- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: SL复习笔记2.3.3 Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic Potential Energy
- Elastic potential energy is defined as
The energy stored within a material (e.g. in a spring) when it is stretched or compressed
- It can be found from the area under the force-extension graph for a material deformed within its limit of proportionality
- A material within its limit of proportionality obeys Hooke’s law
- Therefore, for a material obeying Hooke’s Law, elastic potential energy can be calculated using:
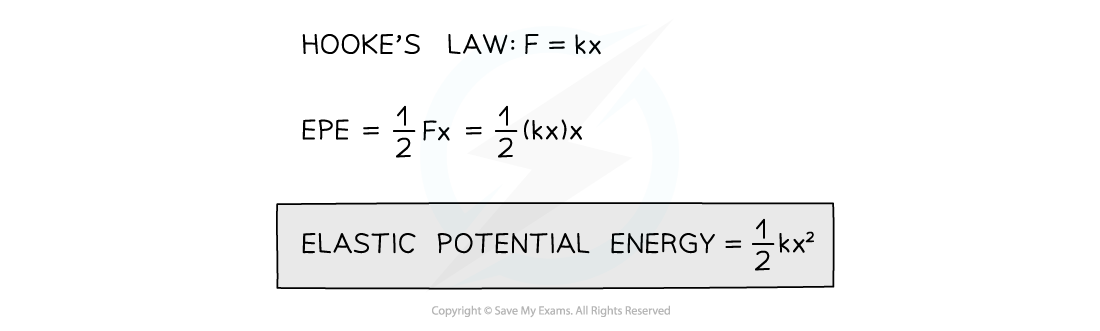
- Where:
- k = force constant of the spring (N m–1)
- x = extension (m)
- In your data booklet the extension x is written as Δx
- This just means the change in x
- It is very dangerous if a wire under large stress suddenly breaks
- This is because the elastic potential energy of the strained wire is converted into kinetic energy
EPE = KE
½ kx2 = ½ mv2
v ∝ x
- This equation shows that the greater the extension of a wire, x, the greater the speed, v, it will have on breaking
