- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: SL复习笔记2.3.1 Proteins
Amino Acids & Polypeptides
Proteins
- Proteins are polymers (and macromolecules) made of monomers called amino acids
- The sequence, type and number of the amino acids within a protein determines its shape and therefore its function
- Proteins are extremely important in cells because they form all of the following:
- Enzymes
- Cell membrane proteins (eg. carrier)
- Hormones
- Immunoproteins (eg. immunoglobulins)
- Transport proteins (eg. haemoglobin)
- Structural proteins (eg. keratin, collagen)
- Contractile proteins (eg. myosin)
- Because all genes code for proteins, all of the reactions necessary for life are dependent on the function of proteins
Amino acids
- Amino acids are the monomers of polypeptides
- There are 20 amino acids found in polypeptides common to all living organisms
- The general structure of all amino acids is a central carbon atom bonded to:
- An amine group -NH2
- A carboxylic acid group -COOH
- A hydrogen atom
- An R group (which is how each amino acid differs and why amino acid properties differ e.g. whether they are acidic or basic or whether they are polar or non-polar)
- The R group can be as simple as another hydrogen atom (glycine), right through to complex aromatic ring structures (eg. phenylalanine)
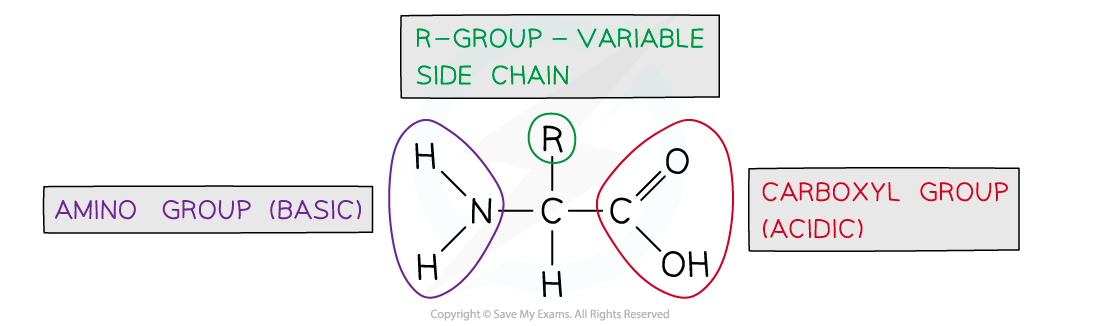
The generalised structure of an amino acid
Peptide bond
- In order to form a peptide bond a hydroxyl group (-OH) is lost from the carboxylic group (-COOH) of one amino acid and a hydrogen atom is lost from the amine group (-NH2) of another amino acid
- The remaining carbon atom (with the double-bonded oxygen) from the first amino acid bonds to the nitrogen atom of the second amino acid
- This is a condensation reaction so water is released
- Dipeptides are formed by the condensation of two amino acids
- Polypeptides are formed by the condensation of many (3 or more) amino acids
- A protein may have only one polypeptide chain or it may have multiple chains interacting with each other
- During hydrolysis reactions, the addition of water breaks the peptide bonds resulting in polypeptides being broken down into amino acids
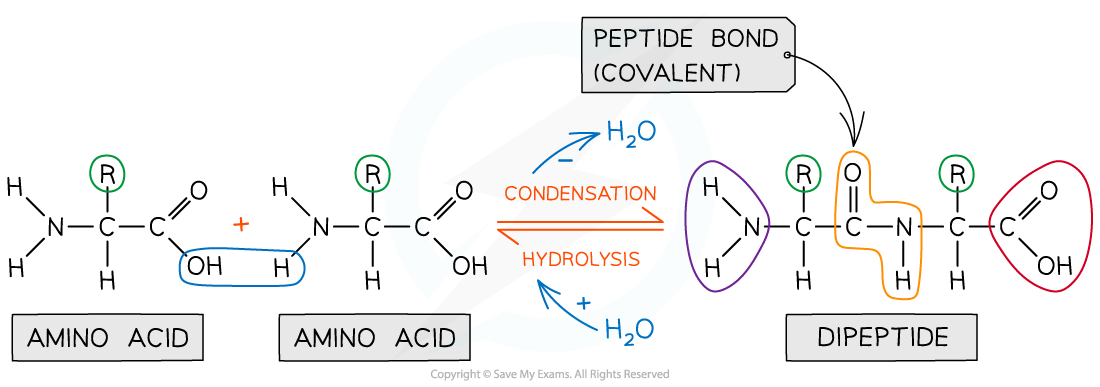
Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction
Exam Tip
You will be expected to recognise whether an unfamiliar molecule is an amino acid or polypeptide so look for the functional groups (amine and carboxyl). When asked to identify the location of the peptide bond, look for where nitrogen is bonded to a carbon that has a double bond with an oxygen atom, note the R group is not involved in the formation of a peptide bond.
