- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: SL复习笔记2.5.3 Skills: DNA Replication
Meselson & Stahl's Experiments
Analysis of Meselson and Stahl’s results to obtain support for the theory of semi-conservative replication of DNA
- Crick and Watson, as they defined the shape of DNA, suggested a credible explanation of how the DNA molecule replicates itself
- This was the theory of semi-conservative replication
- Like any scientific theory, this explanation required evidence to back up the claims
- Five years after their discovery, two other scientists, Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl, provided data to prove Crick and Watsons' theory
Meselson and Stahls' Experiment
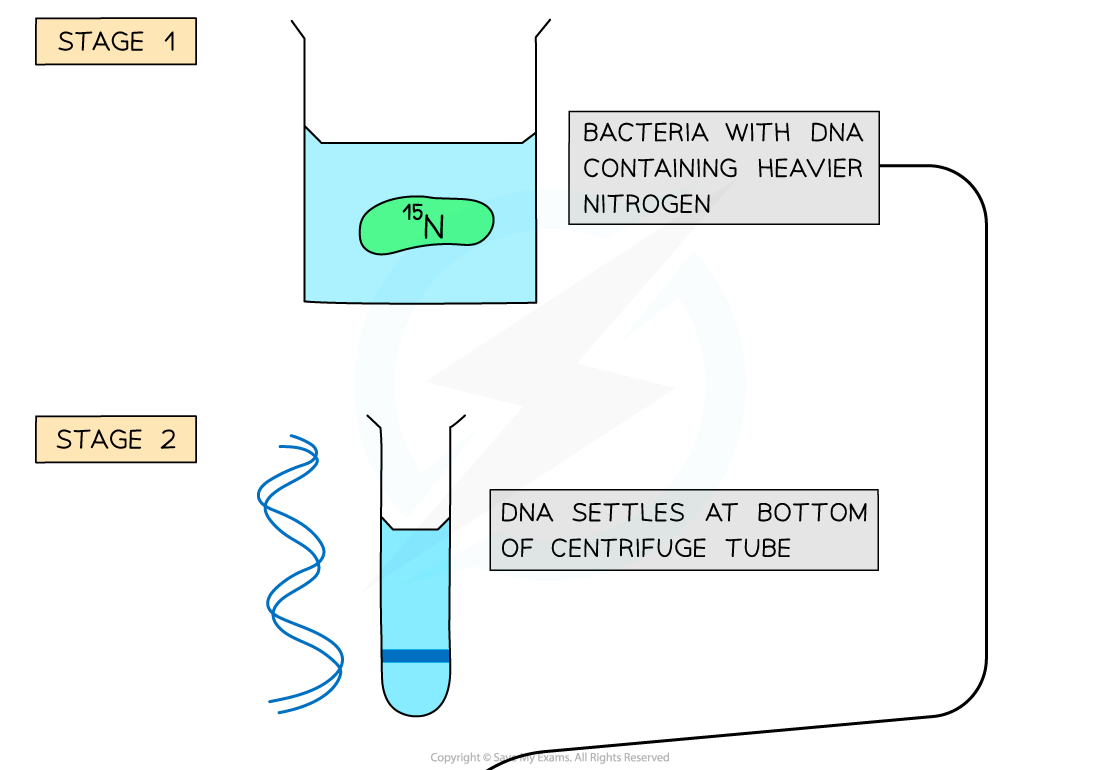
- Bacteria were grown in a broth containing the heavy (15N) nitrogen isotope
- DNA contains nitrogen in its bases
- As the bacteria replicated, they used nitrogen from the broth to make new DNA nucleotides
- After some time, the culture of bacteria had DNA containing only heavy (15N) nitrogen
- A sample of DNA from the 15N culture of bacteria was extracted and spun in a centrifuge
- This showed that the DNA containing the heavy nitrogen settled near the bottom of the centrifuge tube
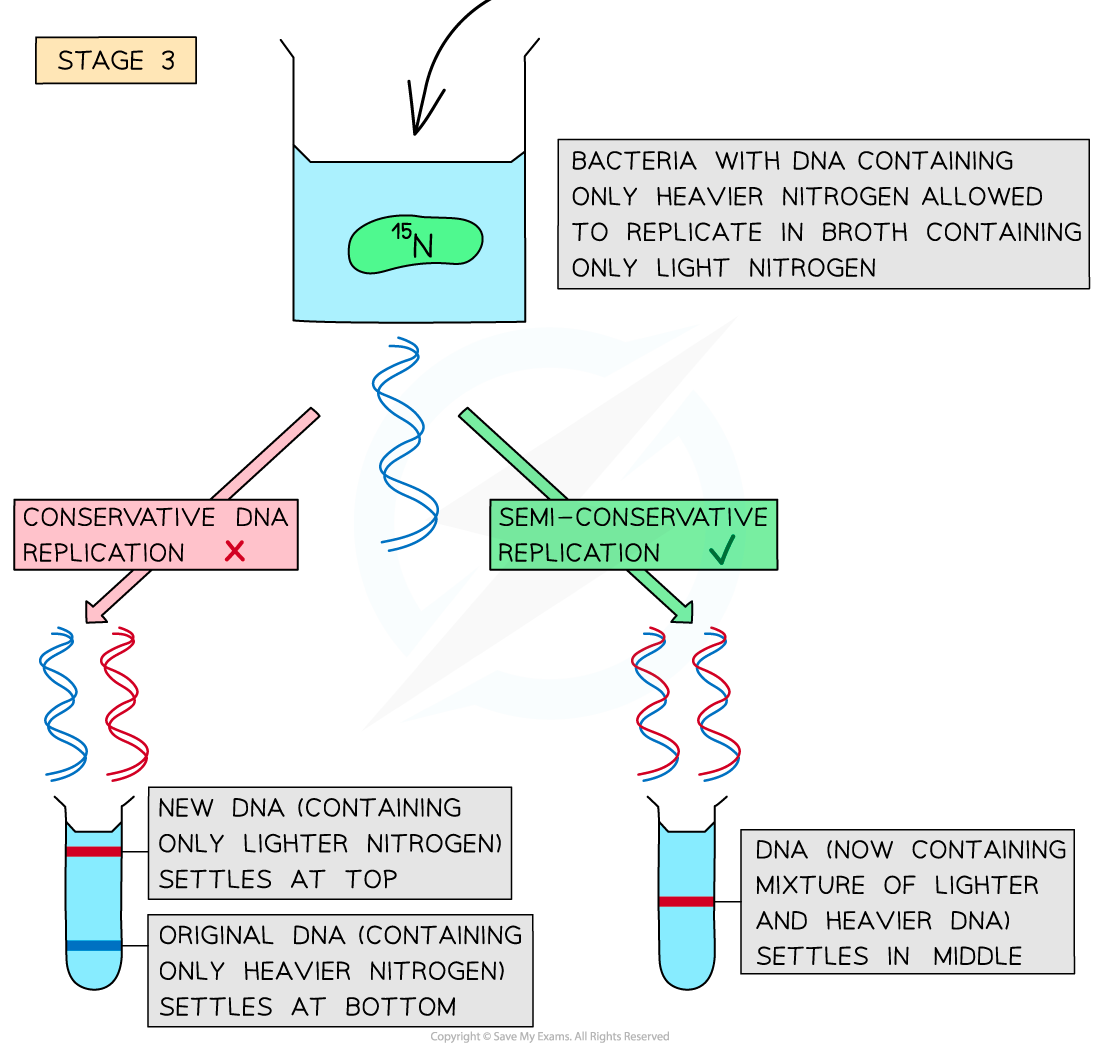
- The bacteria containing only 15N DNA were then taken out of the 15N broth and added to a broth containing only the lighter 14N nitrogen. The bacteria were left for enough time for one round of DNA replication to occur before their DNA was extracted and spun in a centrifuge
