- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: SL复习笔记3.4.4 Cloning
Cloning
- Clones are groups of genetically identical organisms, derived from a single original parent cell
- A cloned cell is a cell that is genetically identical to the cell that it originated from
- Sexual reproduction produces a zygote when gametes fuse
- In a single birth, this zygote is not cloned and will itself reproduce sexually as an adult
- Identical twins are clones of each other as they are formed from one zygote splitting into two parts, which each develops into an embryo
- Clones form naturally and artificially
- The simple gardening technique of taking plant cuttings relies on cloning
- Other organisms are manipulated to form multiple clones when grown commercially eg. large-scale growth of crop plants, to ensure a uniform crop and good crop yields
- This ensures that desirable characteristics appear in the phenotypes of every organism
Cloning: Natural Methods
- Many plant species and some animal species have natural methods of cloning
- Asexual reproduction is much less common in animals than in plants
- Some small animals reproduce asexually by parthenogenesis eg. aphids
- The other naturally occurring incidence of cloning in animals is identical twins
Natural cloning in plants
- Many methods of cloning do not require seeds as it is not sexual reproduction that is occurring, it is asexual reproduction
- A well as runners, plants can propagate asexually using tubers, rhizomes, bulbs, suckers, and offsets
- All modes of natural plant cloning contain modified stems that can generate meristem tissue
- Potato tubers are swollen modified roots that form eyes on their surface
- Eyes can sprout new growth (called 'chitting')
- The starch stored in the tuber fuels the early growth of the new plant
- Ginger forms rhizomes, a modified stem that grows horizontally underground
- New growth stems from nodes in the rhizome, forming new stems and adventitious roots