Worked Example
A car’s shock absorbers make a ride more comfortable by using a spring that absorbs energy when the car goes over a bump. One of these springs, with a force constant of 50 kN m–1 is fixed next to a wheel and compressed a distance of 10 cm.Calculate the energy stored by the compressed spring.
Step 1: List the known values
-
- Force constant, k = 50 kN m–1 = 50 × 103 N m–1
- Compression, x = 10 cm = 10 × 10–2 m
Step 2: Write the relevant equation
EPE = ½ kx2
Step 3: Substitute in the values
EPE = ½ × (50 × 103) × (10 × 10–2)2 = 250 J
Force–Extension graphs
- Work has to be done to stretch a material
- Before a material reaches its elastic limit (whilst it obeys Hooke's Law), all the work is done is stored as elastic potential energy (EPE)
- The work done, or the elastic potential energy is the area under the force-extension graph
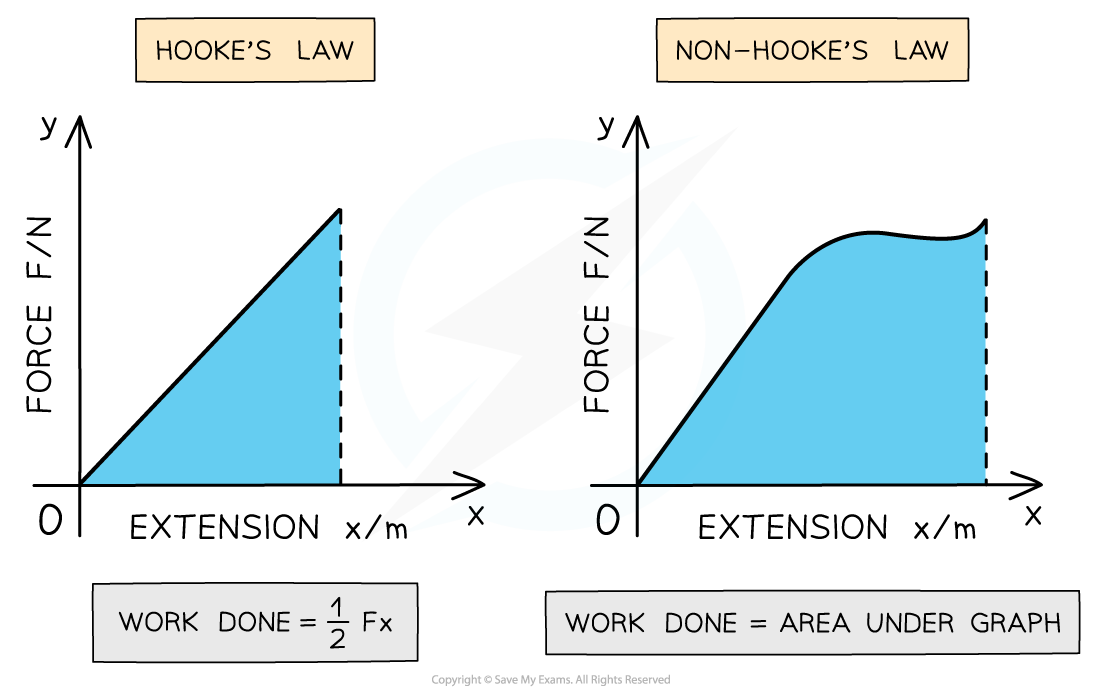 Work done is the area under the force-extension graph
Work done is the area under the force-extension graph
