- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: SL复习笔记1.2.3 Avogadro's Law & Molar Gas Volume
Avogadro's Law
Volumes of gases
- In 1811 the Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro developed a theory about the volume of gases
- Avogadro’s law (also called Avogadro’s hypothesis) enables the mole ratio of reacting gases to be determined from volumes of the gases
- Avogadro deduced that equal volumes of gases must contain the same number of molecules
- At standard temperature and pressure(STP) one mole of any gas has a volume of 22.7 dm3
- The units are normally written as dm3 mol-1(since it is 'per mole')
- The conditions of STP are
- a temperature of 0o C (273 K)
- pressure of 100 kPa
Stoichiometric relationships
- The stoichiometry of a reaction and Avogadro's Law can be used to deduce the exact volumes of gaseous reactants and products
- Eg. in the combustion of 50 cm3 of propane, the volume of oxygen needed is (5 x 50) 250 cm3, and (3 x 50) 150 cm3 of carbon dioxide is formed, using the ratio of propane: oxygen: carbon dioxide, which is 1: 5: 3 respectively, as seen in the equation
C3H8 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 3CO2 (g) + 4H2O (l)
- Remember that if the gas volumes are not in the same ratio as the coefficients then the amount of product is determined by the limiting reactant so it is essential to identify it first
Worked Example
What is the total volume of gases remaining when 70 cm3 of ammonia is combusted completely with 50 cm3 of oxygen according to the equation shown?
4NH3 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 4NO (g) + 6H2O (l)
Answer:
Step 1: From the equation deduce the molar ratio of the gases, which is NH3 :O2 :NO or 4:5:4 (water is not included as it is in the liquid state)
