- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: HL复习笔记10.1.3 Gravitational & Electrostatic Potential
Gravitational & Electrostatic Potential
Gravitational Potential
- The gravitational potential energy (G.P.E) is the energy an object has when lifted off the ground
- G.P.E is given by the familiar equation:
- The G.P.E on the surface of the Earth is taken to be zero
- This means work is done to lift the object
- The equation is only valid for objects that are close to the Earth's surface
- However, outside the Earth’s immediate influence, G.P.E can be better defined as:
The energy an object possess due to its position in a gravitational field
- The gravitational potential at a point can, therefore, be defined as:
The work done per unit mass in bringing a test mass from infinity to a defined point
- It is represented by the symbol, V and is measured in J kg−1
- Gravitational potential is always a negative value, this is because:
- It is defined as having a value of zero at infinity
- Since the gravitational force is attractive, work must be done on a mass to reach infinity
- On the surface of a mass (such as a planet), gravitational potential has a negative value
- The value becomes less negative, i.e. it increases, with distance from that mass
- Work has to be done against the gravitational pull of the planet to take a unit mass away from the planet
- The gravitational potential at a point depends on:
- The mass of the object producing the gravitational field
- The distance the centre of mass to the point
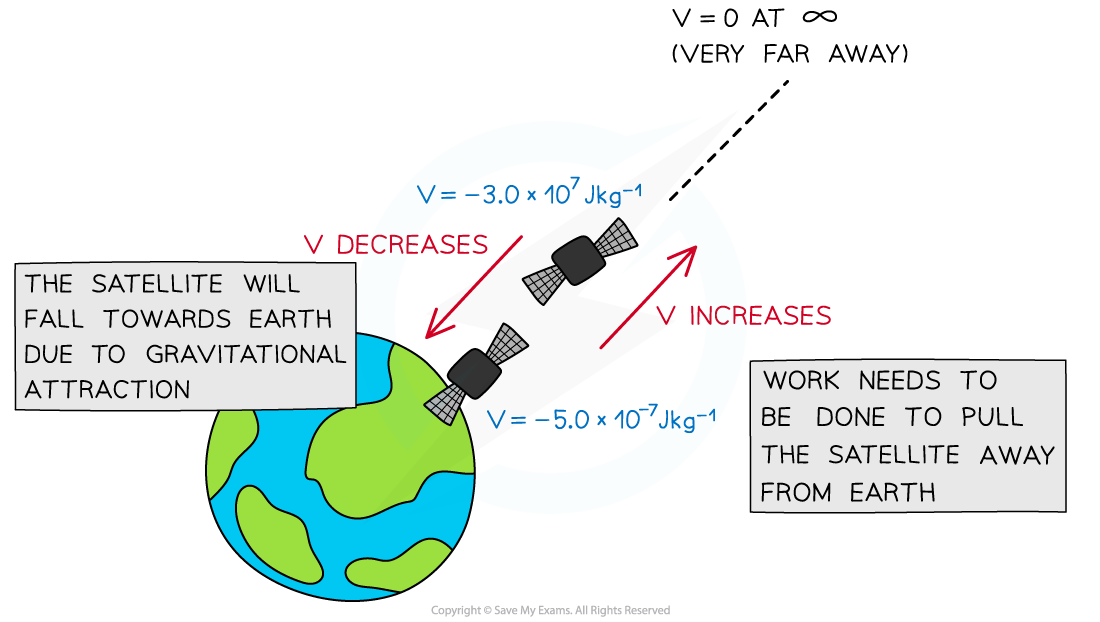
Gravitational potential decreases as the satellite moves closer to the Earth
Gravitational Potential Difference
- Two points at different distances from a mass will have different gravitational potentials because the gravitational potential increases with distance
- So there will also be a gravitational potential difference between the two points, which is represented by the symbol ΔV