- This is true for whether the material obeys Hooke’s law or not
- For the region where the material obeys Hooke’s law, the work done is the area of a right-angled triangle under the graph
- For the region where the material doesn’t obey Hooke’s law, the area is the full region under the graph. To calculate this area, split the graph into separate segments and add up the individual areas of each
Breaking Stress
- As greater force is applied on a material, the stress on it increases
- The breaking stress is the maximum stress a material can stand before it fractures (breaks)
- A material with high breaking stress is considered ductile, which means it can extend more before breaking because of plastic deformation
- A common example of this is copper, as well as being a good electrical conductor, copper is ductile so it is a suitable material for making wires
- The ultimate tensile stress (UTS) is sometimes also marked on a stress-strain graph
- This is the maximum stress that the material can withstand
- The UTS and breaking stress can depend on the condition of the material such as its temperature
- This is very important for engineers when considering materials for a particular structure
- The material might need to stand extreme temperatures and loads which are taken into consideration
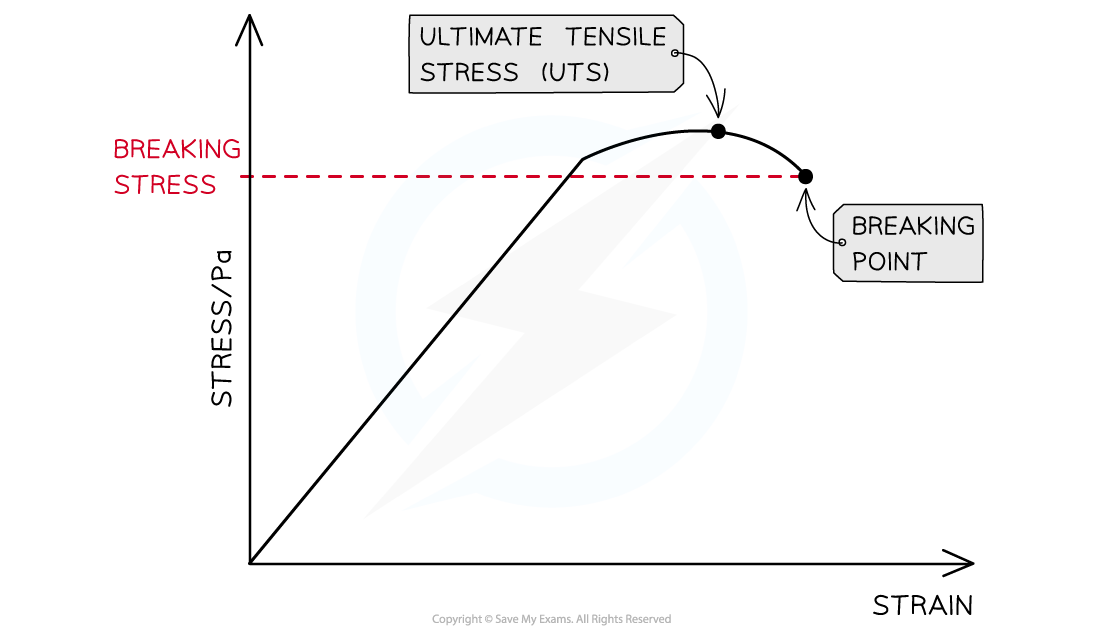
The ultimate breaking stress is the point on the stress-strain graph of maximum stress. The breaking point is where the material fractures
Worked Example
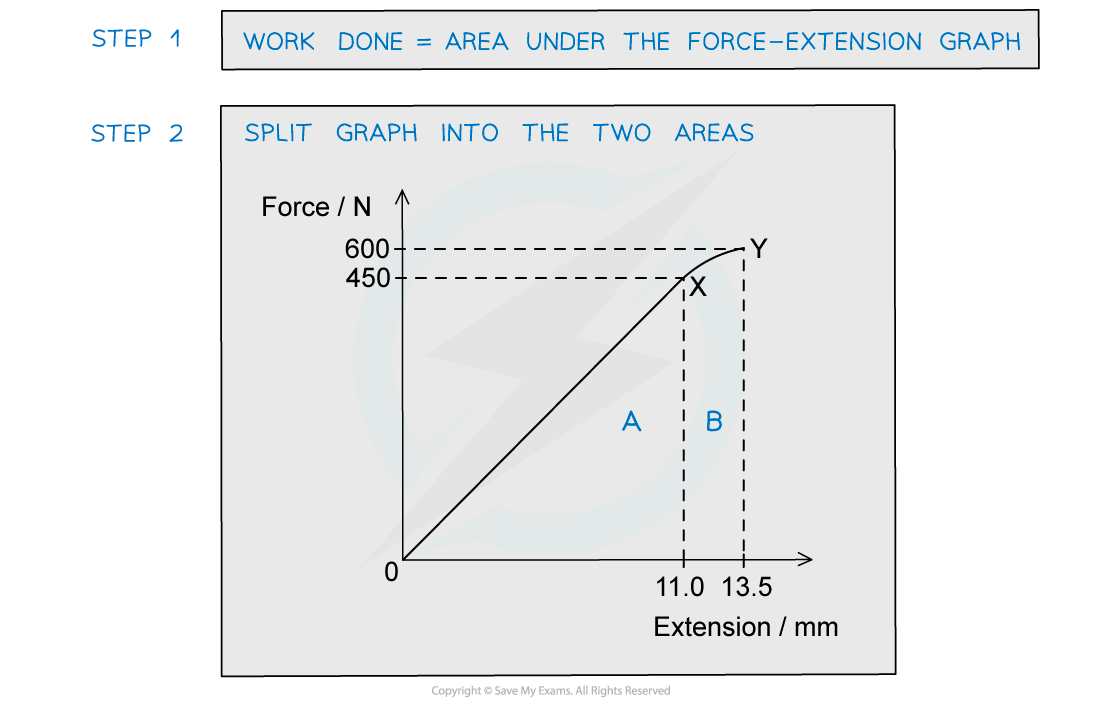
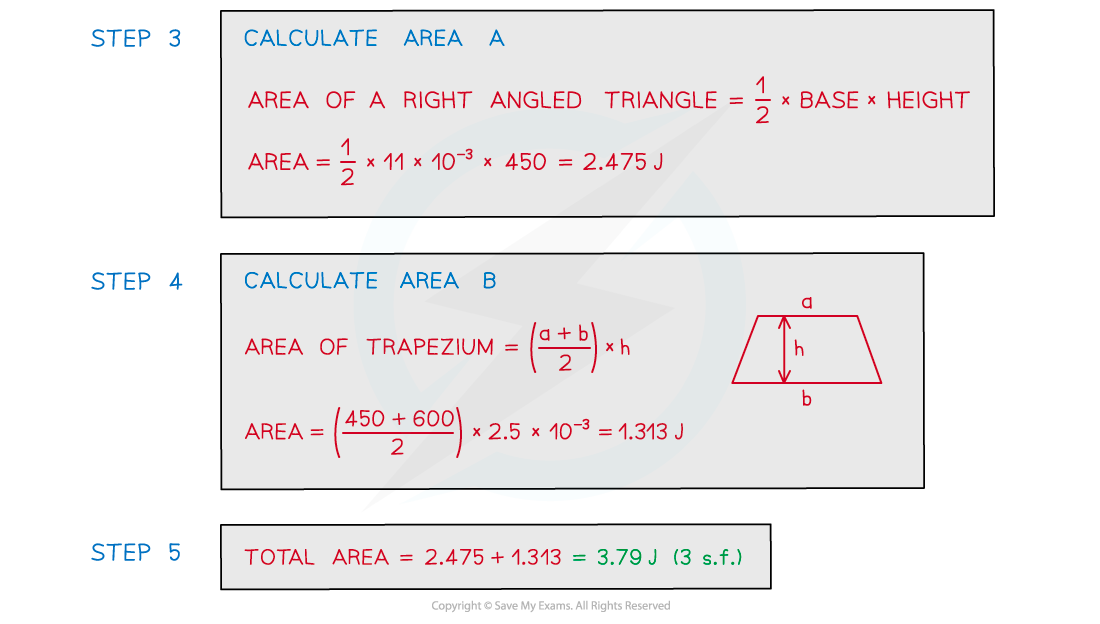
The graph shows the behaviour of a sample of a metal when it is stretched until it starts to undergo plastic deformation.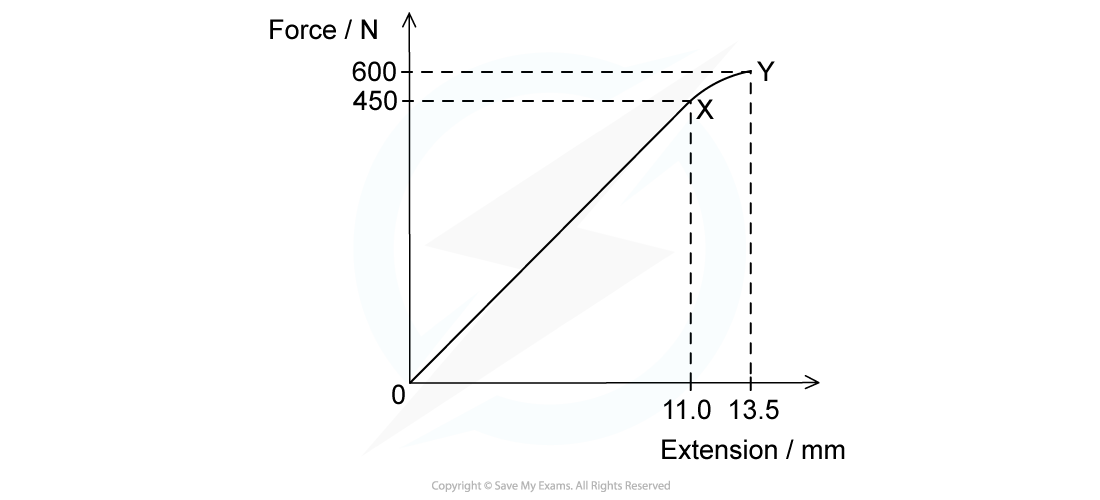 Calculate the total work done in stretching the sample from zero to an extension of 13.5 mm.Simplify the calculation by treating the curve XY as a straight line.
Calculate the total work done in stretching the sample from zero to an extension of 13.5 mm.Simplify the calculation by treating the curve XY as a straight line.