- The section used in cookery is the rhizome
- Onions and garlic form bulbs that can grow adventitious roots underground and leafy shoots above ground
- Suckers are growths that appear from the root systems of many trees and shrubs, which can provide meristematic tissue for vegetative propagation
- Examples are poplars, cherries and plums
- Offsets are small, virtually complete daughter plants that have been asexually produced on the mother plant
- Examples are tulips and lilies
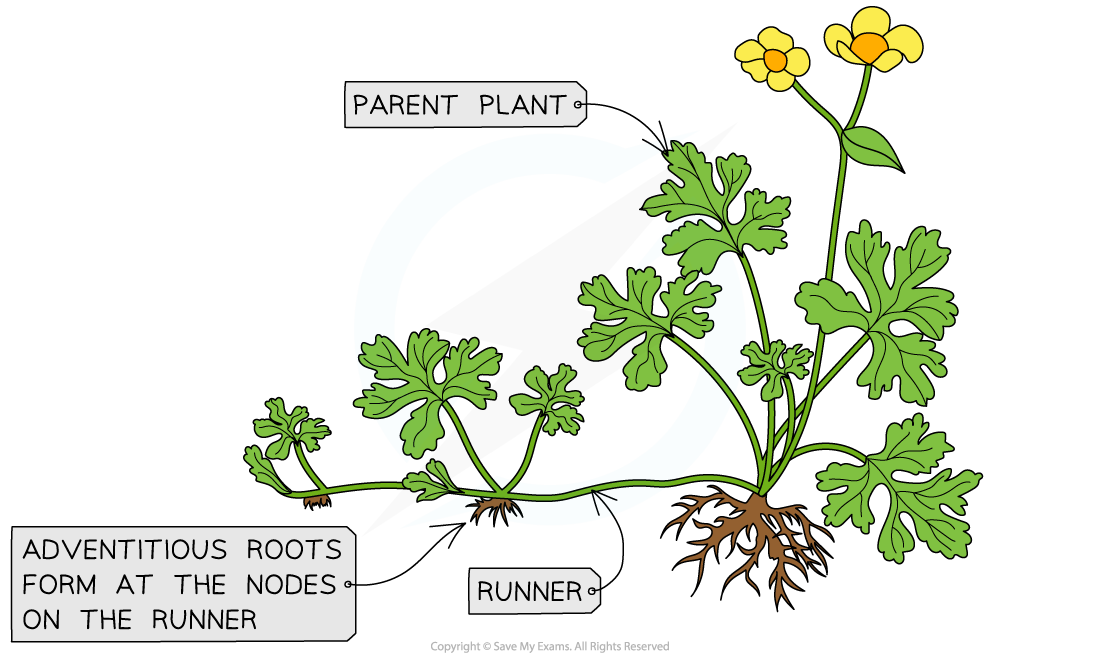
An example of natural cloning in plants with runners that form adventitious roots
Identical twins
- An egg is fertilised by a sperm as in a singleton birth
- This forms a zygote
- The single zygote undergoes a few cell cycles (mitotic divisions) to become an embryo
- This is why identical twins are referred to as monozygotic
- At the embryo stage, the embryo splits in two; the exact causes of this kind of split are not well understood
- The two embryos that form are identical (have exactly the same genotype) and develop in utero (i.e. in the uterus) together
- The result is the birth of identical offspring, always of the same gender, with identical phenotypes
- Because non-identical twins are formed from separate eggs and sperm, they are not clones
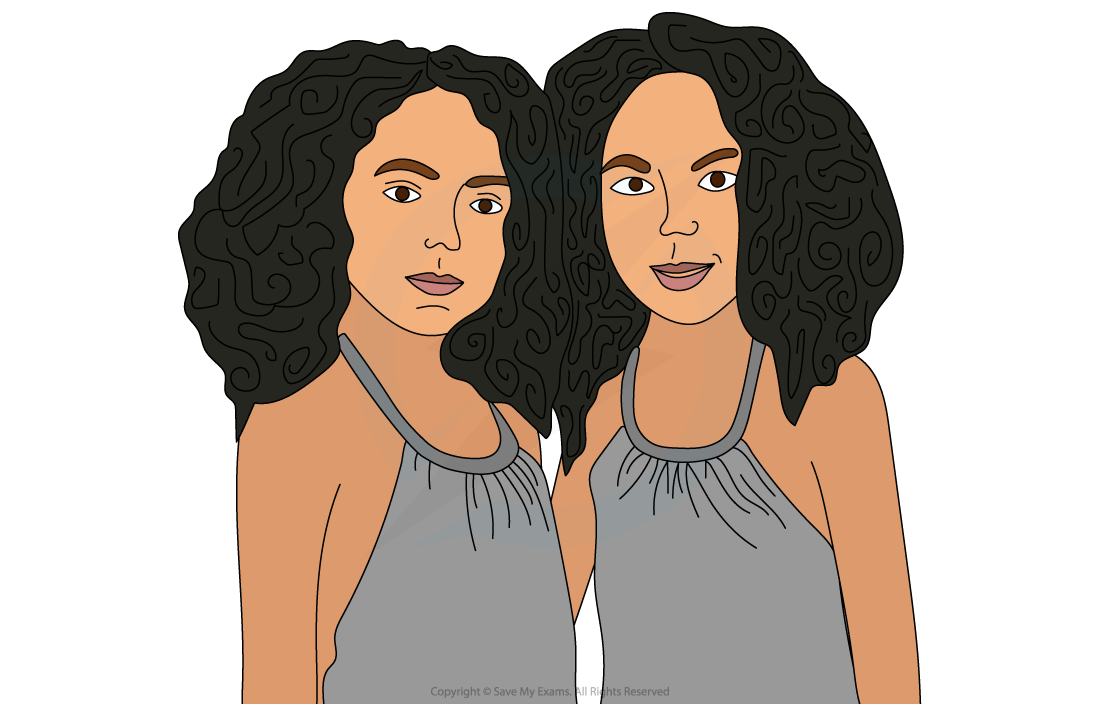

Identical twins are natural clones when a zygote splits into two parts and each part develops into a separate embryo
Exam Tip
Although identical (monozygotic) twins share the same genome at the moment when the embryo splits, identical twins are not clones in the true sense of the word. Because mutations occur with every cell cycle, Twin A will possess slightly different DNA base sequences to Twin B at the time of birth. The older the twins get, the more their genomes become dissimilar as mutations accumulate. They will still look very alike throughout their lives unless there are large differences in their environments as they grow up.
