- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: SL复习笔记6.5.2 Nerve Impulses
Resting Potential
- Neurones transmit information in the form of impulses, which travel extremely quickly along the neurone from one end to the other
- Note that an impulse is not an electrical current that flows along neurones as if they were wires
- Instead, an impulse is a momentary reversal in the electrical potential difference across the neurone cell surface membrane
- The electrical potential difference across a membrane can also be described as the voltage across a membrane, the difference in charge across a membrane, or the membrane potential
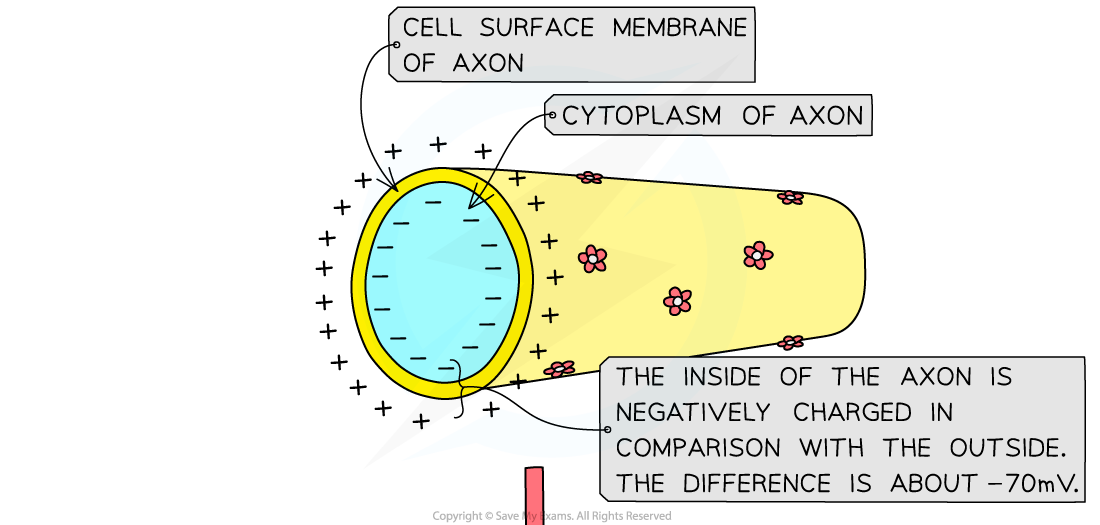
- In an axon that is not transmitting an impulse the inside of the axon always has a negative electrical potential, or charge, compared to outside the axon, which has a positive electrical potential
- This membrane potential in a resting neurone is known as resting potential
- The resting potential is usually about -70 millivolts (mV)
- This means that the inside of the resting axon has a more negative electrical charge than the outside by about 70 mV
- Two main processes contribute to establishing and maintaining resting potential:
- The active transport of sodium ions and potassium ions
- A difference in rates of diffusion of sodium ions and potassium ions
- In addition to these two main processes, negatively charged proteins inside the axon also contribute to the negative resting potential
The active transport of sodium ions and potassium ions
- Carrier proteins called sodium-potassium pumps are present in the cell surface membranes of neurones
