- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: HL复习笔记11.2.8 Rectification
Rectification
- Rectification is defined as:
The process of converting alternating current and voltage into direct current and voltage
- Rectification is used in electronic equipment which requires a direct current
- For example, mains voltage must be rectified from the alternating voltage produced at power stations
- There are two types of rectification:
- Half-wave rectification
- Full-wave rectification
- For half-wave rectification:
- The graph of the output voltage Vout against time is a sine curve with the positive cycles and a flat line (Vout = 0) on the negative cycle
- This is because the diode only conducts in the positive direction
- For full-wave rectification:
- The graph of the output voltage Vout against time is a sine curve where the positive cycles and the negative cycles are both curved ‘bumps’
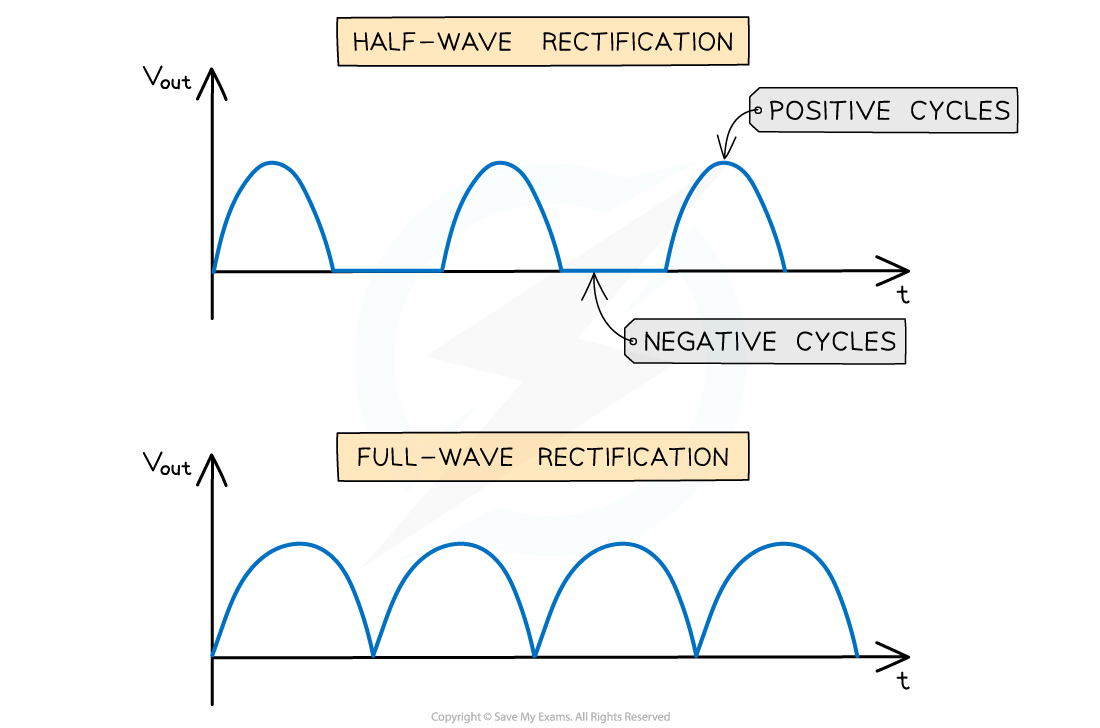
- The graph of the output voltage Vout against time is a sine curve where the positive cycles and the negative cycles are both curved ‘bumps’
The difference between the graphs of full-wave and half-wave rectification
Half-Wave Rectification
- Half-wave rectification consists of a single diode
- An alternating input voltage is connected to a circuit with a load resistor and diode in series
- The diode will only conduct during the positive cycles of the input alternating voltage,
- Hence there is only current in the load resistor during these positive cycles
- The output voltage Vout across the resistor will fluctuate against time in the same way as the input alternating voltage except there are no negative cycles
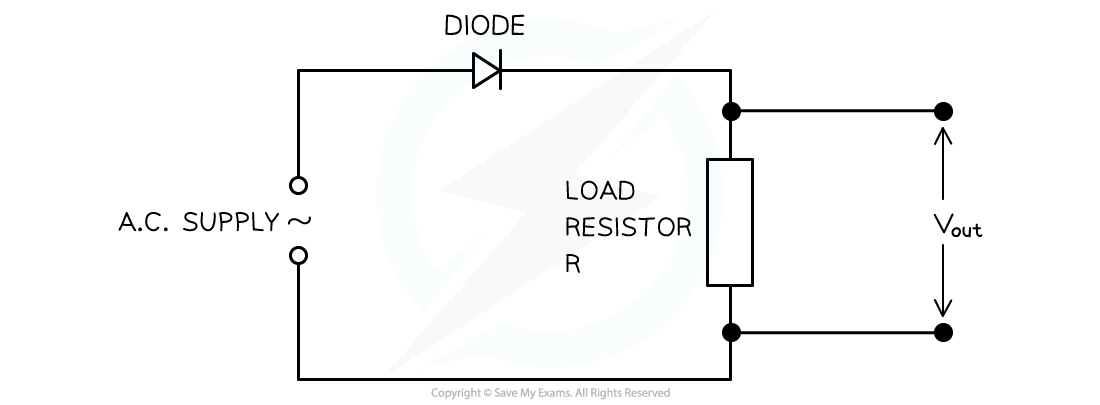
Half-wave rectification requires a single diode and the graph is represented by only the positive cycles
- This type of rectification means half of the time the voltage is zero
