- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: SL复习笔记3.2.2 Ideal Gas Equation
Ideal Gas Equation
Avogadro's Law
- Avogadro's Law states:
For a gas at constant temperature and pressure, the number of moles n is directly proportional to the volume V of the gas
- This can be expressed in equation form as:
![]()
- This means that two different gases of equal temperatures, pressures and volumes have the same number of particles N
- Note that the number of particles N is directly proportional to the number of moles n
Equation of State for an Ideal Gas
- Boyle's Law, Charles's Law and Gay-Lussac's law can be combined with Avogadro's law to give a single constant, known as the ideal gas constant, R
- Combining the four equations leads to the equation of state of an ideal gas
![]()
![]()
- Where:
- p = pressure in pascals (Pa)
- V = volume in metres cubed (m3)
- T = temperature in kelvin (K)
- n = number of moles in the gas (mol)
- R = 8.31 J K–1 mol–1 (ideal gas constant)
Worked Example
A gas has a temperature of –55°C and a pressure of 0.5 MPa. It occupies a volume of 0.02 m3.Calculate the number of gas particles.
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
-
- Temperature, T = –55°C = 218 K
- Pressure, p = 0.5 MPa = 0.5 × 106 Pa
- Volume, V = 0.02 m3
Note the conversions:
-
- The pressure p must be converted from megapascals (MPa) into pascals (Pa)
- The temperature must be converted from degrees Celsius (°C) into kelvin (K)
Step 2: Write down the equation of state of ideal gases
![]()
Step 3: Rearrange the above equation to calculate the number of moles n
![]()
Step 4: Substitute numbers into the equation
-
- From the data booklet, R = 8.31 J K–1 mol–1
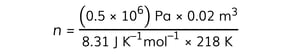 n = 5.5 mol
n = 5.5 mol
Step 5: Calculate the number of particles N
-
- Write down the relationship between number of particles and number of moles
N = nNA
-
- From the data booklet, NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol–1 (Avogadro constant)
N = 5.5 mol × (6.02 × 1023) mol–1
N = 3.3 × 1024
Exam Tip
When using the equation of state of ideal gases, always remember to convert temperatures from degrees Celsius (°C) to kelvin (K).Note that the number of moles n is not the same as the number of particles N:
- When a question asks to calculate the number of particles in a sample of gas, you should first use the equation of state to determine the number of moles n of the gas, and then calculate the number of particles using N = nNA
- If a question gives the number of particles in a sample of gas instead of the number of moles, you should first use n = N/NA to calculate the number of moles of the gas, and then use the equation of state to perform any further calculation (e.g. volume, pressure, etc.)
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









