- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: HL复习笔记10.2.3 Potential Gradient & Difference
Potential Gradient
Electric Potential Gradient
- An electric field can be defined in terms of the variation of electric potential at different points in the field:
The electric field at a particular point is equal to the negative gradient of a potential-distance graph at that point
- The potential gradient is defined by the equipotential lines
- These demonstrate the electric potential in an electric field and are always drawn perpendicular to the field lines
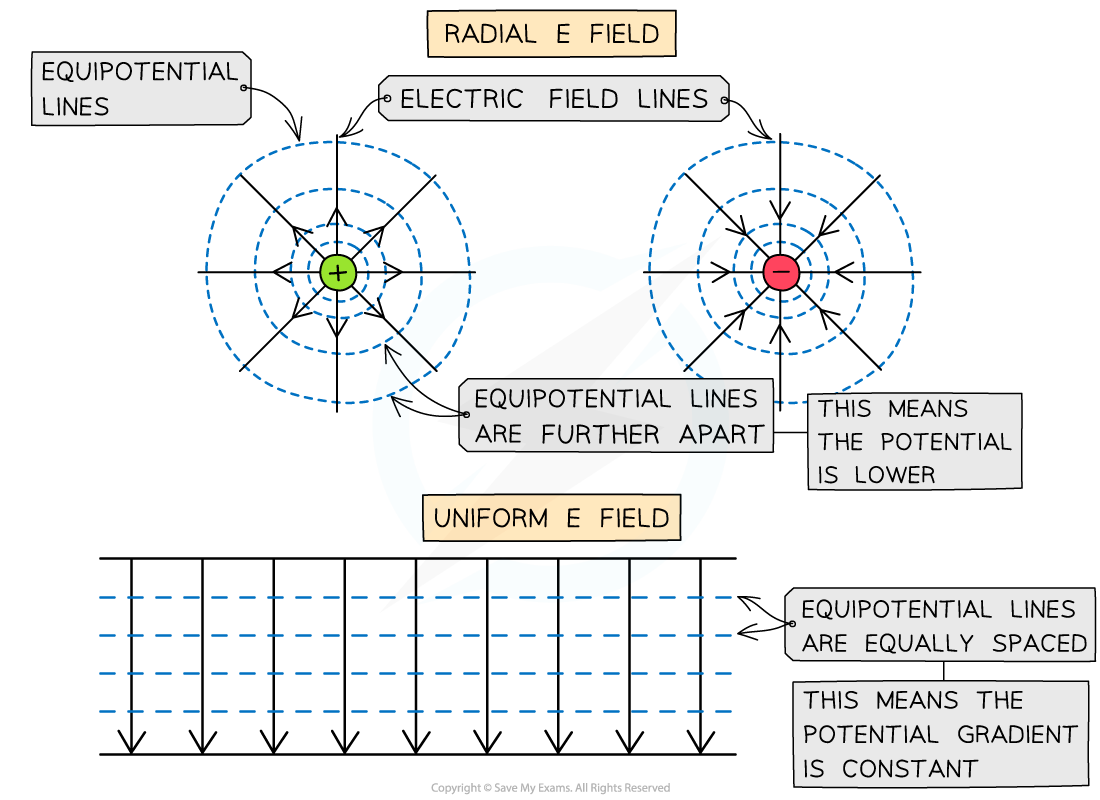
Equipotential lines around a radial field or uniform field are perpendicular to the electric field lines
- Equipotential lines are lines of equal electric potential
- Around a radial field, the equipotential lines are represented by concentric circles around the charge with increasing radius
- The equipotential lines become further away from each other
- In a uniform electric field, the equipotential lines are equally spaced
- The potential gradient in an electric field is defined as:
The rate of change of electric potential with respect to displacement in the direction of the field
- The electric field strength is equivalent to this, except with a negative sign:
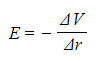 Where:
Where:
- E = electric field strength (V m-1)
- ΔV = change in potential (V)
- Δr = displacement in the direction of the field (m)
- The minus sign is important to obtain an attractive field around a negative charge and a repulsive field around a positive charge

The electric potential around a positive charge decreases with distance and increases with distance around a negative charge
- The electric potential changes according to the charge creating the potential as the distance r increases from the centre:
- If the charge is positive, the potential decreases with distance
