- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: SL复习笔记2.5.1 DNA & RNA Structure
Nucleic Acids: Structure
- The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides
- Both DNA and RNA are polymers that are made up of many repeating units called nucleotides
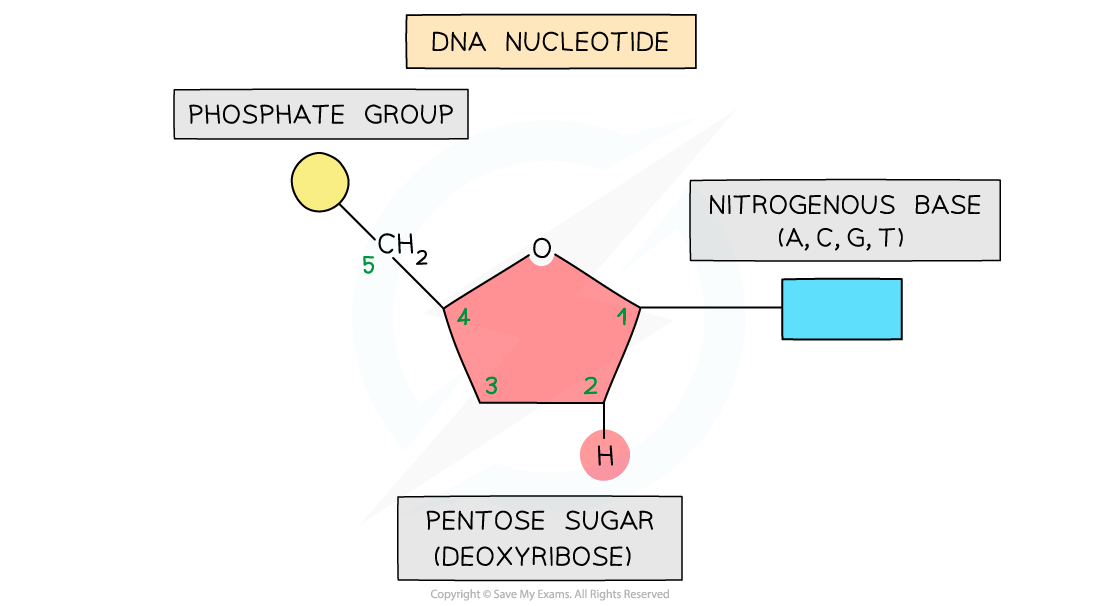
- Each nucleotide is formed from:
- A pentose sugar (a sugar with 5 carbon atoms)
- A nitrogen-containing organic base (with either 1 or 2 rings of atoms)
- A phosphate group (this is acidic and negatively charged)
- The base and phosphate group are both covalently bonded to the sugar
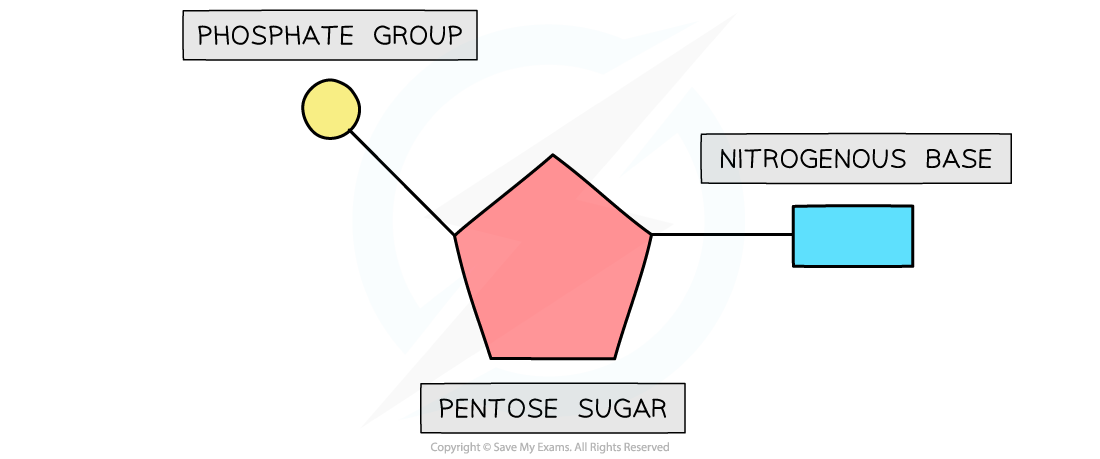
The basic structure of a nucleotide
- Nucleotides join together in chains to form DNA or RNA strands
- The phosphate group of one nucleotide forms a covalent bond to the pentose sugar of the next one
- This carries on to form a large polymer
- This forms a 'sugar-phosphate backbone' with a base linked to each sugar
- The polymer of nucleotides is known as a strand
- DNA is double-stranded, RNA is usually single-stranded
- There are just 4 separate bases that can be joined in any combination/sequence
- Because the sugar and phosphate are the same in every nucleotide
