- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: HL复习笔记12.2.6 The Law of Radioactive Decay
The Law of Radioactive Decay
- Since radioactive decay is spontaneous and random, it is useful to consider the average number of nuclei which are expected to decay per unit of time
- This is known as the average decay rate
- As a result, each radioactive element can be assigned a decay constant
- The decay constant λ is defined as:
The probability that an individual nucleus will decay per unit of time
- When a sample is highly radioactive, this means the number of decays per unit time is very high
- This suggests it has a high level of activity
- Activity, or the number of decays per unit time can be calculated using:
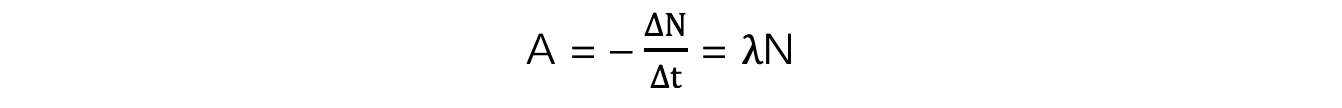
- Where:
- A = activity of the sample (Bq)
- ΔN = number of decayed nuclei
- Δt = time interval (s)
- λ = decay constant (s-1)
- N = number of nuclei remaining in a sample
- In radioactive decay, the number of undecayed nuclei falls very rapidly, without ever reaching zero
- Such a model is known as exponential decay
- The graph of number of undecayed nuclei against time has a very distinctive shape:
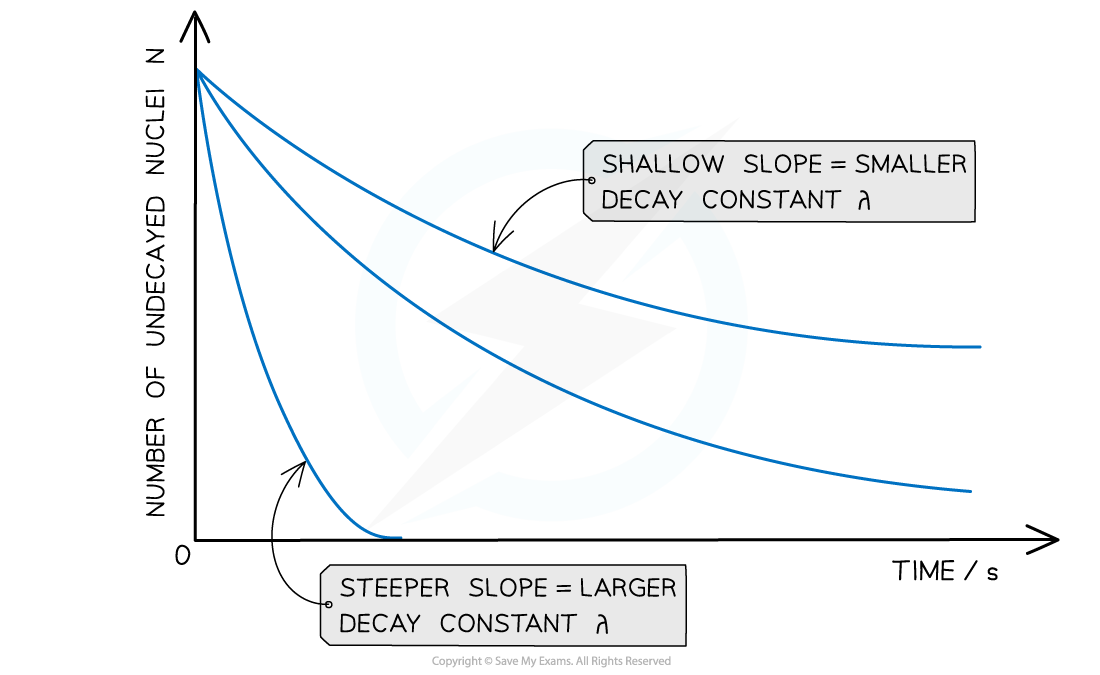
Radioactive decay follows an exponential pattern. The graph shows three different isotopes each with a different rate of decay
- The key features of this graph are:
- The steeper the slope, the larger the decay constant λ (and vice versa)
- The decay curves always start on the y-axis at the initial number of undecayed nuclei (N0)
- The law of radioactive decay states:
The rate of decay of a nuclide is proportional to the amount of radioactive material remaining
- The number of undecayed nuclei N can be represented in exponential form by the equation:
N = N0 e–λt
- Where:
- N0 = the initial number of undecayed nuclei (when t = 0)
- N = number of undecayed nuclei at a certain time t
- λ = decay constant (s-1)
- t = time interval (s)
- The number of nuclei can be substituted for other quantities
- For example, the activity A is directly proportional to N, so it can also be represented in exponential form by the equation:
A = A0 e–λt
- Where:
- A = activity at a certain time t (Bq)
- A0 = initial activity (Bq)