- The power available from a half-wave rectified supply is reduced
Full-Wave Rectification
- Full-wave rectification requires a bridge rectifier circuit
- This consists of four diodes connected across an input alternating voltage supply
- The output voltage Vout is taken across a load resistor
- During the positive cycles of the input voltage, one terminal if the voltage supply is positive and the other negative
- Two diodes opposite each other that are in forward bias will conduct
- The other two in reverse bias will not conduct
- A current will flow in the load resistor with the positive terminal at the top of the resistor
- During the negative cycles of the input voltage, the positive and negative terminals of the input alternating voltage supply will swap
- The two diodes that were in forward bias will now be in reverse bias and not conduct
- The other two in reverse bias will now be in forward bias and will conduct
- The current in the load resistor will still flow in the same direction as before
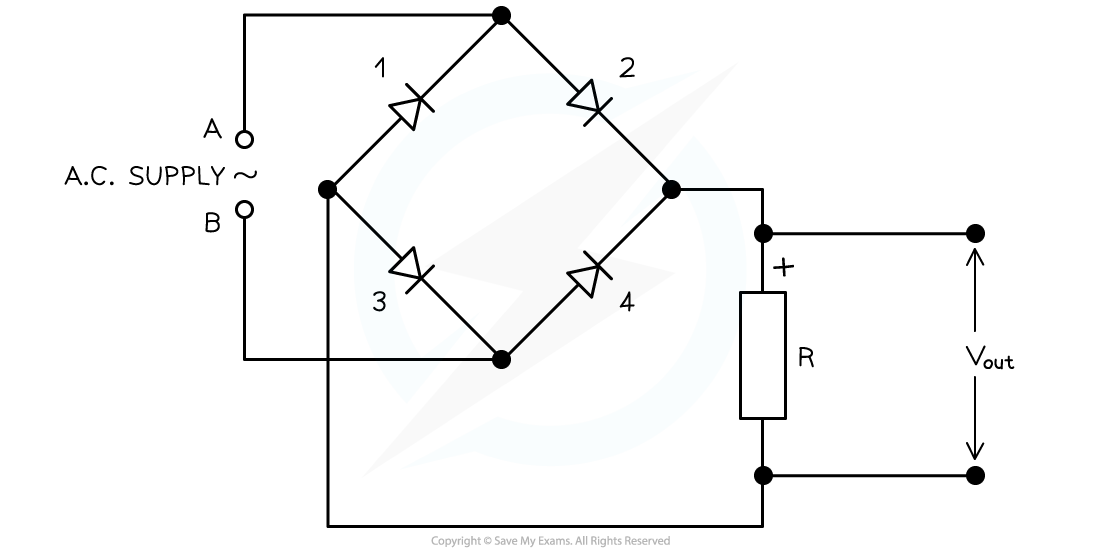
When A is positive and B is negative, diodes 2 and 3 will conduct and 1 and 4 will not. When A is negative and B is positive, diodes 1 and 4 will conduct and diodes 2 and 3 will not. The current in the load resistor R will flow downwards
- In both the positive and negative cycles, the current in the load resistor is the same
- Each diode pair is the same as in half-wave rectification
- Since there are two pairs, this equates to full-wave rectification overall
- The main advantage of full-wave rectification compared to half-wave rectification is that there is more power available
- Therefore, greater power is supplied on every half cycle
Worked Example
A bridge rectifier consists of four ideal diodes A, B, C and D as connected in the figure shown below.
