- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: SL复习笔记4.3.1 Types of Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular Forces
- There are no covalent bonds between molecules in molecular covalent compounds. There are, however, forces of attraction between these molecules, and it is these which must be overcome when the substance is melted and boiled
- These forces are known as intermolecular forces
- There are three main types of intermolecular forces:
- London(dispersion) forces
- Dipole-dipole attraction
- Hydrogen bonding
London (dispersion) forces
- The electrons in atoms are not static; they are in a state of constant motion
- It is therefore likely that at any given time the distribution of electrons will not be exactly symmetrical - there is likely to be a slight surplus of electrons on one side of the atoms
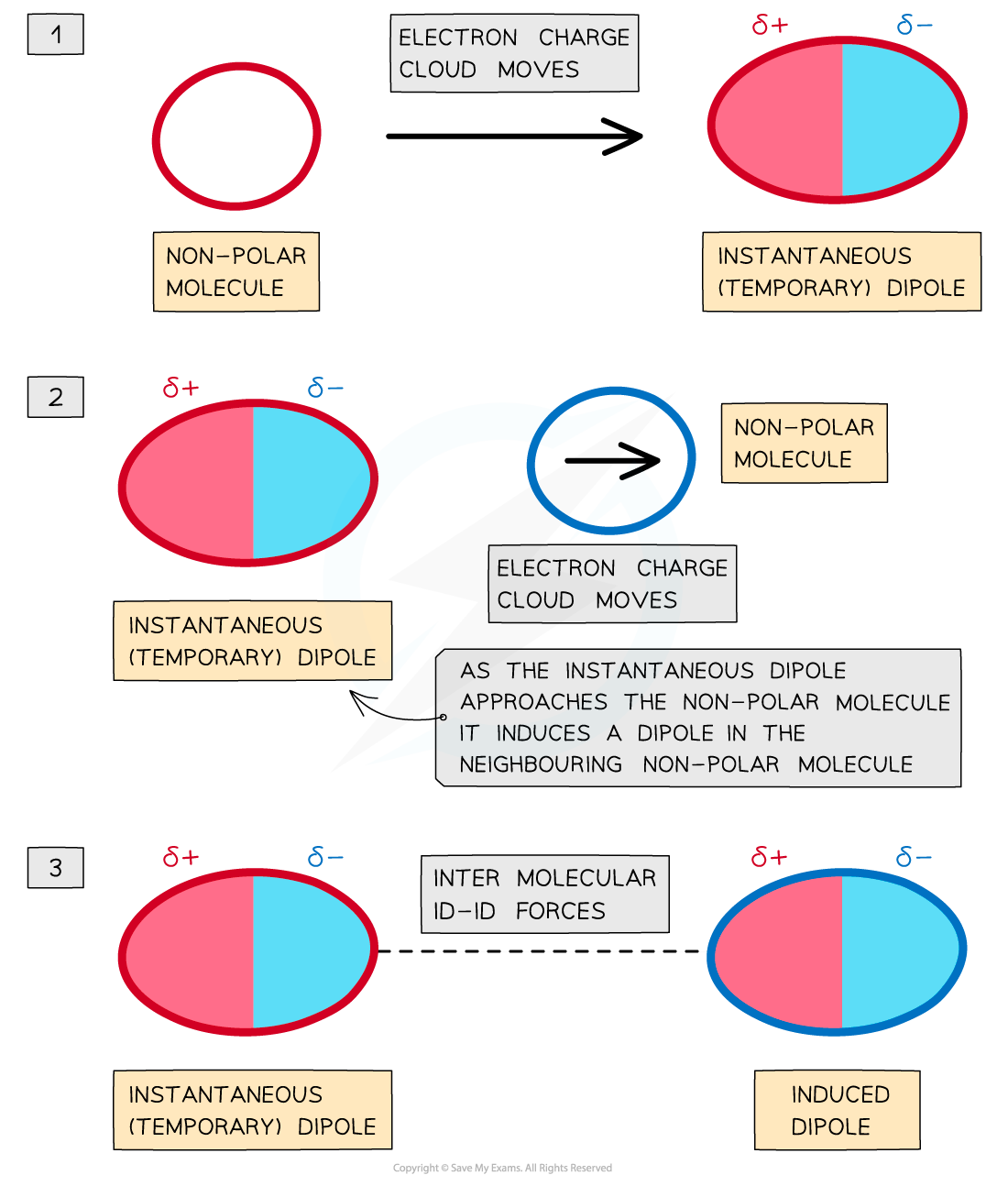 London (Dispersion) forces
London (Dispersion) forces
- This is known as a temporary dipole
- It lasts for a very short time as the electrons are constantly moving
- Temporary dipoles are constantly appearing and disappearing
- Consider now an adjacent atom. The electrons on this atom are repelled by the negative part of the dipole and attracted to the positive part and move accordingly
- This is a temporary induced dipole
- There is a resulting attraction between the two atoms, and this known as London (dispersion) forces, after the German chemist, Fritz London
- London (dispersion) forces are present between all atoms and molecules, although they can be very weak
- They are the reason all compounds can be liquefied and solidified
- London (dispersion) forces tend to have strengths between 1 kJmol-1 and 50 kJmol-1.