- If conservative DNA replication had occurred, the original template DNA molecules would only contain the heavier nitrogen and would settle at the bottom of the tube, whilst the new DNA molecules would only contain the lighter nitrogen and would settle at the top of the tube
- If semi-conservative replication had occurred, all the DNA molecules would now contain both the heavy 15N and light 14N nitrogen and would therefore settle in the middle of the tube (one strand of each DNA molecule would be from the original DNA containing the heavier nitrogen and the other (new) strand would be made using only the lighter nitrogen)
- Meselson and Stahl confirmed that the bacterial DNA had undergone semi-conservative replication.
- The DNA from this second round of centrifugation settled in the middle of the tube, showing that each DNA molecule contained a mixture of the heavier and lighter nitrogen isotopes
- If more rounds of replication were allowed to take place, the ratio of 15N:14N would go from 1:1 after the first round of replication, to 3:1 after the second and 7:1 after the third
- This experiment proved Crick and Watsons' theory correct
NOS: Obtaining evidence for scientific theories; Meselson and Stahl obtained evidence for the semi-conservative replication of DNA
- Meselson and Stahl's experiment is a great example of how scientists can obtain evidence to back up a theory about a biological process
Meselson and Stahls' experiment provided unequivocal proof that DNA replicates via semi-conservative DNA replication
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