Amino Acid Diversity
- The same 20 amino acids make up most of the proteins found on Earth
- Around 500 amino acids have been found in nature, but only 20 are commonly found in proteins
- Eleven of these can be naturally synthesised within cells by humans
- The other nine amino acids are essential (have to be in the human diet)
- You don't need to remember the names of the amino acids, but it's useful to see their names, which are usually abbreviated to three letters
- Ala, Arg, Asn, Asp, Cys, Gln, Glu, Gly, His*, Ile*, Leu*, Lys*, Met*, Phe*, Pro, Ser, Thr*, Trp*, Tyr, Val*
- * indicates the essential amino acids
- Because the R groups vary so much between the 20 amino acids, there is a lot of chemical diversity between the amino acids
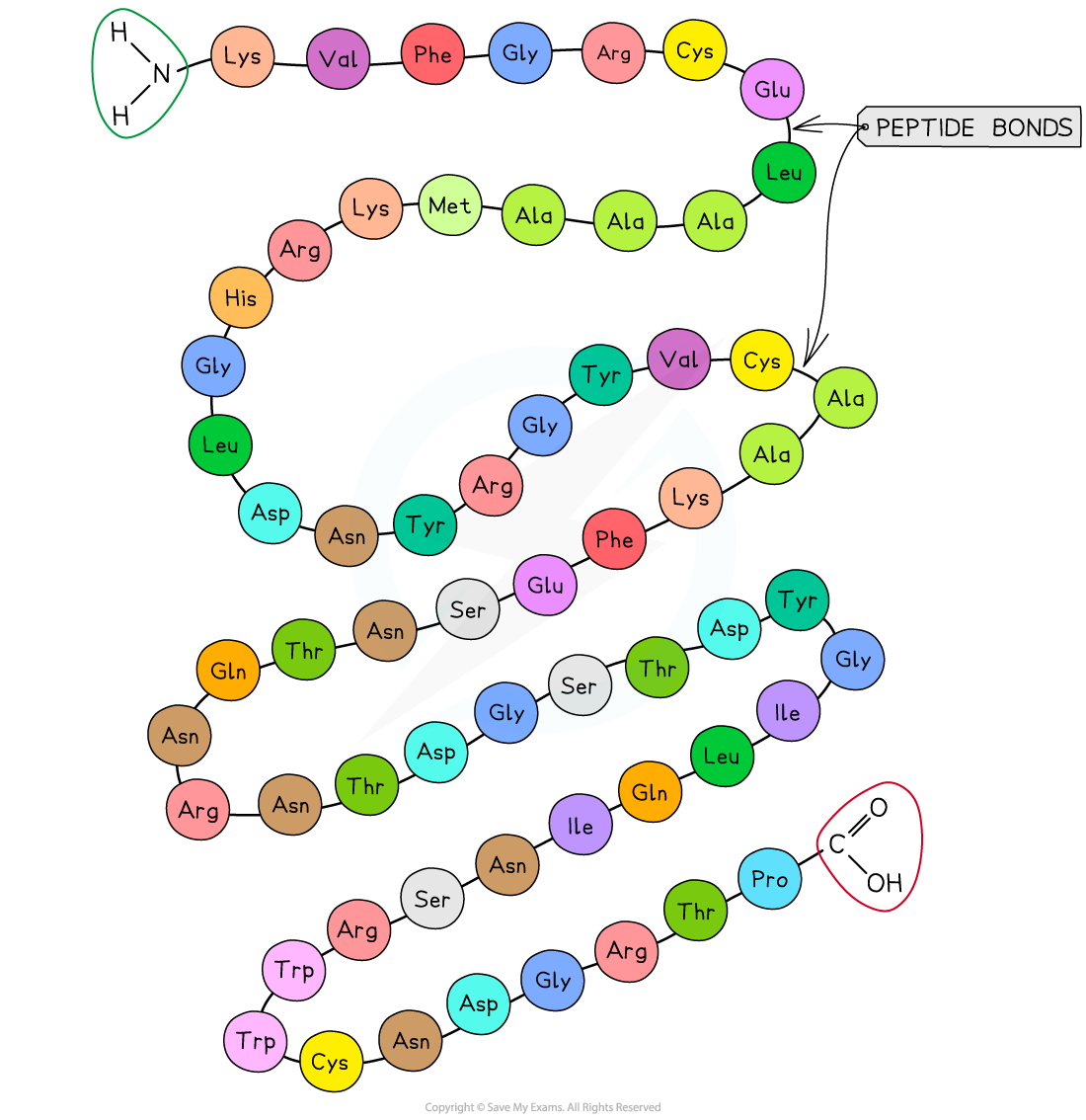
An amino acid sequence of a short polypeptide. The three-letter abbreviations indicate the specific amino acid (there are 20 commonly found in cells of living organisms).