- The strength of the London( dispersion) forces in between molecules depends on two factors:
- the number of electrons in the molecule
- Surface area of the molecules
Number of electrons
- The greater the number of electrons in a molecule, the greater the likelihood of a distortion and thus the greater the frequency and magnitude of the temporary dipoles
- The dispersion forces between the molecules are stronger and the melting and boiling points are larger
- The [popover id="1iji1iYH5LAecIpp" label="enthalpies of vaporisation"] and boiling points of the noble gases illustrate this factor:
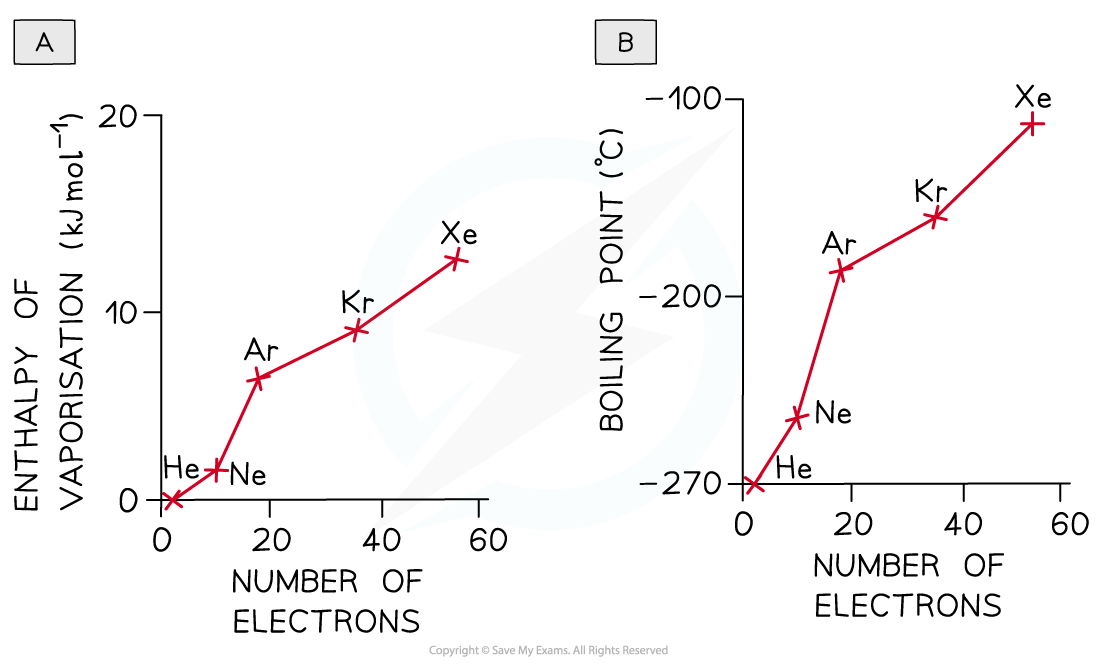
As the number of electrons increases more energy is needed to overcome the forces of attraction between the noble gases atoms
Surface area
- The larger the surface area of a molecule, the more contact it will have with adjacent molecules