Step 2: We can see that oxygen will run out first (the limiting reactant) and so 50 cm3 of O2 requires 4/5 x 50 cm3 of NH3 to react = 40 cm3
Step 3: Using Avogadro's Law, we can say 40 cm3 of NO will be produced
Step 4: There will be of 70-40 = 30 cm3 of NH3 left over
Therefore the total remaining volume will be 40 + 30 = 70 cm3 of gases
Exam Tip
Since gas volumes work in the same way as moles, we can use the 'lowest is limiting' technique in limiting reactant problems involving gas volumes. This can be handy if you are unable to spot which gas reactant is going to run out first.Divide the volumes of the gases by the cofficients and whichever gives the lowest number is the limiting reactant
- E.g. in the previous problem we can see that
- For NH3 70/4 gives 17.5
- For O2 50/5 gives 10, so oxygen is limiting
Molar Gas Volume
- The molar gas volume of 22.7 dm3 mol-1 can be used to find:
- The volume of a given number of moles of gas:
volume of gas (dm3) = amount of gas (mol) x 22.7 dm3 mol-1
-
- The number of moles of a given volume of gas:
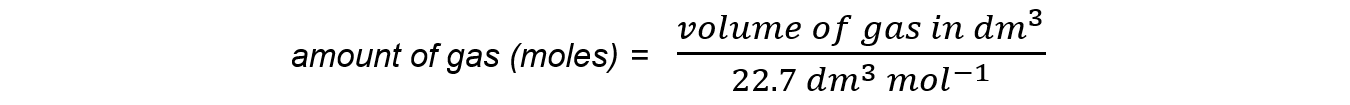
- The relationships can be expressed using a formula triangle
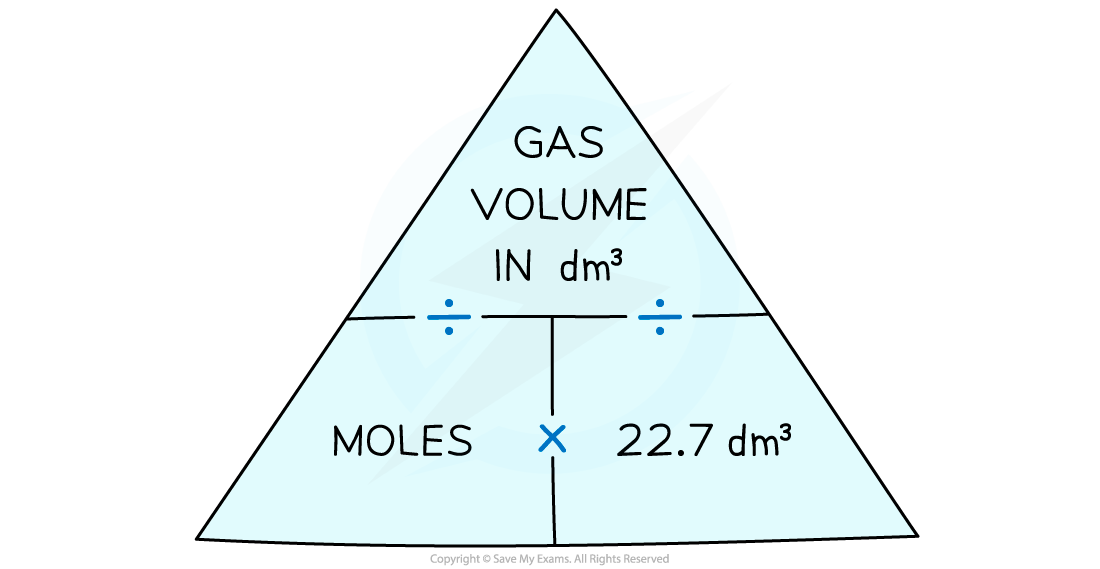
To use the gas formula triangle cover the one you want to find out about with your finger and follow the instructions
Worked Example
What is the volume occupied by 3.0 moles of hydrogen at stp ?
Answer:
volume of gas (dm3) = amount of gas (mol) x 22.7 dm3 mol-1
3.0 mol x 22.7 dm3 mol-1= 68 dm3
Worked Example
How many moles are in the following volumes of gases?
- 7.2 dm3 of carbon monoxide
- 960 cm3 of sulfur dioxide
Answer 1:
Use the formula:
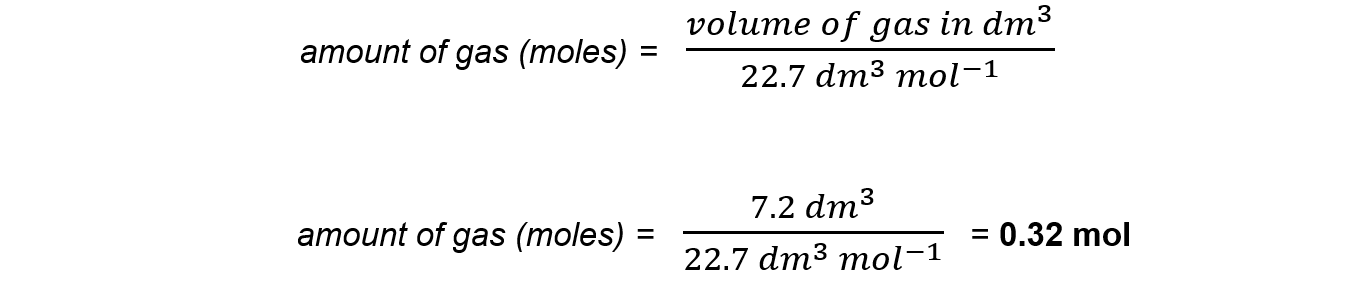 Answer 2:
Answer 2:
Step 1: Convert the volume from cm3 to dm3
960/1000 = 0.960 dm3
Step 2: Use the formula
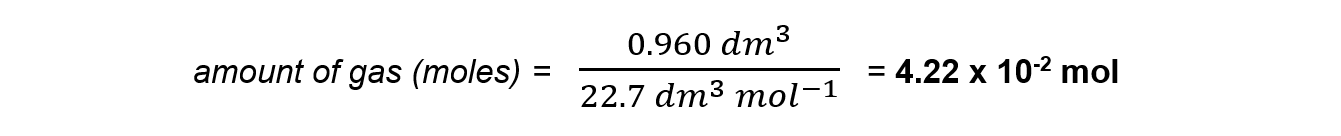
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