- Gravitational potential difference, ΔV, is given by:
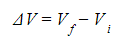 Where:
Where:
- Vf = final gravitational potential (J kg−1)
- Vi = initial gravitational potential (J kg−1)
- A difference in gravitational potential will give a difference in gravitational potential energy, which can also be calculated
Calculating Gravitational Potential
- The equation for gravitational potential V is defined by the mass M and distance r:
 Where:
Where:
- V = gravitational potential (J kg-1)
- G = Newton’s gravitational constant
- M = mass of the body producing the gravitational field (kg)
- r = distance from the centre of the mass to the point mass (m)
- The gravitational potential always is negative near an isolated mass, such as a planet, because:
- The potential when r is at infinity (∞) is defined as 0
- Work must be done to move a mass away from a planet (V becomes less negative)
- It is also a scalar quantity, unlike the gravitational field strength which is a vector quantity
- Gravitational forces are always attractive, this means as r decreases, positive work is done by the mass when moving from infinity to that point
- When a mass is closer to a planet, its gravitational potential becomes smaller (more negative)
- As a mass moves away from a planet, its gravitational potential becomes larger (less negative) until it reaches 0 at infinity
- This means when the distance (r) becomes very large, the gravitational force tends rapidly towards 0 at a point further away from a planet
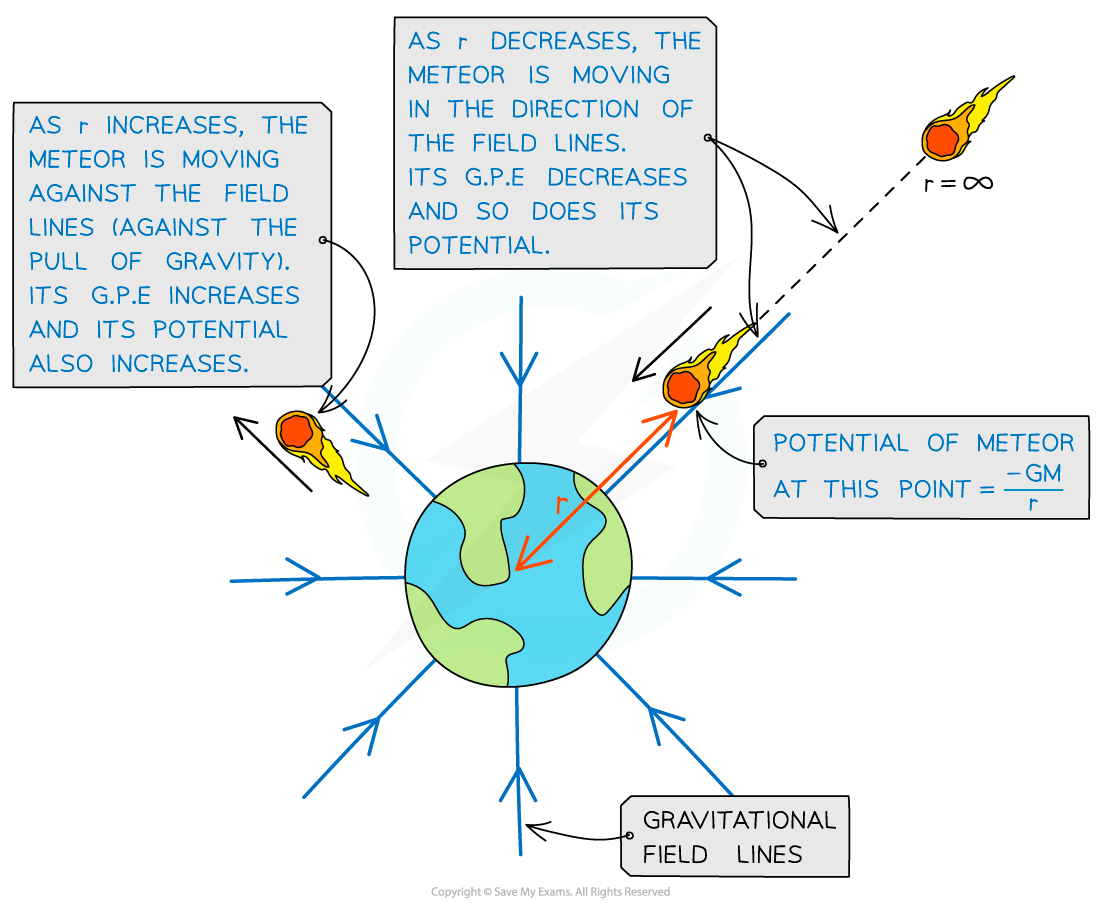
Gravitational potential increases and decreases depending on whether the object is travelling towards or against the field lines from infinity
Worked Example
A planet has a diameter of 7600 km and a mass of 3.5 × 1023 kg. A rock of mass 528 kg accelerates towards the planet from infinity.