- These pumps use ATP to actively transport sodium ions (Na⁺) out of the axon and potassium ions (K⁺) into the axon
- The two types of ion are pumped at an unequal rate; for every 3 sodium ions that are pumped out of the axon, only 2 potassium ions are pumped in
- This creates a concentration gradient across the membrane for both sodium ions and potassium ions
Difference in rates of diffusion of sodium ions and potassium ions
- Because of the concentration gradient generated by the sodium-potassium pumps, both sodium and potassium ions will diffuse back across the membrane
- The neurone cell surface membrane has sodium ion channels and potassium ion channels that allow sodium and potassium ions to move across the membrane by facilitated diffusion
- The neurone membrane is much less permeable to sodium ions than potassium ions, so potassium ions inside the neurone can diffuse out at a faster rate than sodium ions can diffuse back in
- This results in far more positive ions on the outside of the neurone than on the inside, generating a negative charge inside the neurone in relation to the outside
- The result of this is that the neurone has a resting membrane potential of around -70 millivolts (mV)
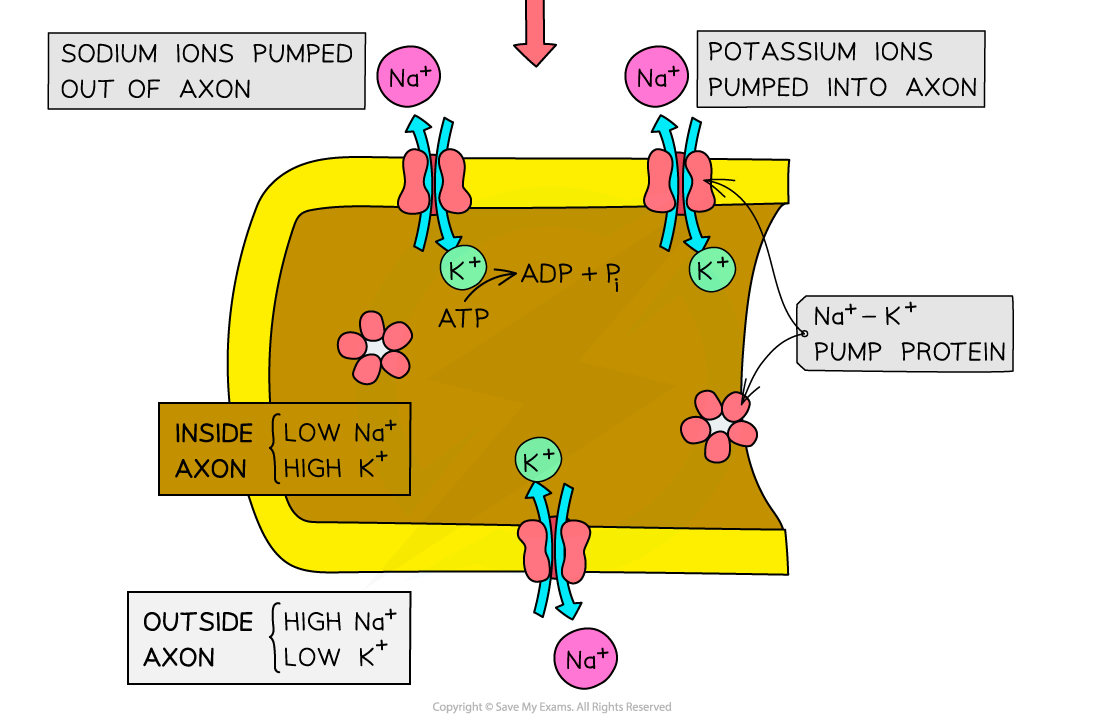
Sodium-potassium pumps in the membrane of a resting neurone generate a concentration gradient for both sodium ions and potassium ions. This process, together with the facilitated diffusion of potassium ions back out of the cell at a faster rate than sodium ions diffuse back into the cell, generates a negative resting potential across the membrane.