- This sequence is the basis of the genetic code as a store of genetic information
Exam Tip
A common error is to describe DNA or RNA as polymers of bases; more correctly, they are polymers of nucleotides
DNA & RNA: Comparison
- Like DNA, the nucleic acid RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a polynucleotide – it is made up of many nucleotides linked together in a chain
- Like DNA, RNA nucleotides contain the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G) and cytosine (C)
- Unlike DNA, RNA nucleotides never contain the nitrogenous base thymine (T) – in place of this they contain the nitrogenous base uracil (U)
- Unlike DNA, RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar ribose (instead of deoxyribose)
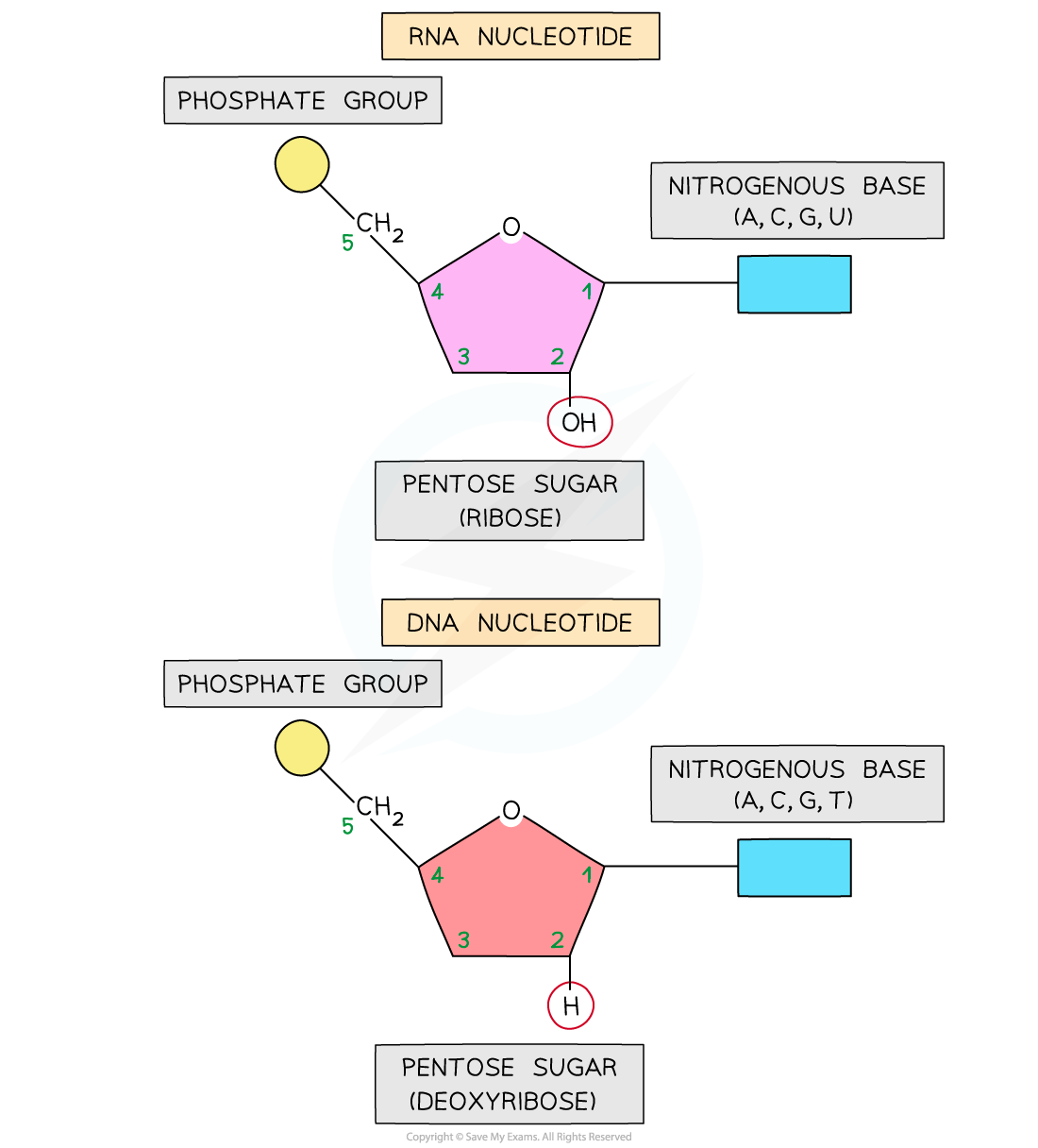
An RNA nucleotide compared with a DNA nucleotide
- Unlike DNA, RNA molecules are only made up of one polynucleotide strand (they are single-stranded)
- Unlike DNA, RNA polynucleotide chains are relatively short compared to DNA
- Like DNA, the sugar-phosphate bonds (between different nucleotides in the same strand) are strong covalent bonds