- The greater its ability to induce a dipole in an adjacent molecule, the greater the London (dispersion) forces and the higher the melting and boiling points
- This point can be illustrated by comparing different isomers containing the same number of electrons:
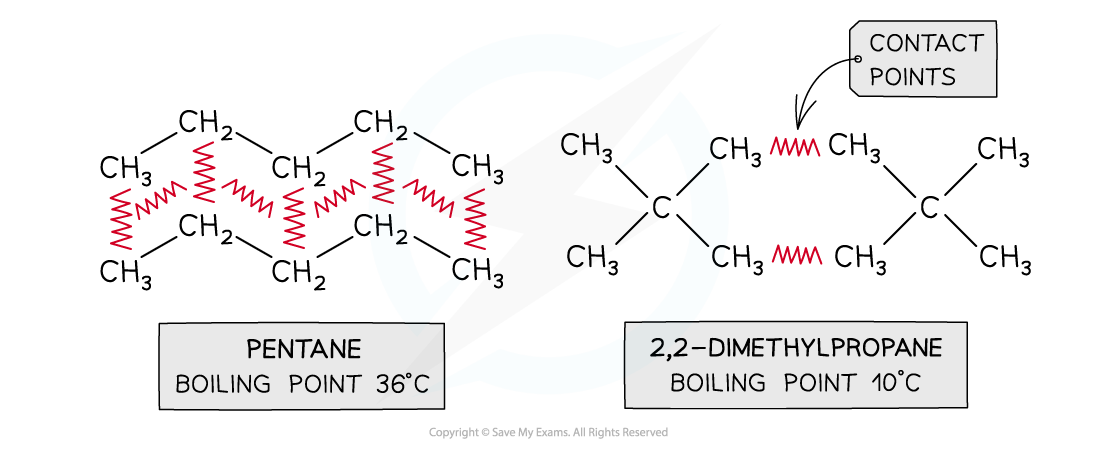
Boiling points of molecules with the same numbers of electrons but different surface areas
Dipole-dipole atttractions
- Temporary dipoles exist in all molecules, but in some molecules there is also a permanent dipole
- In addition to the London (dispersion) forces caused by temporary dipoles, molecules with permanent dipoles are also attracted to each other by permanent dipole-dipole bonding
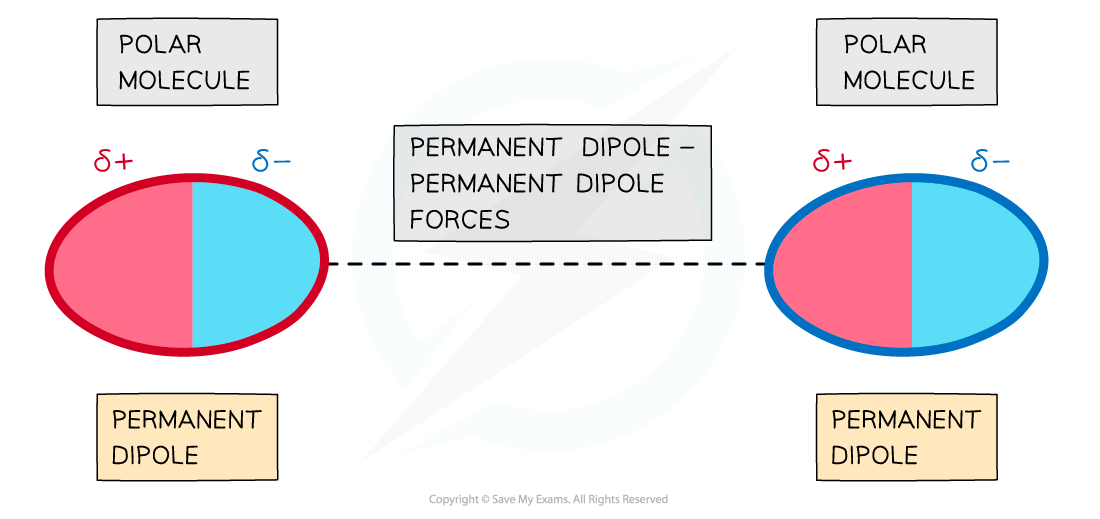
The delta negative end of one polar molecule will be attracted onwards the delta positive end of a neighbouring polar molecule
- This is an attraction between a permanent dipole on one molecule and a permanent dipole on another.