- If the charge is negative, the potential increases with distance
- This is because the test charge is positive
Gravitational Potential Gradient
- A gravitational field can be defined in terms of the variation of gravitational potential at different points in the field:
The gravitational field at a particular point is equal to the negative gradient of a potential-distance graph at that point
- The potential gradient is defined by the equipotential lines
- These demonstrate the gravitational potential in a gravitational field and are always drawn perpendicular to the field lines
- The potential gradient in a gravitational field is defined as:
The rate of change of gravitational potential with respect to displacement in the direction of the field
- Gravitational field strength, g and the gravitational potential, V can be graphically represented against the distance from the centre of a planet, r
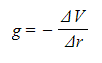 Where:
Where:
- g = gravitational field strength (N kg-1)
- ΔV = change in gravitational potential (J kg-1)
- Δr = distance from the centre of a point mass (m)
- The graph of V against r for a planet is:
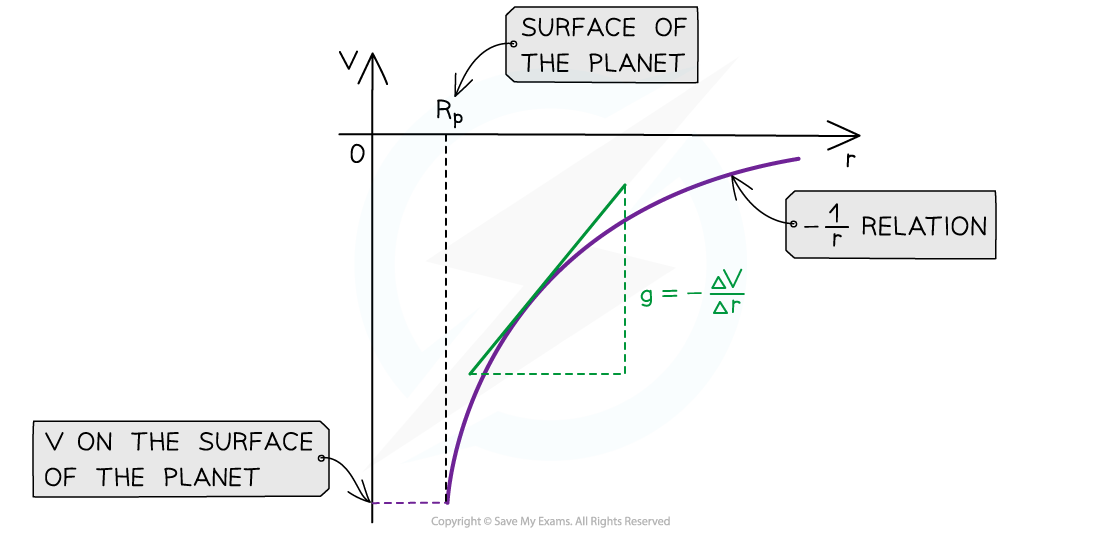
- The key features of this graph are:
- The values for V are all negative
- As r increases, V against r follows a -1/r relation
- The gradient of the graph at any particular point is the value of g at that point
- The graph has a shallow increase as r increases
- To calculate g, draw a tangent to the graph at that point and calculate the gradient of the tangent
- This is a graphical representation of the equation:
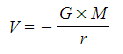 where G and M are constant
where G and M are constant
Worked Example
Determine the change in gravitational potential when travelling from 3 Earth radii (from Earth’s centre) to the surface of the Earth.