- The received count rate C is related to the activity of the sample, hence it can also be represented in exponential form by the equation:
C = C0 e–λt
- Where:
- C = count rate at a certain time t (counts per minute or cpm)
- C0 = initial count rate (counts per minute or cpm)
Exam Tip
The symbol e represents the exponential constant - it is approximately equal to e = 2.718
On a calculator, it is shown by the button ex
The inverse function of ex is ln(y), known as the natural logarithmic function - this is because, if ex = y, then x = ln(y)
Make sure you are confident using the exponential and natural logarithmic functions, they are a major component of the mathematics in this topic!
Problems Involving the Radioactive Decay Law
Worked Example
Strontium-90 decays with the emission of a β-particle to form Yttrium-90. The decay constant of Strontium-90 is 0.025 year -1.
Determine the activity A of the sample after 5.0 years, expressing the answer as a fraction of the initial activity A0.
Step 1: Write out the known quantities
-
- Decay constant, λ = 0.025 year -1
- Time interval, t = 5.0 years
- Both quantities have the same unit, so there is no need for conversion
Step 2: Write the equation for activity in exponential form
A = A0 e–λt
Step 3: Rearrange the equation for the ratio between A and A0
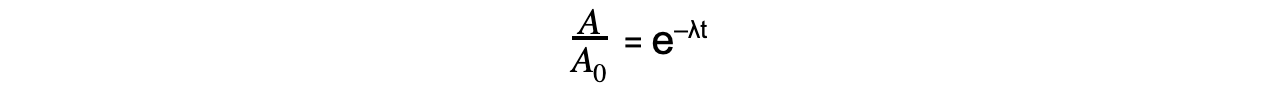
Step 4: Calculate the ratio A/A0
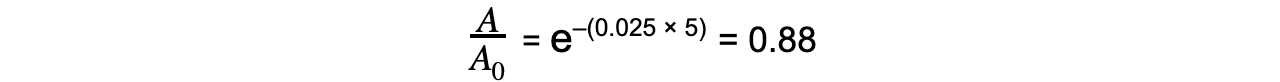
-
- Therefore, the activity of Strontium-90 decreases by a factor of 0.88, or 12%, after 5 years
Worked Example
Americium-241 is an artificially produced radioactive element that emits α-particles.
In a smoke detector, a sample of americium-241 of mass 5.1 µg is found to have an activity of 5.9 × 105 Bq. The supplier’s website says the americium-241 in their smoke detectors initially has an activity level of 6.1 × 105 Bq.
Part (a)
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
-
-
- Mass = 5.1 μg = 5.1 × 10-6 g
- Molecular mass of americium = 241
- NA = the Avogadro constant
-
Step 2: Write down the equation relating to the number of nuclei, mass and molecular mass
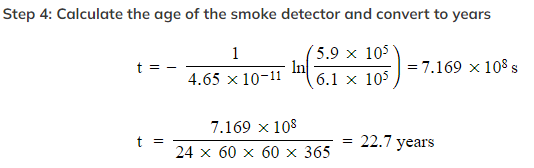 Therefore, the smoke detector is 22.7 years old
Therefore, the smoke detector is 22.7 years old
转载自savemyexams


最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