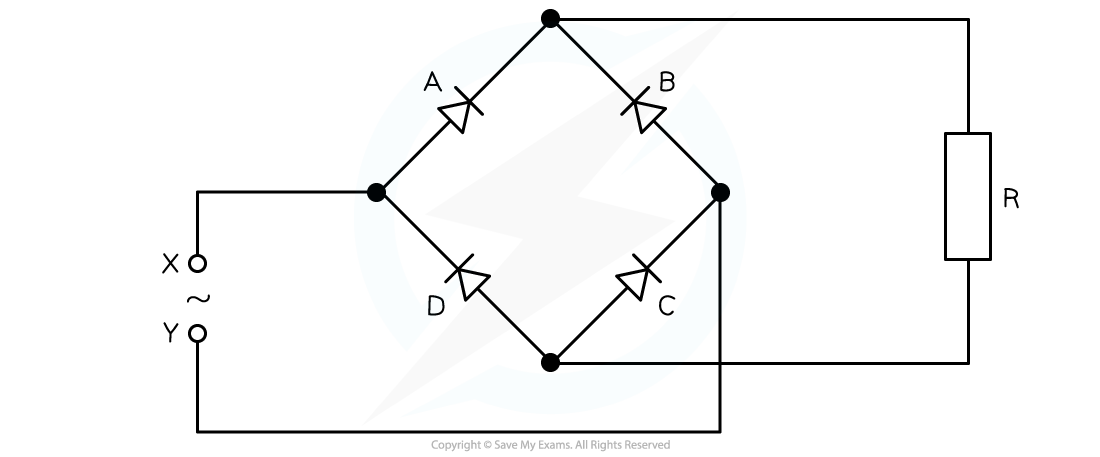
An alternating supply is applied between the terminal X and Y.
Identify which diodes are conducting when terminal X of the supply is positive.
- Draw path of the current direction with diodes in forward bias
- Remember that conventional current flow is from positive to negative and only travels through the paths with diodes in forward bias
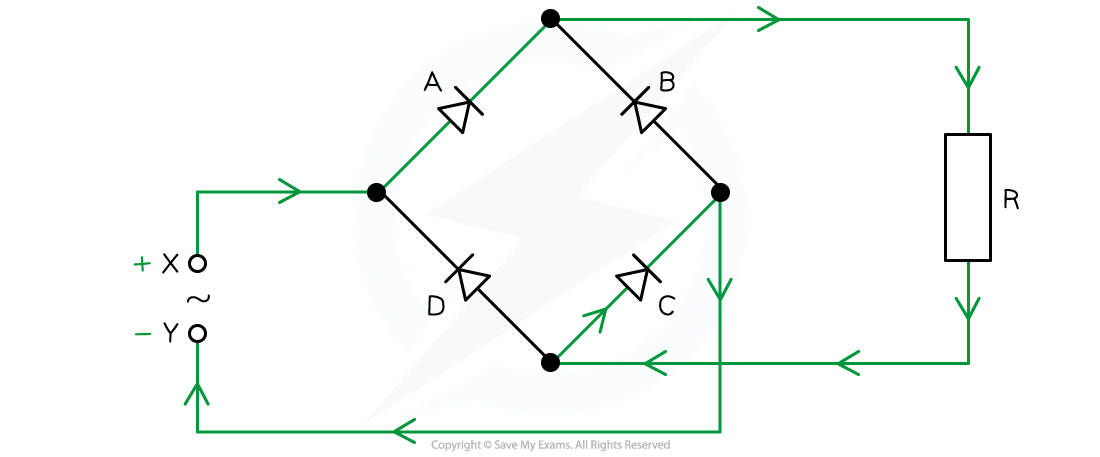
- Therefore, the answer is: diodes A and C
Exam Tip
Being able to reproduce the diode bridge correctly and explain the cycles of full-wave rectification are important physics concepts that may occur during an examination. It is worth learning to draw and explain full-wave rectification accurately
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