Cloning: Animals
- The process of embryo twinning (sometimes called splitting or fragmentation) produces offspring that are clones of each other but not of their parents
- It has been a routine procedure carried out to boost yields of livestock and promote desirable characteristics since the 1980s
- The key step is the deliberate division of the embryo into two half embryos
- Both halves contain cells that are pluripotent
- The embryo is split at around the eight-cell stage
- These are then inserted into a surrogate mother for gestation and birth
- The surrogate gives birth to identical twins
- In some cases, embryos are split into single identical cells, each of which can be implanted into a separate surrogate mother animal
- Although embryo twinning guarantees desirable characteristics in the offspring, it is not possible to predict how many offspring will be produced within a herd of livestock, something of vital importance to a farmer
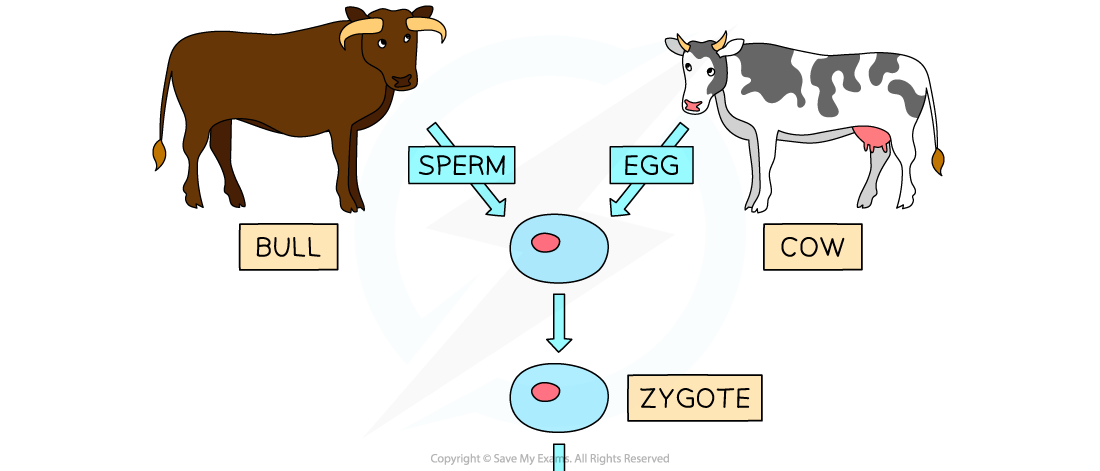
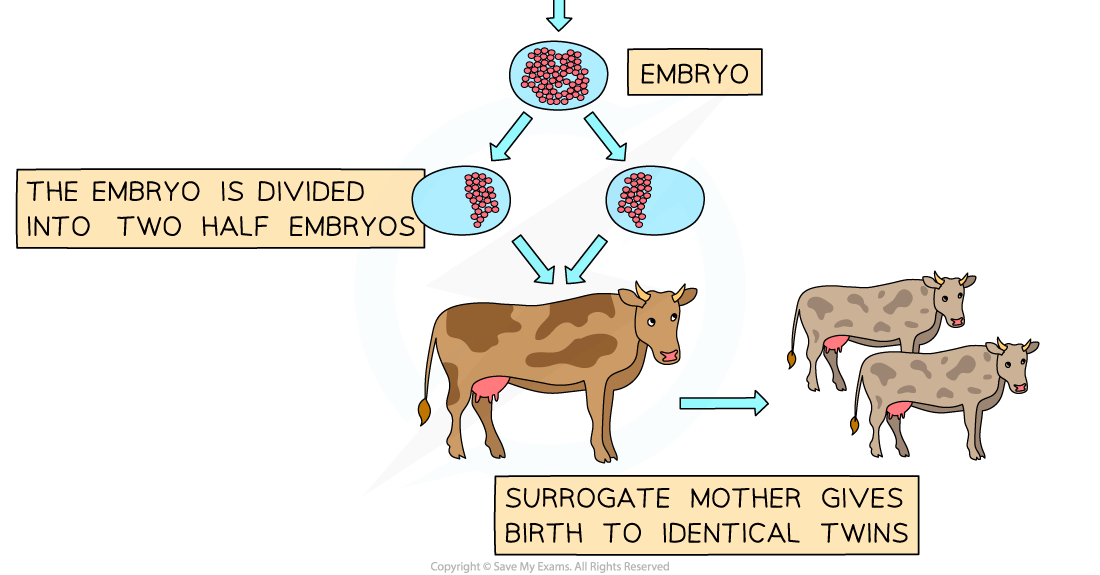
Embryo twinning of cattle by splitting the embryo
Therapeutic cloning
