- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: SL复习笔记3.1.2 Alleles
Alleles
- A gene codes for a specific polypeptide that can affect a specific trait or characteristic in an organism
- Eg. blood type
- Alternative forms of a gene can exist, these various specific forms are called alleles
- Note that although alleles are different forms of the same gene, they all still occupy the same locus on the chromosome
- New alleles occur through mutations
- Multiple alleles can exist for a gene that determines a specific trait
- Each allele results in a different variation of that trait
- Eg. blood types A, B, AB and O
- Each allele results in a different variation of that trait
- The chromosomes of eukaryotic cells occur in homologous pairs (there are two copies of each chromosome, one copy inherited from each parent) which means that cells have two copies of every gene
- As a result, a cell possesses two alleles of every gene within its nucleus
- When the two alleles at a locus are the same/identical they are described as homozygous
- When the two alleles at a locus are different they are described as heterozygous
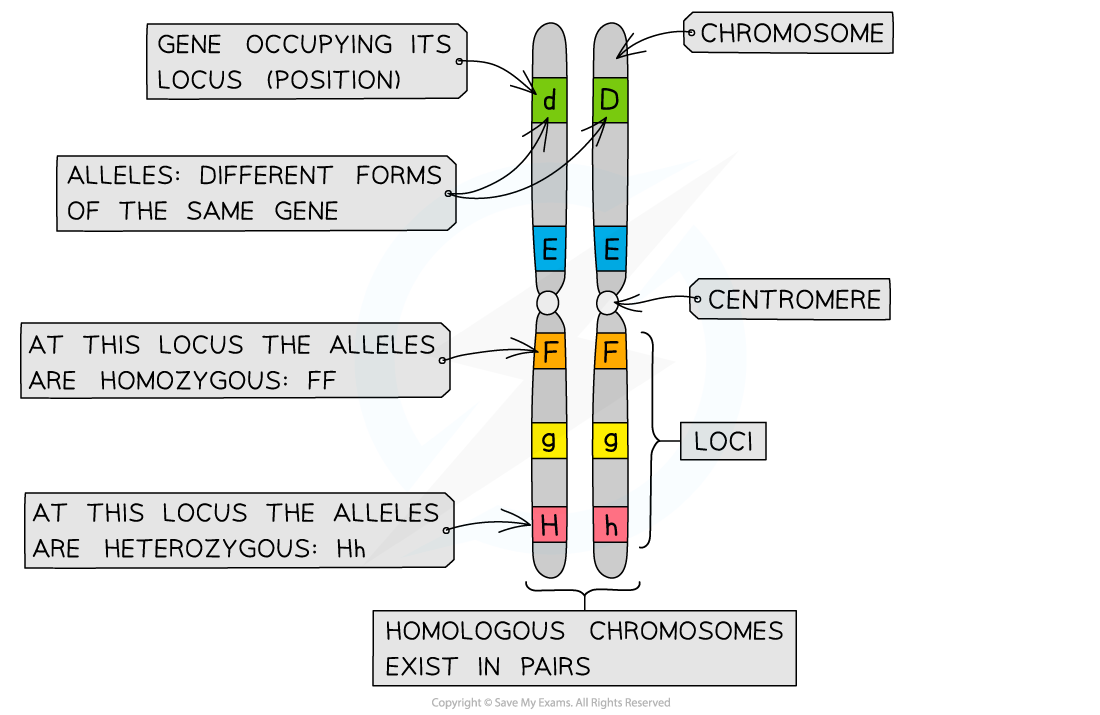
Chromosomes showing genes, loci and alleles
Differences between Alleles
- Alleles differ from each other by one or only a few bases
- Even a very small change in base sequence can bring about a large effect in gene function, with a large knock-on effect on the phenotype
- Even though different alleles of a gene have slightly different base sequences, they still occupy the same locus on the chromosome
- Since the Human Genome Project, sophisticated techniques can analyse different alleles
- These techniques are becoming faster, more accurate and more accessible to individuals
- Comparable sequences can be analysed down to individual bases to determine evolutionary relationships
- The more differences in base sequence, the further apart two species are in evolutionary terms
- The exact positions where bases differ between alleles are called SNPs or snips (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms)
- An allele can have several snips but still only differ by a few bases from its other allele
Exam Tip
Use the term allele wherever possible in written answers, as it's always a more precise term than gene.
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