- Like DNA, the nitrogenous bases stick out sideways from the sugar-phosphate backbone
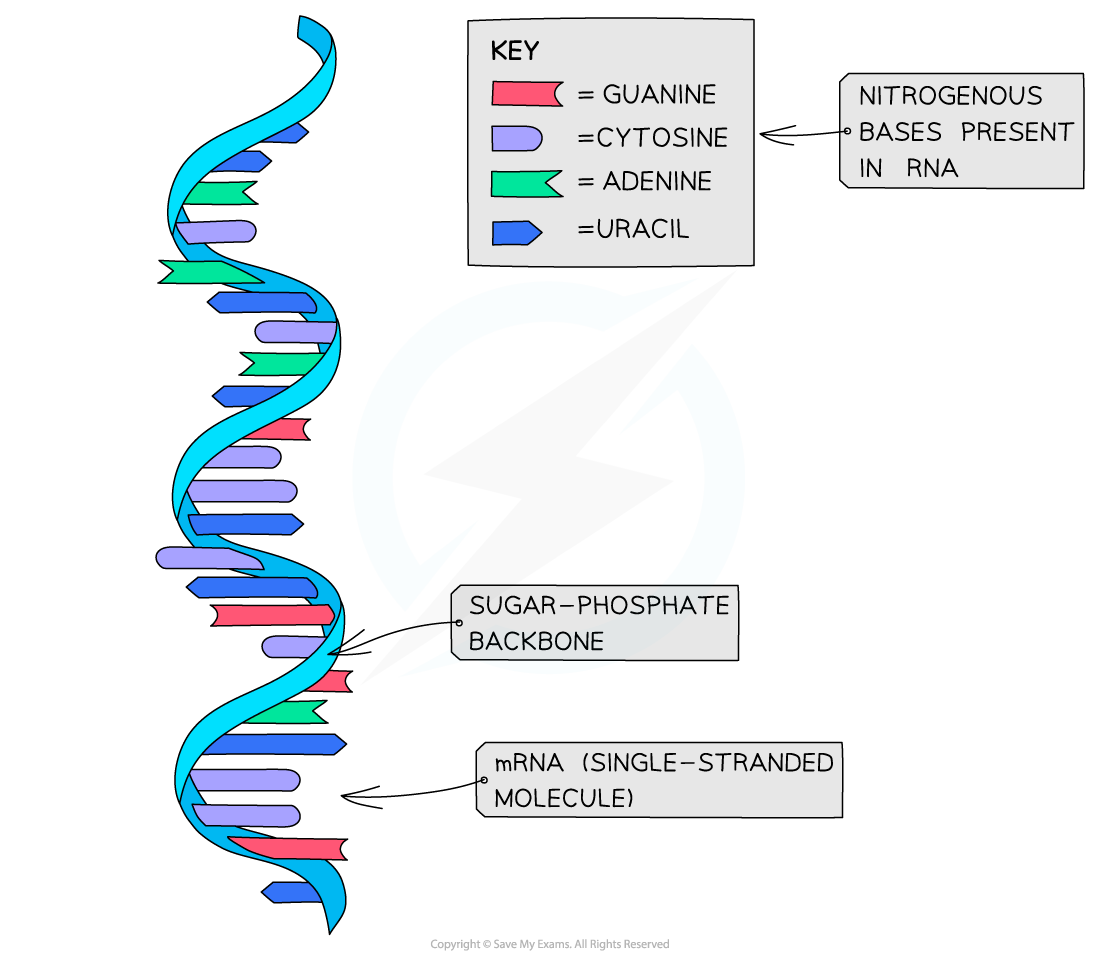
The structure of RNA
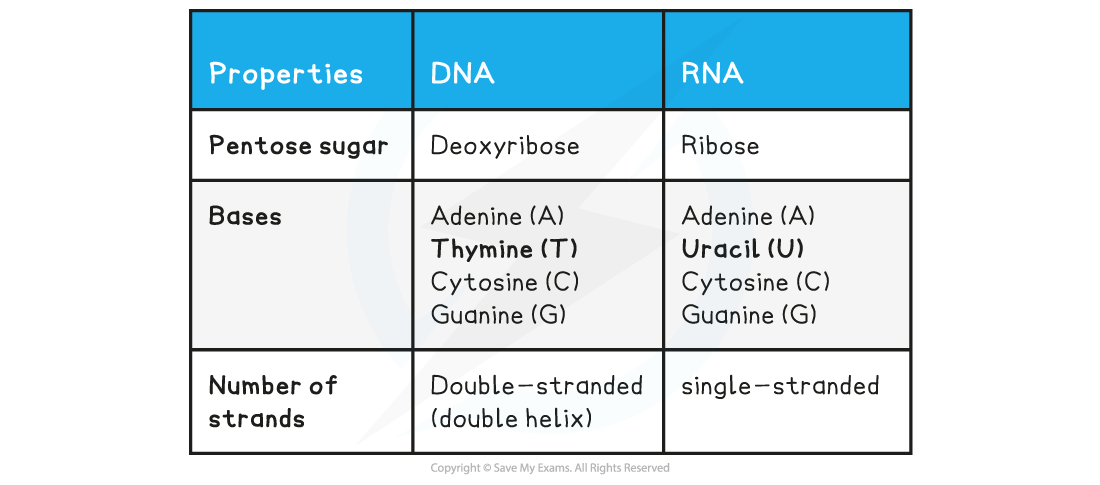
Nucleotide Structure Summary Table
Exam Tip
You need to know the difference between DNA and RNA molecules (base composition, number of strands, pentose sugar present).
Double Helix Structure
- DNA is a double helix made of two antiparallel strands of nucleotides linked by hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs
- The nucleic acid DNA is a polynucleotide – it is made up of many nucleotides bonded together in a long chain
A DNA nucleotide
- DNA molecules are made up of two polynucleotide strands lying side by side, running in opposite directions – the strands are said to be antiparallel
- Each DNA polynucleotide strand is made up of alternating deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups bonded together to form the sugar-phosphate backbone
- Each DNA polynucleotide strand is said to have a 3’ end and a 5’ end (these numbers relate to which carbon atom on the pentose sugar could be bonded with another nucleotide)