- Dipole-dipole bonding usually results in the boiling points of the compounds being slightly higher than expected from temporary dipoles alone
- it slightly increases the strength of the intermolecular attractions
- The effect of dipole-dipole bonding can be seen by comparing the melting and boiling points of different substances which should have London(dispersion) forces of similar strength
Comparing butane and propanone
- For small molecules with the same number of electrons, dipole-dipole attractions are stronger than dispersion forces
- Butane and propanone have the same number of electrons
- Butane is a nonpolar molecule and will have only dispersion forces
- Propanone is a polar molecule and will have dipole-dipole attractions and dispersion forces
- Therefore, more energy is required to break the intermolecular forces between propanone molecules than between butane molecules
- The result is that propanone has a higher boiling point than butane
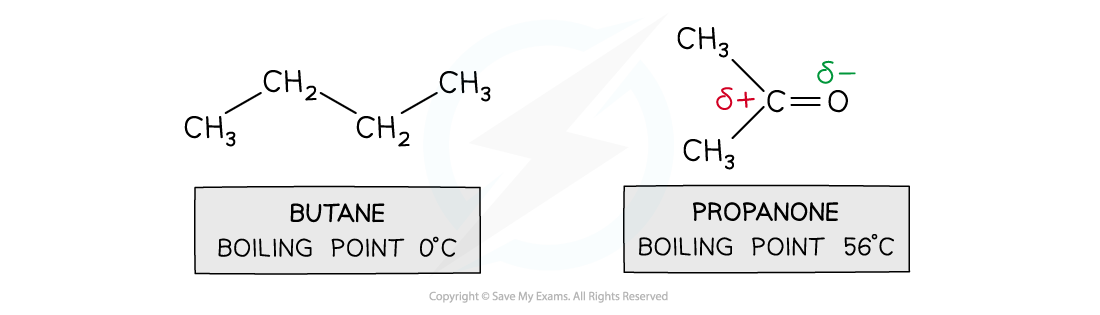 Comparing substances with permanent and temporary dipoles in smaller molecules with an equal number of electrons
Comparing substances with permanent and temporary dipoles in smaller molecules with an equal number of electrons
Hydrogen bonding
- Hydrogen bonding is the strongest type of intermolecular force
- Hydrogen bonding is a special type of permanent dipole – permanent dipole bonding
- For hydrogen bonding to take place the following is needed:
- A species which has an O or N or F (very electronegative) atom with an available lone pair of electrons