Action Potential
- Once resting potential is reached, the neurone membrane is said to be polarised
- To initiate a nerve impulse in a neurone, the neurone membrane needs to be depolarised
- Depolarisation is the reversal of the electrical potential difference across the membrane
- The depolarisation of the membrane occurs when an action potential is generated
- Action potentials lead to the reversal of resting potential from around -70 mV to around +40 mV
- Action potentials involve the rapid movement of sodium ions and potassium ions across the membrane of the axon
- An action potential is the potential electrical difference produced across the axon membrane when a neurone is stimulated e.g. when an environmental stimulus is detected by a receptor cell
How an action potential is produced
- Some of the ion channels in the membrane of a neurone are voltage gated, meaning that they open and close in response to changes in the electrical potential across the membrane
- Voltage gated ion channels are closed when the membrane is at rest, but they are involved in the generation and transmission of action potentials
- Note that not all of the channels in a neurone membrane are voltage gated e.g. some types of potassium ion channel are open when a neurone is at rest to enable potassium ions to diffuse out of the axon and generate resting potential
- When a neurone is stimulated, the following steps occur:
- A small number of sodium ion channels in the axon membrane open
- Sodium ions begin to move into the axon down their concentration gradient
- There is a greater concentration of sodium ions outside the axon than inside due to the action of sodium-potassium pumps
- This reduces the potential difference across the axon membrane as the inside of the axon becomes less negative
- If enough sodium ions enter the axon and the potential difference is reduced enough, voltage gated sodium ion channels open, leading to a further, large influx of sodium ions