- Because the strands run in opposite directions (they are antiparallel), one is known as the 5’ to 3’ strand and the other is known as the 3’ to 5’ strand
- The nitrogenous bases of each nucleotide project out from the backbone towards the interior of the double-stranded DNA molecule
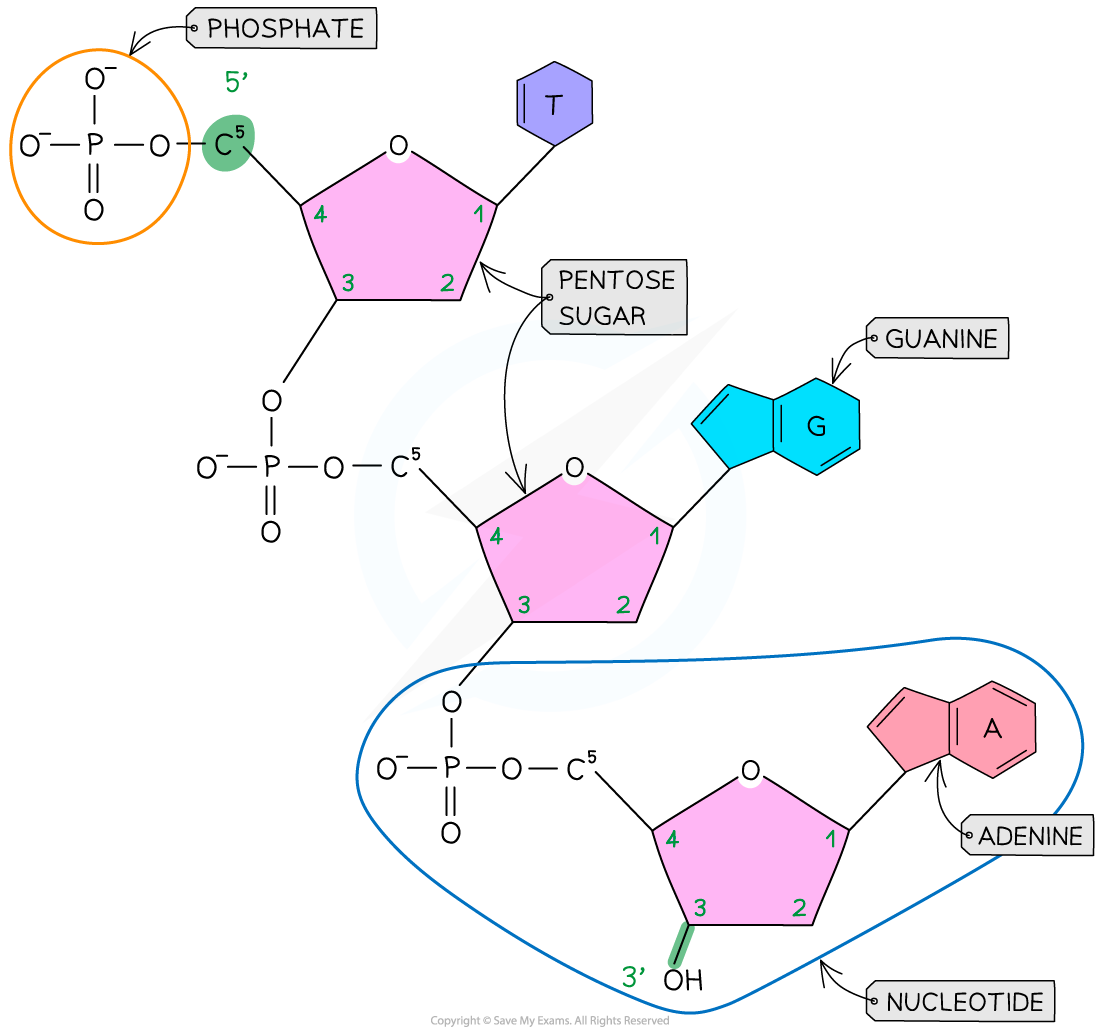
A single DNA polynucleotide strand showing 3 nucleotides in a sequence
Hydrogen bonding
- The two antiparallel DNA polynucleotide strands that make up the DNA molecule are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases
- These hydrogen bonds always occur between the same pairs of bases:
- The purine adenine (A) always pairs with the pyrimidine thymine (T) – two hydrogen bonds are formed between these bases
- The purine guanine (G) always pairs with the pyrimidine cytosine (C) – three hydrogen bonds are formed between these bases
- This is known as complementary base pairing
- These pairs are known as DNA base pairs
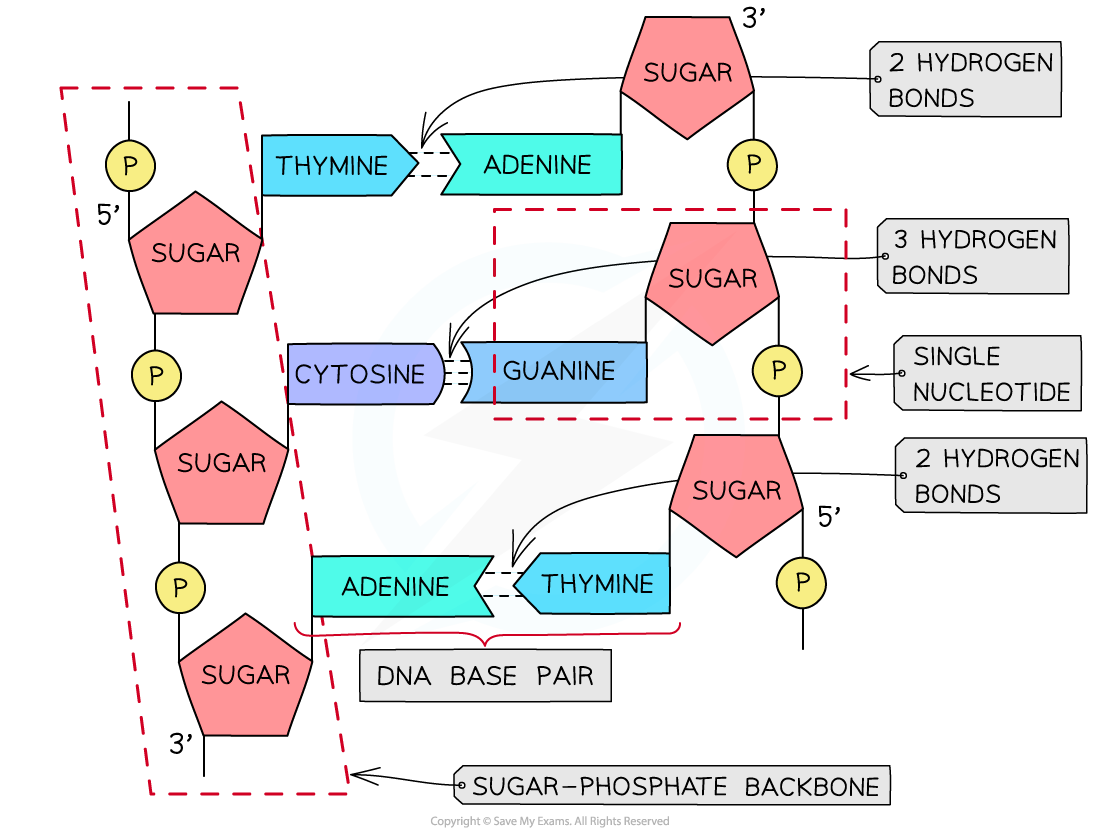
A section of DNA – two antiparallel DNA polynucleotide strands held together by hydrogen bonds
Double helix
- DNA is not two-dimensional as shown in the diagram above
- DNA is described as a double helix
