- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: SL复习笔记1.2.1 Reacting Masses
Reacting Masses & Limiting Reactants
- The number of moles of a substance can be found by using the following equation:
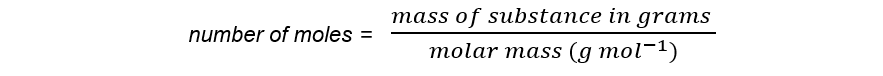
- It is important to be clear about the type of particle you are referring to when dealing with moles
- Eg. 1 mole of CaF2 contains one mole of CaF2 formula units, but one mole of Ca2+ and two moles of F- ions
Reacting masses
- The masses of reactants are useful to determine how much of the reactants exactly react with each other to prevent waste
- To calculate the reacting masses, the chemical equation is required
- This equation shows the ratio of moles of all the reactants and products, also called the stoichiometry, of the reaction
- To find the mass of products formed in a reaction the following pieces of information are needed:
- The mass of the reactants
- The molar mass of the reactants
- The balanced equation
Worked Example
Calculate the mass of magnesium oxide that can be made by completely burning 6.0 g of magnesium in oxygen.
magnesium (s) + oxygen (g) → magnesium oxide (s)
Answer:
Step 1: The symbol equation is:
2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
Step 2: The relative atomic masses are:
magnesium : 24.31 oxygen : 16.00
Step 3: Calculate the moles of magnesium used in reaction
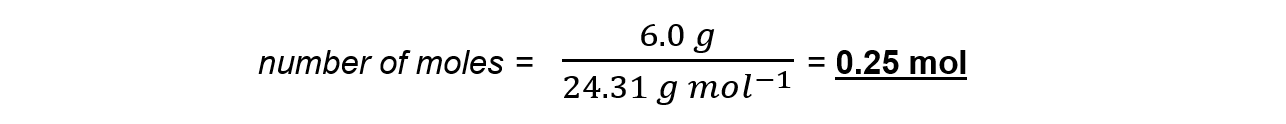
Step 4: Find the ratio of magnesium to magnesium oxide using the balanced chemical equation
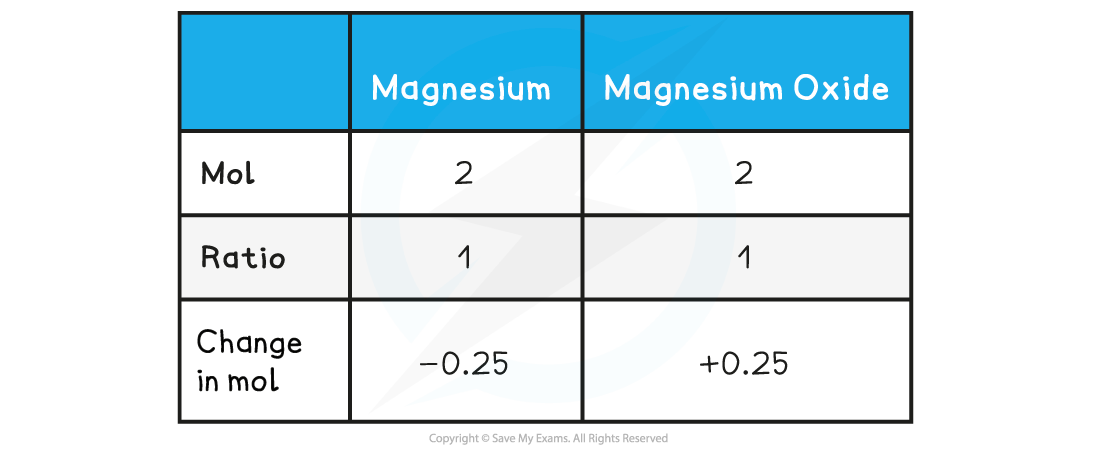
Therefore, 0.25 mol of MgO is formed
Step 5: Find the mass of magnesium oxide
mass = mol x M
mass = 0.25 mol x 40.31 g mol-1
mass = 10.08 g
Therefore, mass of magnesium oxide produced is 10 g (2 sig figs)
Excess & limiting reactants
- Sometimes, there is an excess of one or more of the reactants (excess reactant)
- The reactant which is not in excess is called the limiting reactant
- To determine which reactant is limiting:
- The number of moles of the reactants should be calculated
- The ratio of the reactants shown in the equation should be taken into account eg:
C + 2H2 → CH4
What is limiting when 10 mol of carbon are reacted with 3 mol of hydrogen?
- Hydrogen is the limiting reactant and since the ratio of C : H2 is 1:2 only 1.5 mol of C will react with 3 mol of H2
Exam Tip
An easy way to determine the limiting reactant is to find the moles of each substance and divide the moles by the coefficient in the equationThe lowest number resulting is the limiting reactant
- In the example above:
- divide 10 moles of C by 1, giving 10
- divide 3 moles of H by 2, giving 1.5, so hydrogen is limiting
Worked Example
9.2 g of sodium metal is reacted with 8.0 g of sulfur to produce sodium sulfide, Na2S.Which reactant is in excess and which is limiting?
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate the moles of each reactant
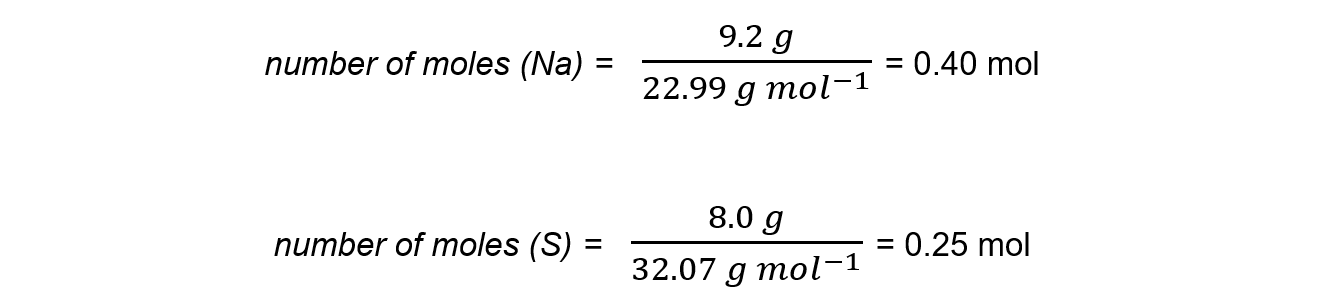
Step 2: Write the balanced equation and determine the coefficients
2Na + S → Na2S
Step 3: Divide the moles by the coefficient and determine the limiting reagent
-
- divide 0.40 moles of Na by 2, giving 0.20- lowest
- divide 0.25 moles of S by 1, giving 0.25
Therefore, sodium is limiting and sulfur is in excess
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









