- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: SL复习笔记6.6.4 Reproduction: Sex Determination in Males
SRY Gene
- In sexual reproduction in humans, a sperm from a male fuses with, or fertilises, an egg from a female to form a zygote, which then develops into an embryo
- To begin with the embryo develops in the same way regardless of its sex, and embryonic gonads develop that will either become ovaries in females or testes in males
- The factor that determines whether the embryonic gonads will develop into ovaries or testes is the presence or absence of a single gene known as the SRY gene
- The SRY gene is located on the Y chromosome, meaning that is only present in roughly 50% of embryos
- The SRY gene codes for a DNA-binding protein known as TDF, or testis determining factor, which stimulates the expression of further genes responsible for the development of testes
- If the SRY gene is present in the embryo's DNA, the embryonic gonads will develop into testes
- If the embryo has two X chromosomes, and therefore the SRY gene is not present in its DNA, the embryonic gonads will develop into ovaries
Testosterone
- During embryonic development, at the time when the embryo is developing into a foetus, the testes develop testosterone-secreting cells which produce and secrete testosterone
- This testosterone causes pre-natal development of male genitalia
- This testosterone secretion declines in the latter stages of pregnancy so that, at birth, the testes are inactive
- During puberty in males, testosterone secretions increase once again
- This leads to:
- The stimulation of sperm production in the testes; a primary sexual characteristic of males
- The development of male secondary sexual characteristics e.g.
- The penis gets larger
- Growth of facial hair
- Deepening of the voice
Secondary sexual characteristics
- Primary sexual characteristics are the features of reproductive organs that differ between males and females
- They are present during development in the uterus
- Secondary sexual characteristics are the changes that occur during puberty as children grow into adults
- They are controlled by the release of hormones
- Oestrogen and progesterone in females
- Testosterone in males
- Some changes occur in both males and females, including:
- The further development of sexual organs
- The growth of body hair
- Emotional changes also occur at this time due to the increased levels of hormones in the body
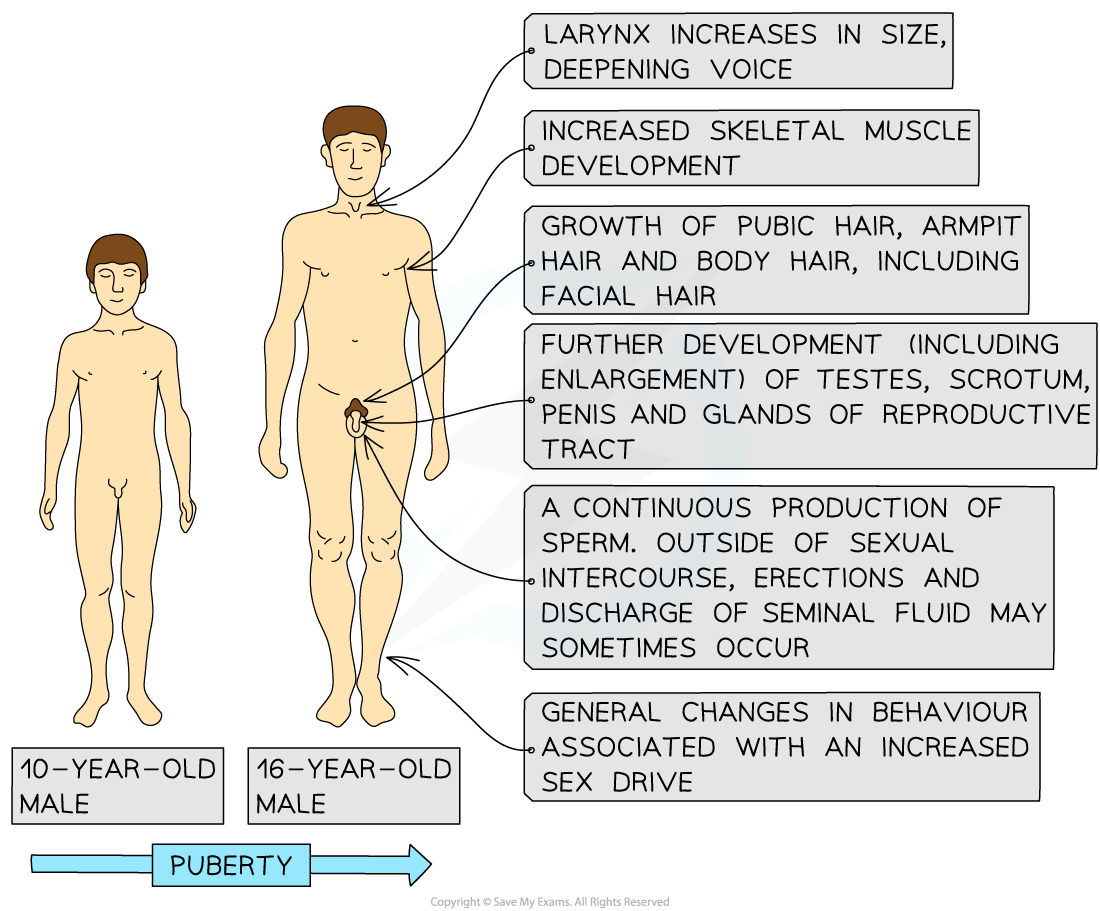
Secondary sexual characteristics of a human male
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