- This refers to the three-dimensional shape that DNA molecules form
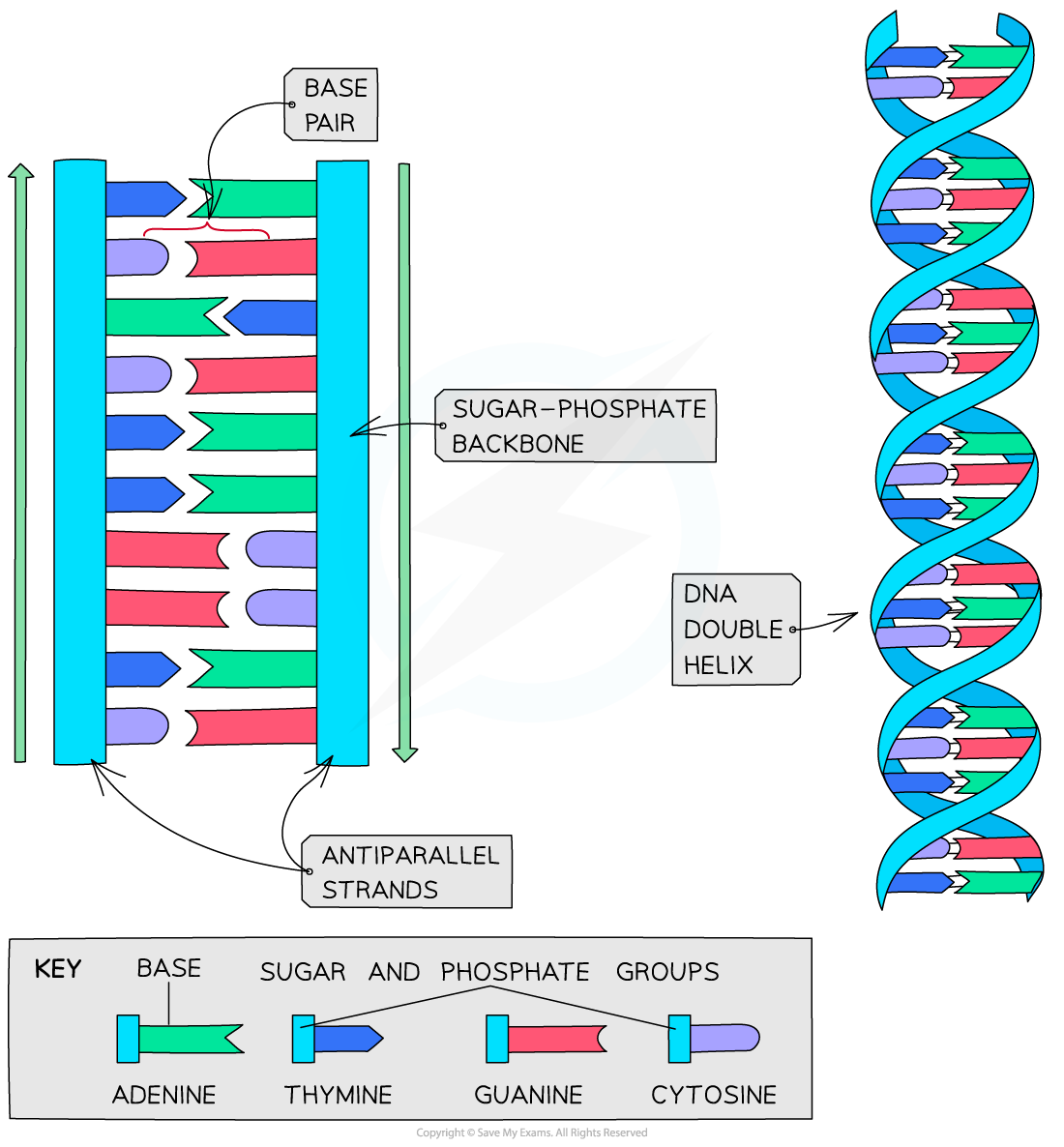
DNA molecules form a three-dimensional structure known as a DNA double helix
Exam Tip
Make sure you can name the different components of a DNA molecule (sugar-phosphate backbone, nucleotide, complementary base pairs, hydrogen bonds) and make sure you are able to locate these on a diagramRemember that covalent bonds join the nucleotides in the sugar-phosphate backbone, and hydrogen bonds join the bases of the two complementary strands togetherRemember that the bases are complementary, so the number of A = T and C = G. You could be asked to determine how many bases are present in a DNA molecule if given the number of just one of the bases.
Crick & Watson
- Francis Crick and James Watson were two Cambridge scientists who worked together to establish the double helix structure of DNA in 1953
- They used data from their previous experiments on the composition of DNA
- Published findings from other research labs played a role in developing their model
- Rosalind Franklin, Edwin Chargaff and Linus Pauling, all of whom were leading research efforts in other universities, contributed important data to Crick & Watson's discovery