- Once the charge has been reversed from -70 mV to around +40 mV, an action potential is said to have been generated
How an action potential is propagated
- Once an action potential has been generated, it can be propagated, or transmitted, along the length of the axon
- The depolarisation of the membrane at the site of the first action potential causes sodium ions to diffuse along the cytoplasm into the next section of the axon, depolarising the membrane in this new section, and causing voltage gated sodium channels to open
- This triggers another action potential in this section of the axon membrane
- This process then repeats along the length of the axon
- In the body, this allows action potentials to begin at one end of an axon and then pass along the entire length of the axon membrane
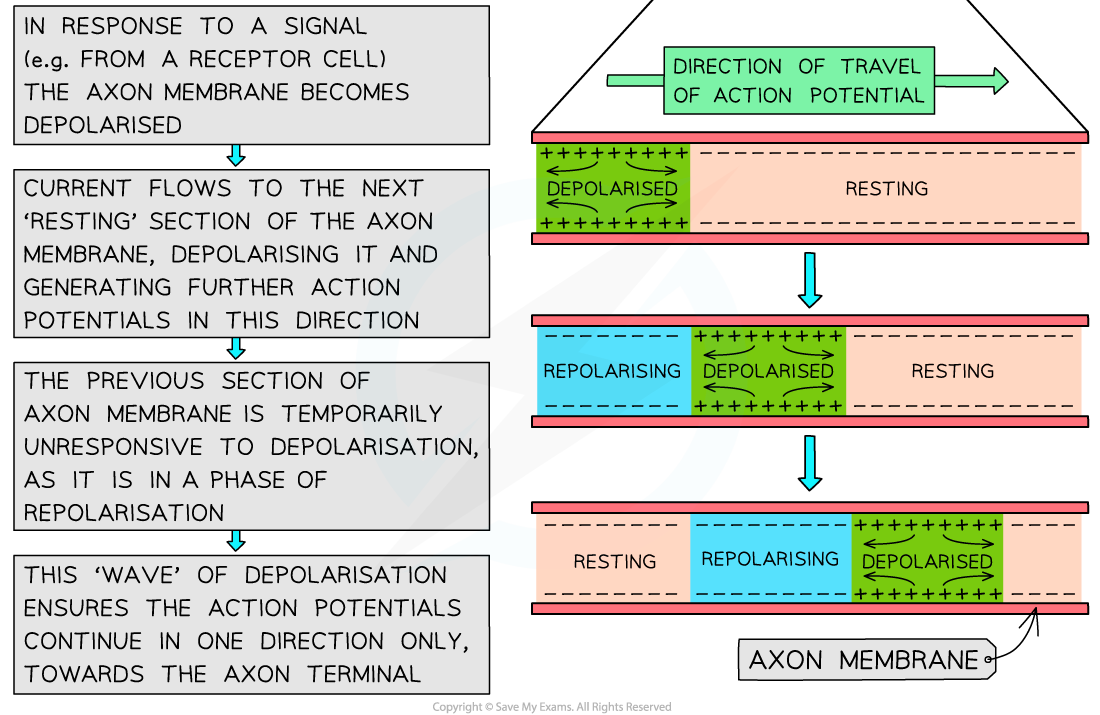
How an impulse is propagated in one direction along the axon of a neurone
Repolarisation
- About 1 ms after an action potential is generated, all the voltage gated sodium channels in this section of membrane close
- Voltage gated potassium channels in this section of axon membrane now open, allowing the diffusion of potassium ions out of the axon, down their concentration gradient
- Remember that the sodium-potassium pumps have not stopped working during the action potential; hence the potassium ion gradient is still present
- This movement of potassium ions causes the inside of the axon to become negatively charged again, a process known as repolarisation
- There is a short period during which the membrane potential is more negative than resting potential; this is known as hyperpolarisation
- The period during which the membrane is hyperpolarised is known as the refractory period
- The membrane is unresponsive to stimulation during the refractory period, so a new action potential cannot be generated at this time
- This makes the action potentials discrete events and means the impulse can only travel in one direction
- This is essential for the successful and efficient transmission of nerve impulses along neurones