Worked Example
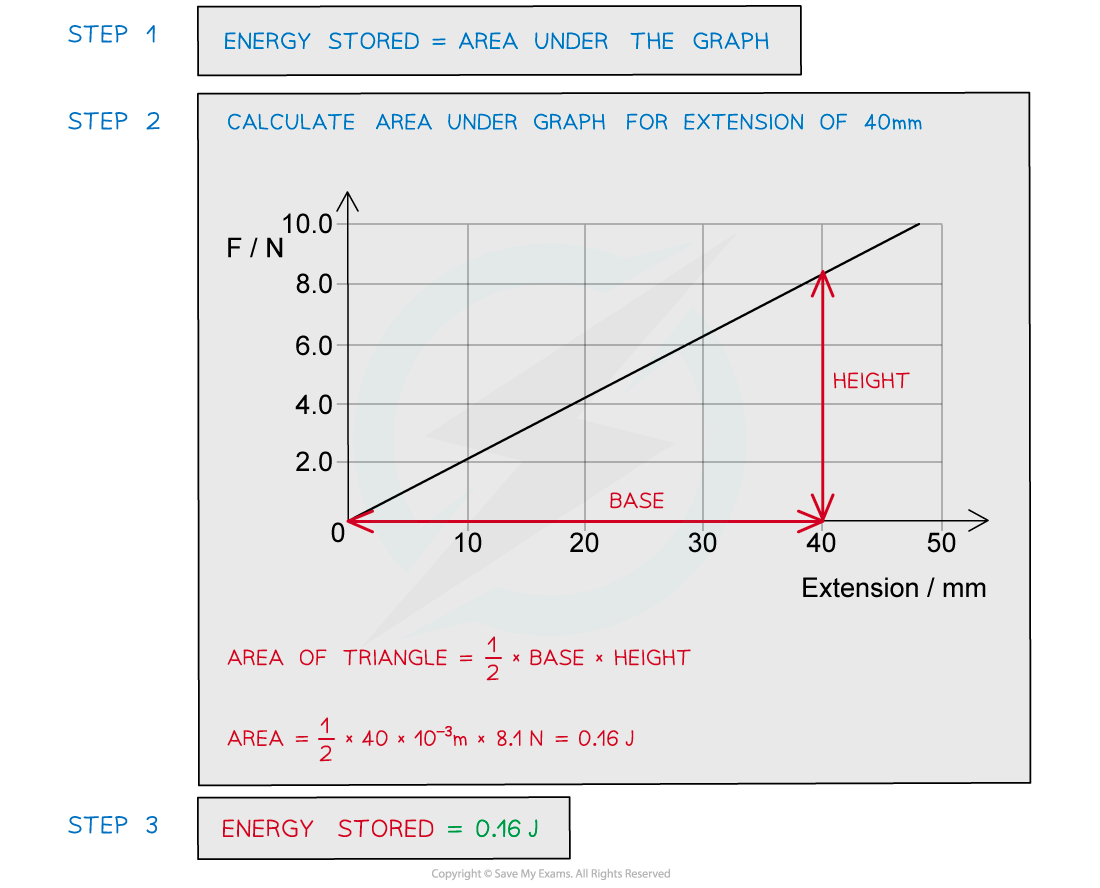
A spring is extended with varying forces; the graph below shows the results.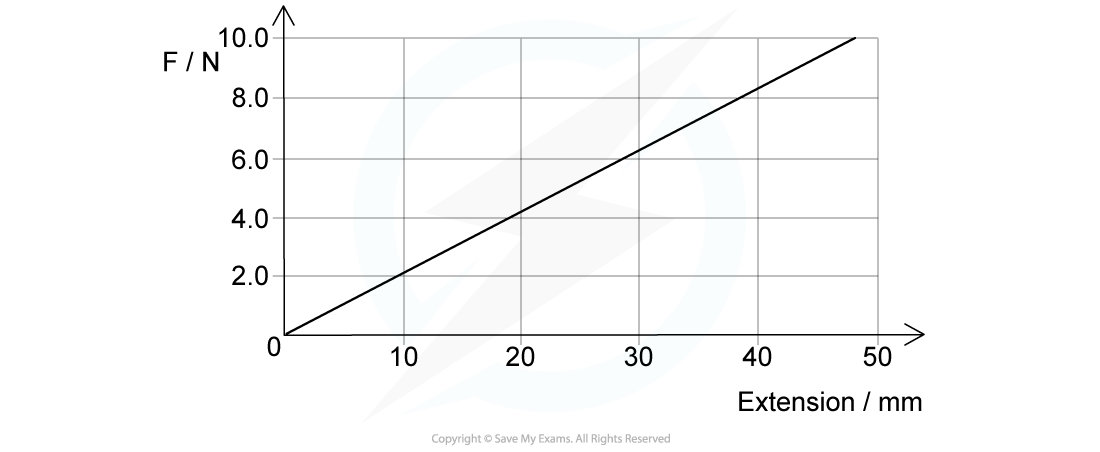 Calculate the energy stored in the spring when the extension is 40 mm.
Calculate the energy stored in the spring when the extension is 40 mm.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