- This suggests that there was a close-knit collaboration, but in fact, there was a lot of competition between the groups to make the breakthrough discovery
- Physical model-making played a large role in their success
- Early versions of the model were rejected for various reasons
- It was not compact enough
- It would have been too unstable (DNA is a highly stable molecule)
- It did not allow equivalent amounts of A and T, and C and G bases to be present (Chargaff's findings)
- It fitted together much better once the second strand was flipped to become antiparallel
- Their final model was constructed carefully with clamps, metal rods for bonds and with the correct bond angles
- Their model was the basis of a lot of genetic research globally in the years that followed
- Notably, Crick and Watson's model sparked work to prove the way in which DNA replicates in cells
NOS: Using models as a representation of the real world; Crick and Watson used model making to discover the structure of DNA
- Models in science are built to represent concepts and ideas in a way that can be pictured by our brains
- Models can be accepted or rejected based on experimental data generated by further research
- Crick and Watson built physical, scale models of DNA to explain biological observations
- Using simple laboratory equipment (clamps, stands, metal rods etc)
- They adapted their models by making them more realistic eg. by building in the correct bond angles within molecules
- They built successive models, using trial-and-error to arrive at the finalised model
- Their first model of DNA was rejected, based on the findings of Rosalind Franklin
- Crick and Watson received the Nobel prize for their work
- Franklin died aged 37 so never received the recognition she deserved for her significant role in defining DNA structure
- Today, sophisticated computer modelling is performed, that
- Takes the place of physical model-making and provides further explanation of the functions of various biomolecules
- Shortens the 'trial-and-error' cycles of model-making as experienced by Crick and Watson
Exam Tip
Crick and Watsons' model has been universally accepted because all further research findings have supported their model.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