- The voltage gated potassium channels then close, and the sodium-potassium pumps work to restore resting potential
- Only once resting potential is restored can the membrane be stimulated again
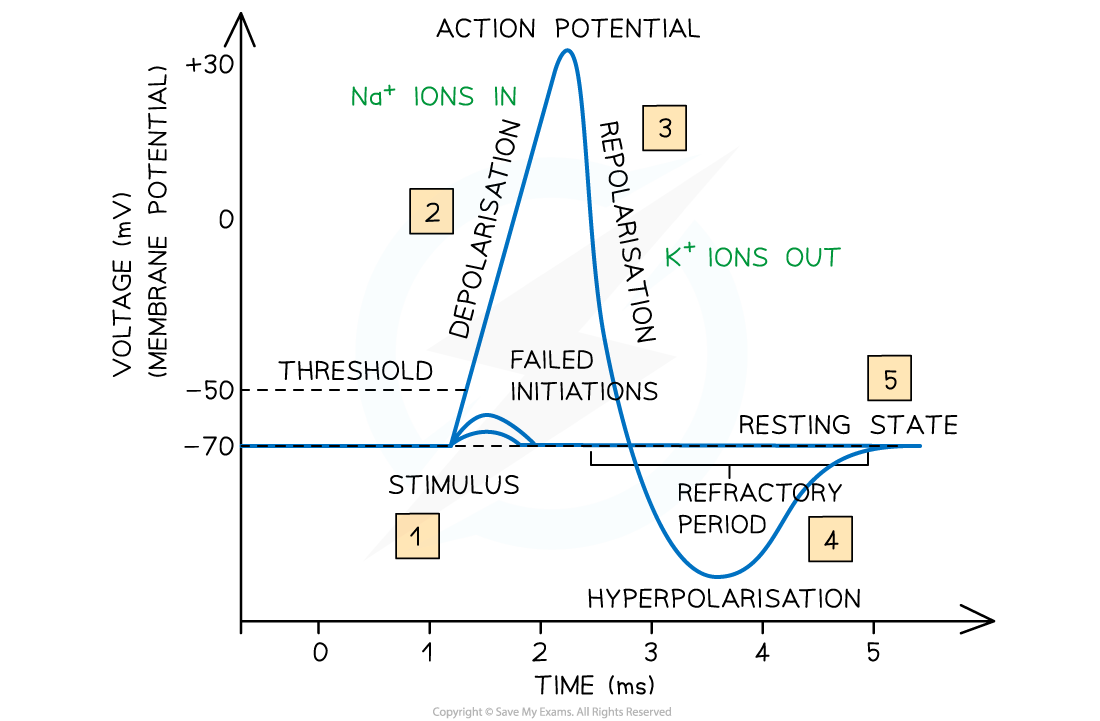
The depolarisation and repolarisation of an action potential can be clearly seen in a graph of membrane potential against time
Threshold Potential
- An action potential is only initiated if the threshold potential is reached
- When a neurone is stimulated, sodium ion channels in the axon membrane open and sodium ions pass into the axon down their concentration gradient
- This causes the inside of the axon to become less negative, but exactly how much less negative it becomes is dependent on the number of sodium ion channels that open
- A large stimulus will cause more channels to open than a small stimulus
- If more channels open, then more sodium ions will enter the axon, causing it to become less negative
- If the potential difference reaches around -50 mV, known as the threshold potential, voltage gated sodium ion channels open and many more sodium ions enter the axon
- This causes the membrane potential to reach around +40 mV
- Once the charge has been reversed from -70 mV to +40 mV, an action potential is generated
The all-or-nothing principle
- Action potentials are either generated or not generated depending on whether the threshold potential is reached; there is no such thing as a small or large action potential
- If a stimulus is weak, only a few sodium ion channels will open and the membrane won’t be sufficiently depolarised to reach the threshold potential; an action potential will not be generated
- If a stimulus is strong enough to raise the membrane potential above the threshold potential then an action potential will be generated
- This is the all-or-nothing principle
- An impulse is only transmitted if the initial stimulus is sufficient to increase the membrane potential above a threshold potential
