Change in price will cause the quantity supplied to drop to zero.改变价格的话供应数量将会变成0。
2∞>PES>1, Relative Elastic
之前已经给大家讲解完了PED, XED和YED,接下来就来讲解一下剩下的一个Price Elasticity of supply。PES的内容和PED大同小异,也是需要对定义,基本内容还有不同数值以及图像做到理解并且熟练记忆,虽然在考试中它的戏份不如PED那么多,但因为比较相似,所以学习起来还是相对简单的。
PES的定义
PES measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied when there is a change in the price.计算公式为:
% of change in quantity supplied / % of change in the price。这里也重新提一下Law of supply:
When price increases,
quantity supplied increases too;
When price decreases,
quantity supplied decreases too.
因为价格变化和供应数量变化是同向的,
所以除了0,其他PES数值一定会是正数。
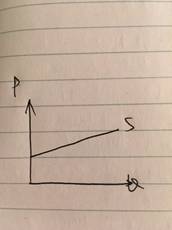
以下开始分类讨论各个PES value。Change in price leads to more than proportionate change in quantity supplied1PES=∞, Perfectly Elastic
Change in price will cause the quantity supplied to drop to zero.改变价格的话供应数量将会变成0。
2∞>PES>1, Relative Elastic

Increase in price will result in more than proportionate decrease in quantity supplied.Decrease in price will result in more than proportionate increase in quantity supplied.
价格上涨将会导致更大幅度的供应数量下跌,
价格下跌将会导致更大幅度的供应数量上涨。
Change in price leads to same percentage change in quantity supplied.1PES=1, Unitary Elastic
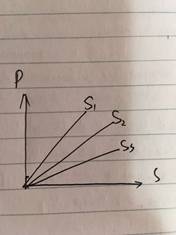 Increase in price will result in the same percentage decrease in quantity supplied.
Increase in price will result in the same percentage decrease in quantity supplied.
注意,PED中的unitary elastic实际是-1,因为数值都为负数所以省略了负号,PES的unitary elastic是+1,
它可以是任何一条通过P-S图像原点的一次函数。
Change in price leads to less than proportionate change in quantity supplied.11>PES>0, Relatively Inelastic
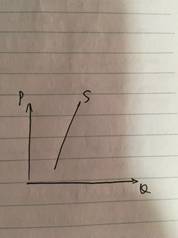
Increase in price will result in less than proportionate decrease in quantity supplied.Decrease in price will result in less than proportionate increase in quantity supplied.
价格上涨将会导致更小幅度的供应数量下跌,
价格下跌将会导致更小幅度的供应数量上涨。
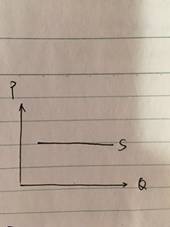
2PES=0, Perfectly Inelastic
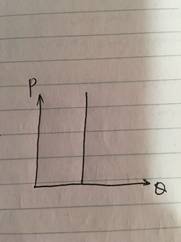
Increase in price results in no change in quantity supplied.不管怎么改变价格,供应数量始终不变。
跟PED一样,PES的图像也是分为五个,对应不同特殊数值或者范围,可以分类进行记忆,但要注意当PED=1和PES=1时的区别


© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1