- This is a technique designed to use cloned cells to replace dead or damaged cells that cause a loss of function in an individual
- Embryos are cloned as in reproductive cloning, but the embryos are removed and subdivided
- Each individual embryo cell is pluripotent and can be cultured and artificially differentiated into any type of specialised cell
- In theory, any specialised cell can be derived by this method
- Crucially, specialised cells with the same genome as the sufferer can be cloned and replaced
- An example is replacing specialised brain tissue in sufferers of Parkinson's Disease
- At present, there is a lot of potential for therapeutic cloning but little clinical progress has been made
Cloning: Using Differentiated Cells
- Methods have been developed for cloning adult animals using differentiated cells
- It would be desirable to clone a differentiated cell because by then it would be easy to assess the organism's characteristics and whether any of its traits were desirable enough to clone
- Pluripotent cells can develop into any specialised cell, but it is difficult to predict whether, once differentiated, they will display desirable characteristics
- Differentiated cells are more difficult to clone because certain genes have been permanently switched off (those genes will never be transcribed again) as the cell has developed its specialised role
- However, pioneering work on Xenopus (the African clawed frog) in the 1950s involved:
- Removal of nuclei from Xenopus tadpoles' somatic cells
- It was significant that the somatic cell was already fully differentiated eg. a skin cell
- Insertion of these nuclei into enucleated Xenopus egg cells (eggs whose own nuclei had been destroyed by UV radiation treatment)
- This resulted in embryos that grew, divided and differentiated into fully-functioning live tadpoles, and ultimately, adult Xenopus frogs
- Whilst this work was successful, cloning mammals from differentiated cells proved much more difficult
- The work on Xenopus frogs laid the platform for the first mammal cloned by nuclear extraction
- It wasn't until the 1990s that the first large mammal, Dolly the sheep, was cloned successfully
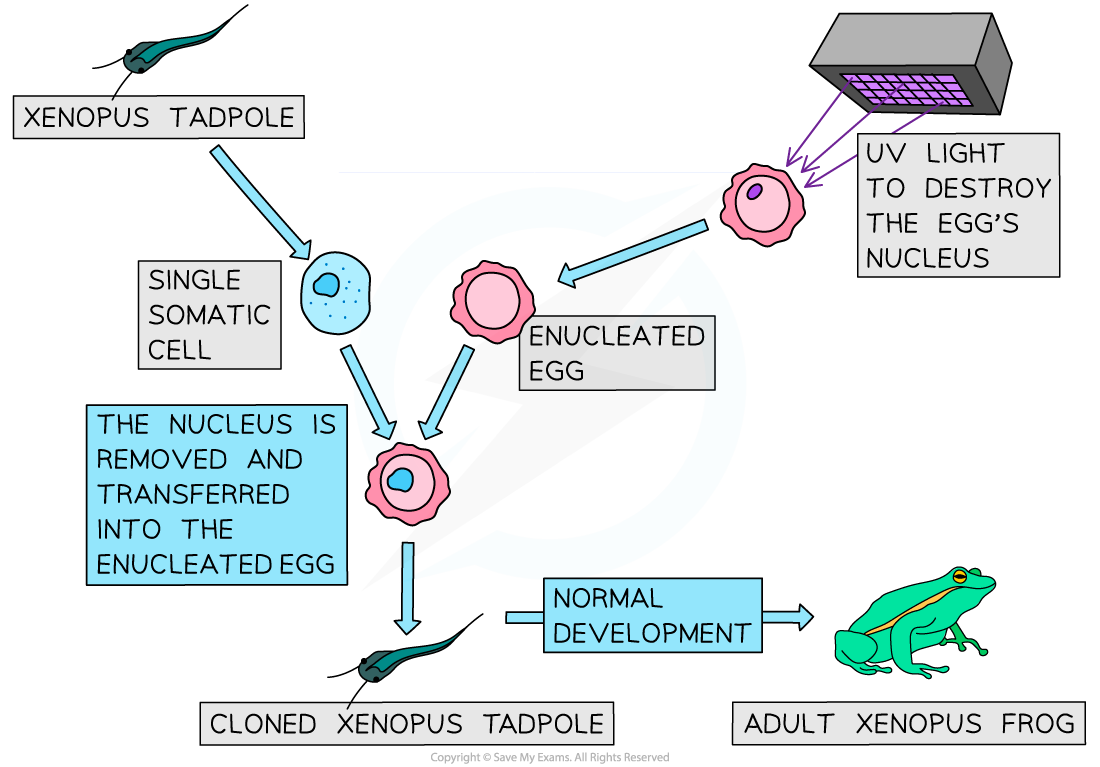
Cloning of Xenopus frogs by nuclear transfer from a differentiated cell
Somatic Cell Transfer
Production of cloned embryos produced by somatic cell nuclear transfer