- Stimulus size can be detected by the brain because as the intensity of a stimulus increases, the frequency of action potentials transmitted along the neurone increases
- This means that a small stimulus may only lead to one action potential, while a large stimulus may lead to several action potentials in a row
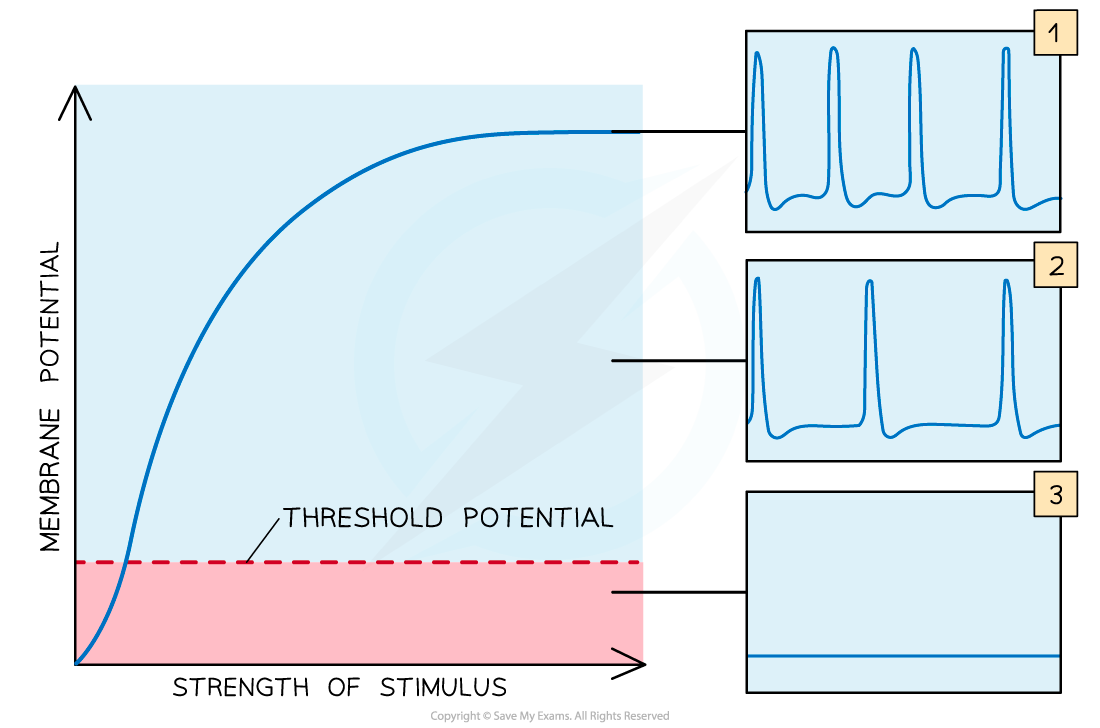
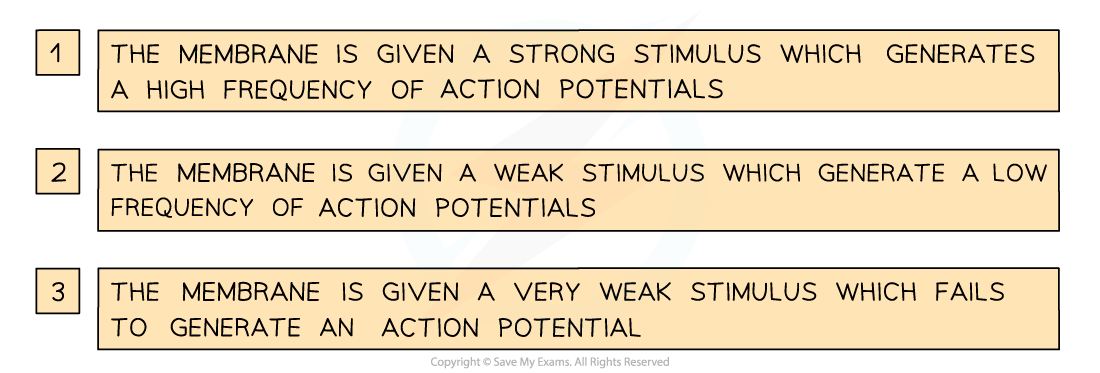
As the strength of a stimulus increases beyond the threshold potential, the frequency of action potentials increases
Local Currents
- The propagation of nerve impulses along axons occurs due to local currents that cause each successive section of the axon to reach the threshold potential
- Inside the depolarised section of the axon
- There is a high concentration of sodium ions due to their recent influx
- This creates a concentration gradient between the section of the axon that has depolarised and the section next to it
- Sodium ions diffuse along inside the axon to the neighbouring section of axon that has not yet become depolarised
- This reduces the negative membrane potential in the new section of axon and, if a threshold is reached, begins the initiation of an action potential
- This enables the original action potential to be propagated
- On the outside of the axon
- There is a higher concentration of sodium ions outside the section of axon that has not yet become depolarised due to the diffusion of sodium ions into the depolarised section
- Sodium ions diffuse from here along the outside of the axon to the section of axon that has just become depolarised
- These movements of sodium ions are known as local currents
- These local currents cause a wave of depolarisation and repolarisation to travel along the axon, resulting in the propagation of a nerve impulse
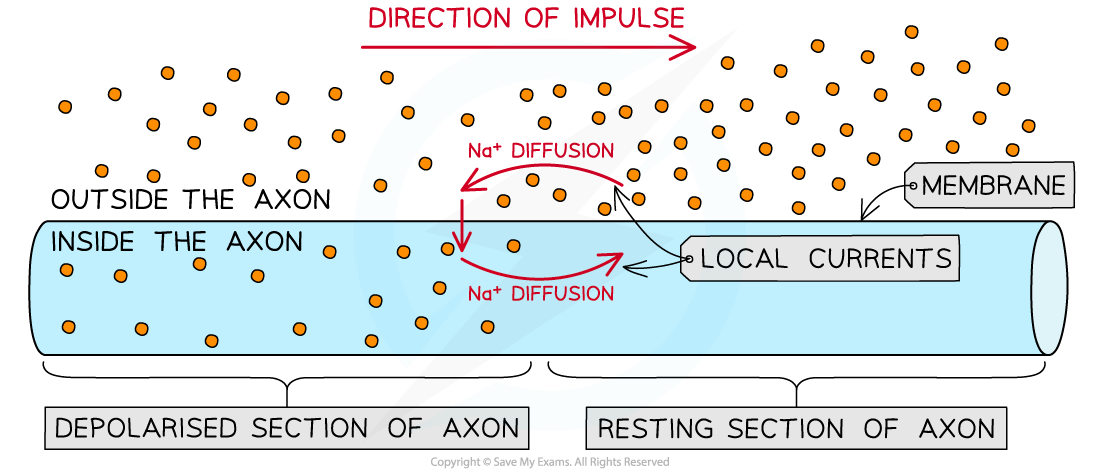
The propagation of nerve impulses along axons occurs due to local currents created by the diffusion of sodium ions
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