- A hydrogen attached to the O, N or F
- When hydrogen is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom, such as O or N, the bond becomes very highly polarised
- The H becomes so δ+ charged that it can form a bond with the lone pair of an O or N atom in another molecule
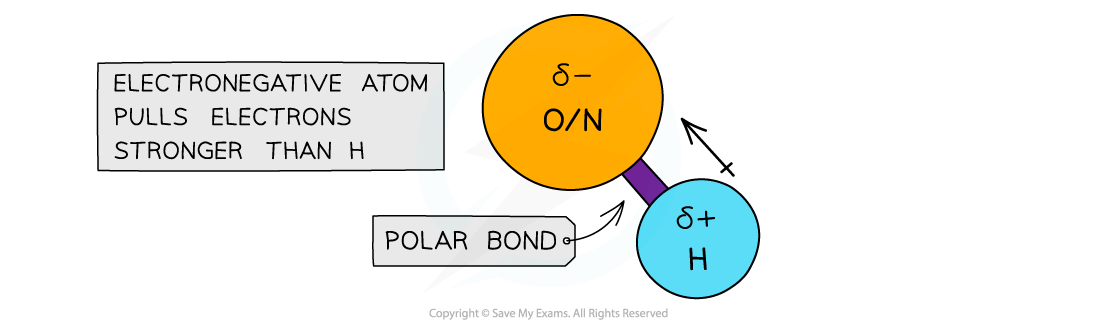
The electronegative atoms O or N have a stronger pull on the electrons in the covalent bond with hydrogen, causing the bond to become polarised
- Hydrogen bonds are represented by dots or dashes between H and the N/O/F element
- The number of hydrogen bonds depends on:
- The number of hydrogen atoms attached to O or N in the molecule
- The number of lone pairs on the O or N
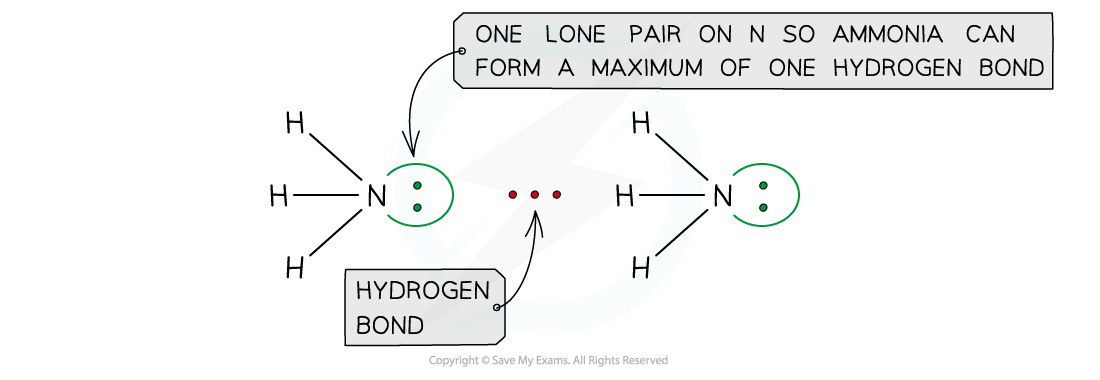
Ammonia can form a maximum of one hydrogen bond per molecule
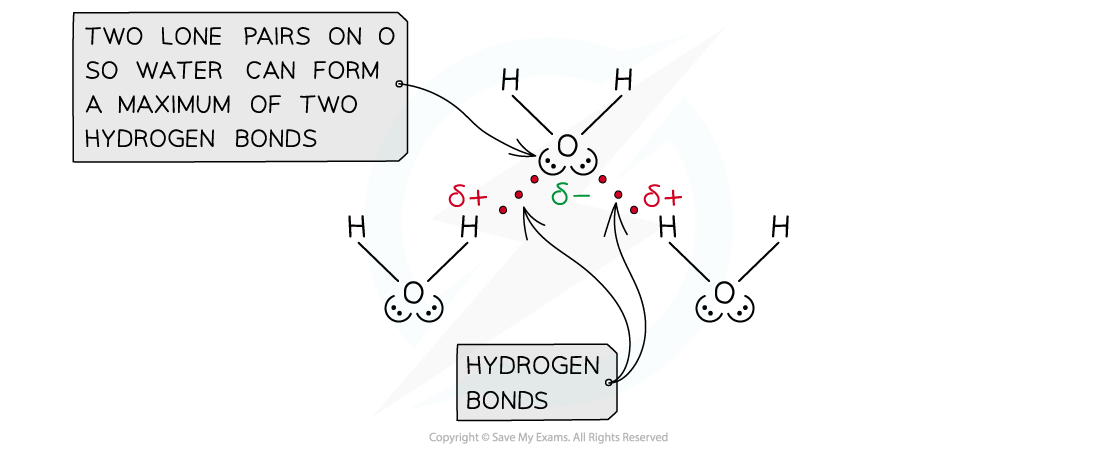
Water can form a maximum of two hydrogen bonds per molecule
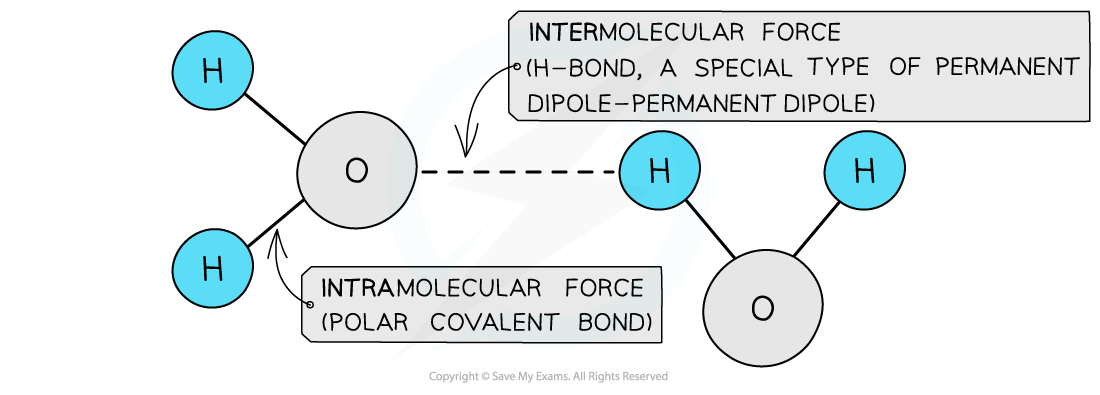
The polar covalent bonds between O and H atoms are intramolecular forces and the permanent dipole – permanent dipole forces between the molecules are intermolecular forces as they are a type of van der Waals’ force
Exam Tip
The term “London (dispersion) forces” refers to instantaneous induced dipole induced dipole forces that exist between any atoms or groups of atoms and should be used for non-polar species. You may be wondering about the term “van der Waals” forces: it is an inclusive term and refers to dipole–dipole, dipole-induced dipole and London (dispersion) forces
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