- This is the method made famous by Dolly the sheep, cloned in Edinburgh, UK in 1996
- Its full name is Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT)
- Dolly made headlines as being the first livestock animal to be created from a clone
- Three separate animals are required:
- The animal being cloned (by donating a cell)
- The female to donate an egg cell
- The surrogate mother
- How the procedure is carried out:
- The animal to be cloned donates a somatic (body) cell
- In Dolly's case, this was an udder cell
- The egg cell is extracted from the egg donor and enucleated (its nucleus is removed by suction and discarded)
- The nucleus from the udder cell is injected into the enucleated egg cell
- The hybrid zygote cell is now treated to encourage it to divide by mitosis
- The embryo is implanted into the surrogate mother for gestation and birth
- The animal to be cloned donates a somatic (body) cell
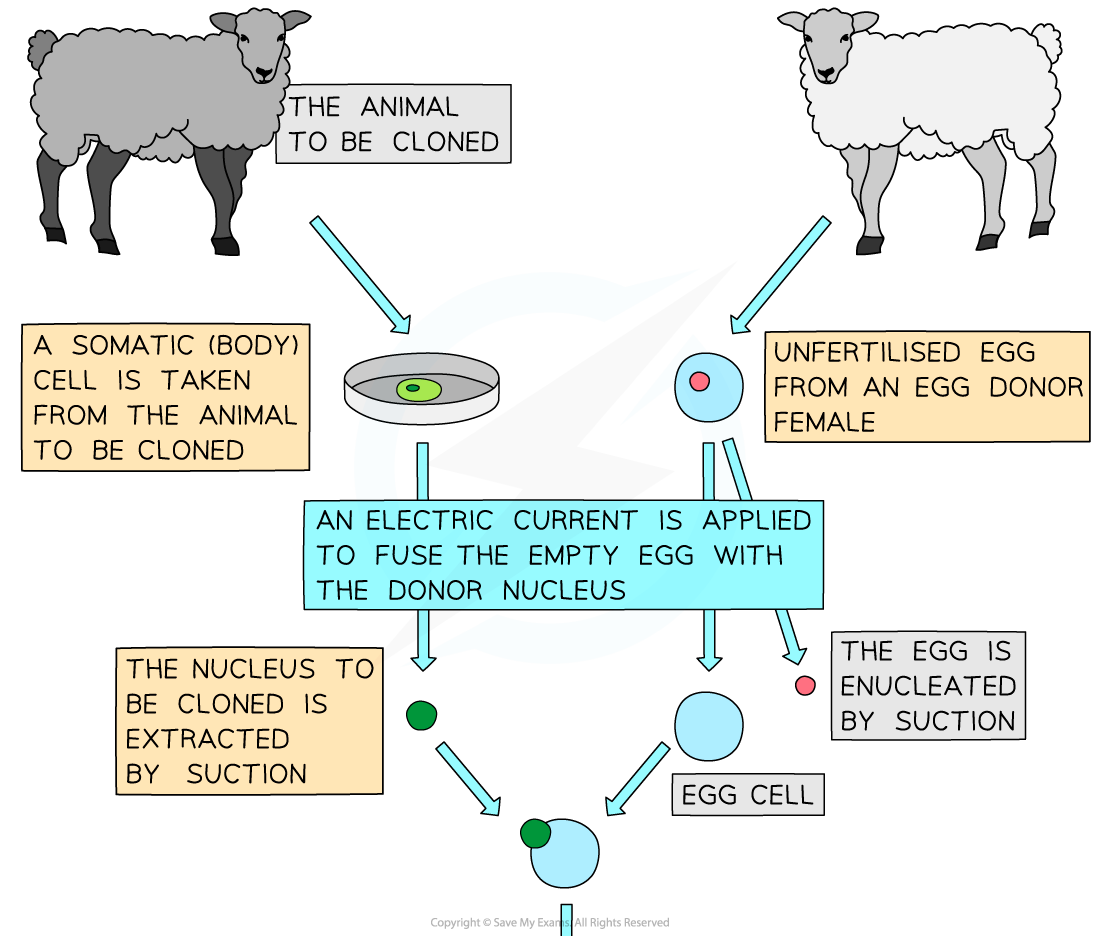
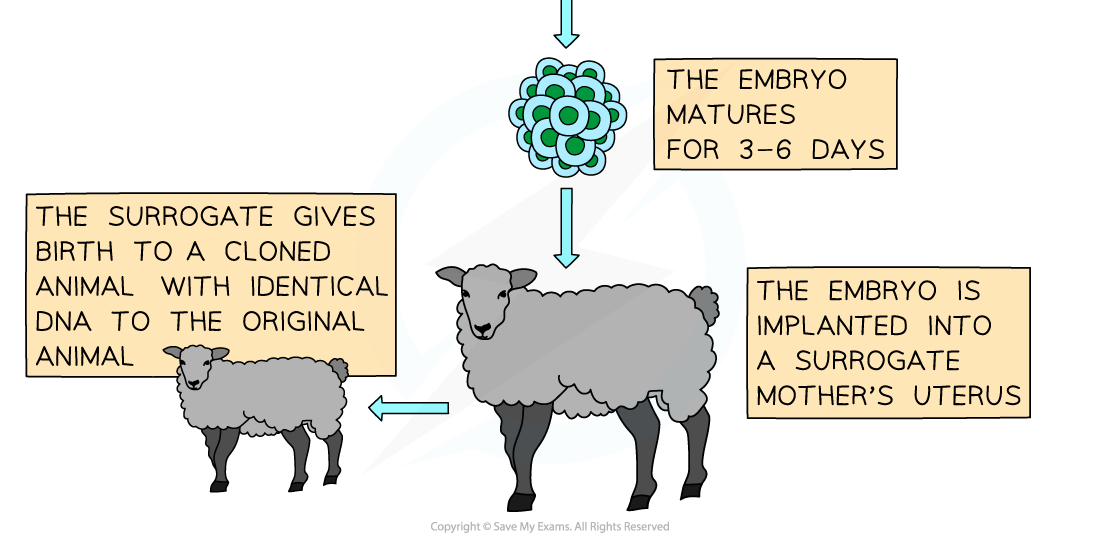
Reproductive cloning of animals by somatic cell nuclear transfer
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