NOS: Looking for patterns, trends and discrepancies; most (but not all) organisms build proteins from the same amino acids.
- All life except for a few species use these 20 amino acids
- The reason why only 20 amino acids are used has been the subject of a lot of differing hypotheses
- That only these 20 were available at the origins of life, so have remained ever since, OR
- That these 20 amino acids are diverse enough to give the wide range of functions that proteins possess, OR
- Because of the theory that all organisms share a common ancestor, the link between the genetic code and amino acid sequence is fixed and is not easily altered, even by mutations
- The almost infinite number of amino acid combinations make polypeptides suitable to determine all the characteristics of life
- Only a few primitive, single-celled organisms use other amino acids
- One unusual amino acid includes the trace element selenium and is found in many polypeptides, though at very low frequencies
- A discrepancy is that in some organisms, the stop codon UAG codes for this unusual amino acid containing selenium
- All life goes by the Central Dogma that all genes code for proteins and the actions of proteins determine all of an organism's characteristics
Polypeptide Diversity
- 20 amino acids can give an almost infinite number of polypeptides
- Polypeptides are assembled at a ribosome by condensing individual amino acids onto a growing chain, one by one
- This allows a choice of 20 amino acids each time one is added
- The mRNA codon determines which amino acid is added
- For a polypeptide chain of 50 amino acids in length (considered a very short protein), there would be 2050 possible combinations of amino acids
- This gives 1.13 x 1065 combinations
- Standard form is preferable for showing such a large number, but writing it out in full shows its size, which is
- 113,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 combinations!
- Given that the average length of a protein is 300 amino acids, the number of possible combinations is so large, we can consider it to be infinite
Genes & Polypeptides
- The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded for by genes
- Despite the huge number of amino acid sequences that could be produced, only a small fraction of these are produced in nature
- Nevertheless, many thousands of different polypeptide sequences are synthesised
- The code for the sequence in which amino acids are joined together is the genetic code, held in a sequence of DNA bases in the genome
- The expression of a gene always results in the production of a polypeptide
- Three consecutive DNA bases are required to code for each amino acid in a polypeptide
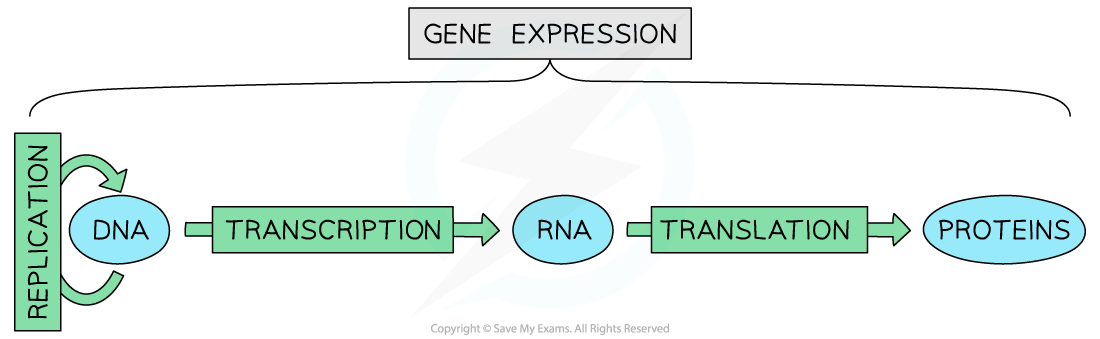
The central dogma of gene expression. All genes code for proteins; proteins carry out the genes’ instructions.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