Assume that the mass of the Earth is 5.97 × 1024 kg and the radius of the Earth is 6.38 × 106 m
-
- Earth’s mass, ME = 5.97 × 1024 kg
- Radius of the Earth, rE = 6.38 × 106 m
- Initial distance, r1 = 3 × rE = 3 × (6.38 × 106) m = 1.914 × 107 m
- Final distance, r2 = 1 × rE = 6.38 × 106 m
- Gravitational constant, G = 6.67 × 10−11 m3 kg−1 s−2
 Exam Tip
Exam TipPotential Difference
- The potential difference is defined as:
The work done by moving a positive test charge from one point to another in an electric field
- The units for potential difference are:
- Joules per Coulomb for electrostatic potential difference
- Joules per Kilogram for gravitational potential difference
- This can be related to the concept of equipotentials where the movement of a small test mass or positive test charge from one equipotential to another visually represents a potential difference
- Further, potential difference also occurs across electrical components which is also known as voltage
Uniform Electric Field Strength
- The magnitude of the electric field strength in a uniform field between two charged parallel plates is defined as:
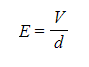 Where:
Where:
- E = electric field strength (V m-1)
- V = potential difference between the plates (V)
- d = separation between the plates (m)
- Note: the electric field strength is now also defined by the units V m-1
- The equation shows:
- The greater the voltage between the plates, the stronger the field
- The greater the separation between the plates, the weaker the field
- This equation cannot be used to find the electric field strength around a point charge (since this would be a radial field)
- The direction of the electric field is from the plate connected to the positive terminal of the cell to the plate connected to the negative terminal

The E field strength between two charged parallel plates is the ratio of the potential difference and separation of the plates
- Note: if one of the parallel plates is earthed, it has a voltage of 0 V
Derivation of Electric Field Strength Between Plates
- When two points in an electric field have a different potential, there is a potential difference between them
- To move a charge across that potential difference, work needs to be done
- Two parallel plates with a potential difference ΔV across them create a uniform electric field
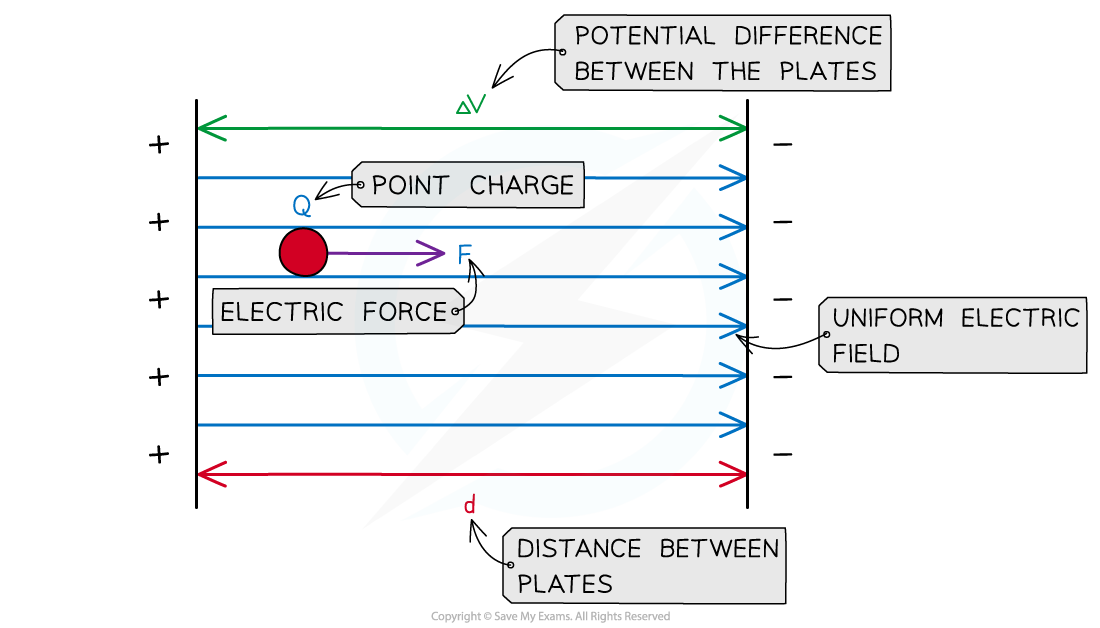
The work done on the charge depends on the electric force and the distance between the plates
- Potential difference is defined as the energy, W, transferred per unit charge, Q, this can also be written as:
 Worked Example
Worked Example
Two parallel metal plates are separated by 3.5 cm and have a potential difference of 7.9 kV.
Calculate the magnitude of the electric force acting on a stationary charged particle between the plates that has a charge of 2.6 × 10-15 C.
-
- Potential difference, V = 7.9 kV = 7.9 × 103 V
- Distance between plates, d = 3.5 cm = 3.5 × 10−2 m
- Charge, Q = 2.6 × 10−15 C
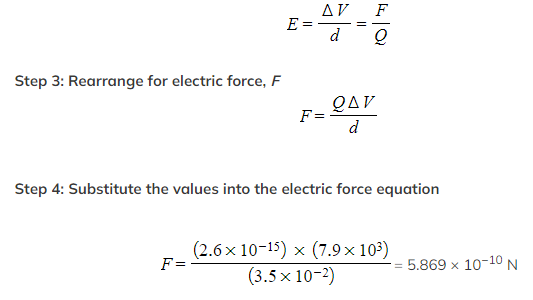 Step 5: State the final answer
Step 5: State the final answer-
-
The magnitude of the electric force acting on this charged particle is 5.9 × 10−10 N
-
Exam Tip
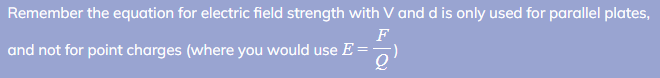
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








