- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: SL复习笔记5.2.6 Reclassification
Cladistics & Reclassification
- The development of DNA sequencing technology means that classification can now be carried out on the basis of evolutionary relationship
- Organisms classified in this way are grouped into clades
- Historically, organisms would have been classified on the basis of observed traits, which often led to organisms being classified into groups that were not true clades
- This resulted from analogous characteristics being incorrectly thought to be homologous
- The use of DNA sequencing to classify organisms has led to discoveries of classification errors and the need to reclassify organisms
- Some species have been reclassified into different groups of organisms
- Some groups of organisms have been split
- Some groups have been merged
- Classifying organisms correctly according to their clade is important to ensure that groups of organisms are close evolutionary relatives
- This means that the characteristics of one group member can be predicted on the basis of the characteristics of another
Example of Reclassification
Reclassification of the figwort family
- The figwort (pronounced 'figwurt') family, also known as the Scrophulariaceae, was at one point the 8th largest family in the angiosperm phylum
- When the group was originally classified in the late 1700s it contained 16 genera, which later expanded to 275 genera
- The classification of the figworts was based on observable traits such as a tube-shaped flower structure
- Examples of members of the original figwort family include foxgloves and yellow rattle
- When DNA sequence analysis began, plant scientists discovered that the shared features of the figwort family were in fact analogous and not evidence of shared ancestry
- Three chloroplast genes were analysed
- It was discovered that the original figwort family was not a true clade
- The figworts were found to contain several separate plant families
- New families were created
- Several genera were moved into other existing families
- The remaining genera were grouped together with two previously missed genera to form the new figwort family, still known as the Scrophulariaceae
- The new figwort family is less than half its original size and is only the 36th largest in the angiosperms, where it had previously been 8th
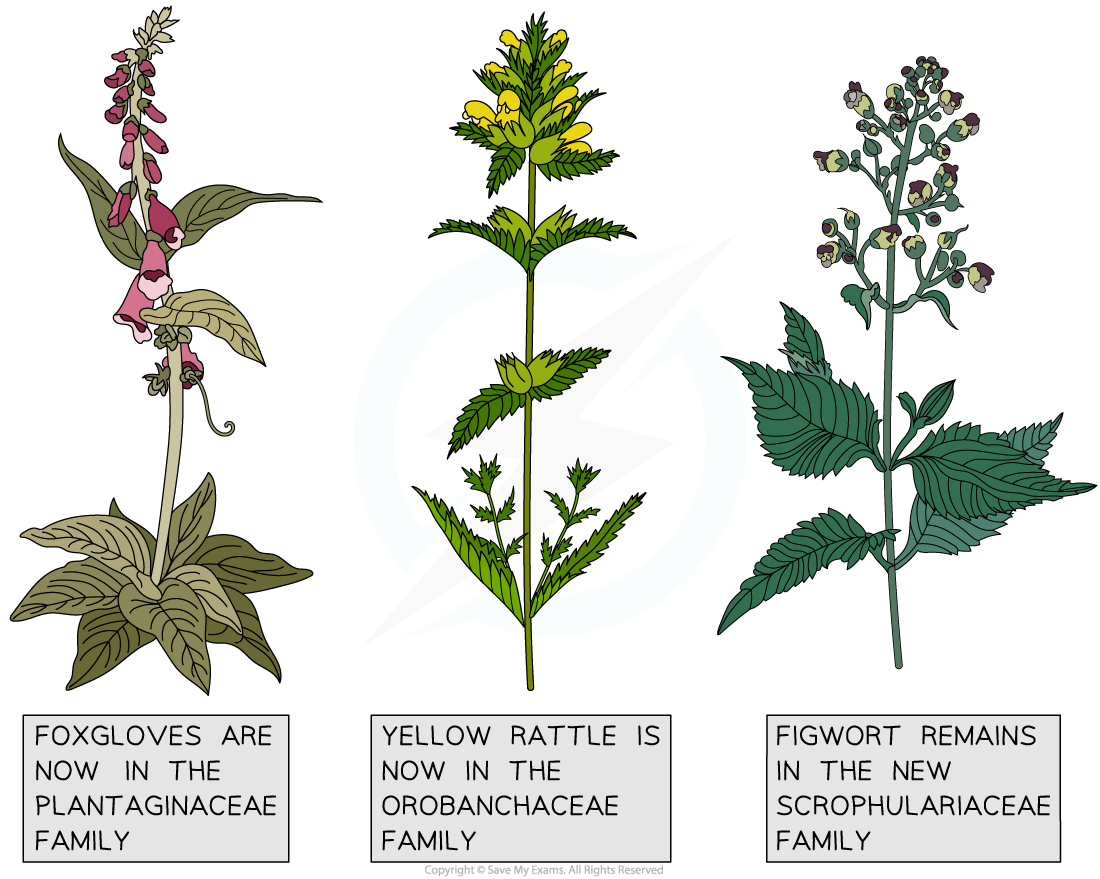
DNA sequencing data led to the reclassification of many species within the original figwort family
NOS: Falsification of theories with one theory being superseded by another; plant families have been reclassified as a result of evidence from cladistics
- A theory is an explanation of observed phenomena that is supported by evidence
- This means that when new evidence is found that no longer supports the theory, it needs to be changed to take the new evidence into account
- Reclassification of organisms on the basis of DNA sequencing data is a good example of this
- Scientists theorise that a group of plants should be classified together on the basis of existing evidence; historically this would have been the evidence of observable traits such as flower shape
- New evidence from DNA sequence analysis shows that existing plant groups are not true clades, and so are not descendants of a common ancestor
- The historical classification theory has therefore been falsified and needs to be changed to take the new evidence into account
- New evidence from DNA and computer analysis is used to calculate the most likely plant evolutionary relationships, and this evidence is used to form a new theory regarding the classification of plants
- Analysis of new DNA data continues all the time, and if evidence is found that doesn't fit with current classification theories then more falsification and reclassification will take place
转载自savemyexams
在线登记
最新发布
翰林课程体验,退费流程快速投诉邮箱: yuxi@linstitute.net 沪ICP备2023009024号-1