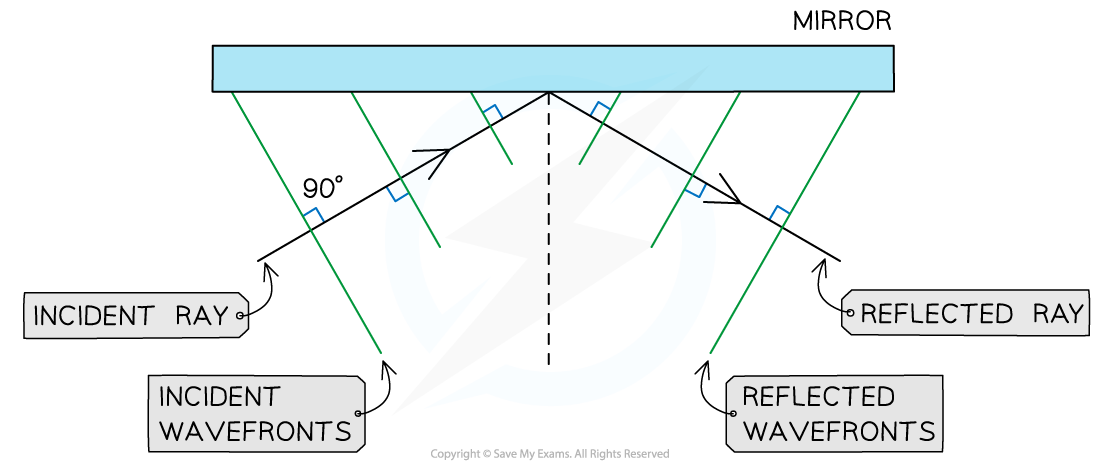
b) Add the incident and reflected wavefronts to the diagram
Step 1: Recall that wavefronts and rays are perpendicular to each other
-
- Add at least three equally spaced wavefronts all perpendicular to the incident ray
- Add at least three equally spaced wavefronts all perpendicular to the reflected ray
Exam Tip
When asked to complete or construct reflection ray diagrams, remember to add:
- arrows on rays to distinguish between incident and reflected rays
- labels to distinguish between incident and reflected wavefronts
In most cases, when dealing with light, you will just need to draw rays. However, you might still be required to draw wavefronts sometimes. Always use a ruler or a straight edge and a shape pencil for the ray diagrams.
Remember that the distance between each wavefront represents the wavelength of the wave. If you intend on the ray not changing wavelength (like in reflection) then make sure the incident and reflected wavefronts are all equally spaced by the same amount.
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