Calculate the gravitational potential of the rock at a distance of 400 km above the planet's surface.
Step 1: Write the gravitational potential equation Graphical Representation of Gravitational Potential
Graphical Representation of Gravitational Potential
- Gravitational field strength, g and the gravitational potential, V can be graphically represented against the distance from the centre of a planet, r
- g, V and r are related by the equation:
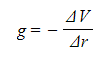 Where:
Where:
- g = gravitational field strength (N kg-1)
- ΔV = change in gravitational potential (J kg-1)
- Δr = distance from the centre of a point mass (m)
- The graph of V against r for a planet is:
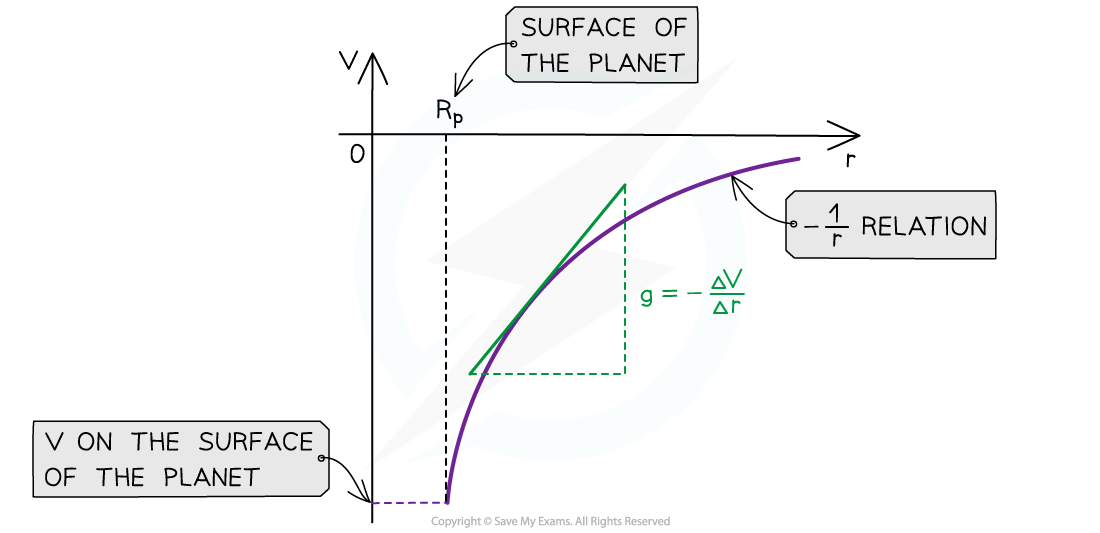
- The key features of this graph are:
- The values for V are all negative
- As r increases, V against r follows a -1/r relation
- The gradient of the graph at any particular point is the value of g at that point
- The graph has a shallow increase as r increases
- To calculate g, draw a tangent to the graph at that point and calculate the gradient of the tangent
- This gives you a graphical representation of the equation:
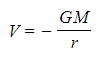
- Where G and M are constant
- The graph of g against r for a planet is:
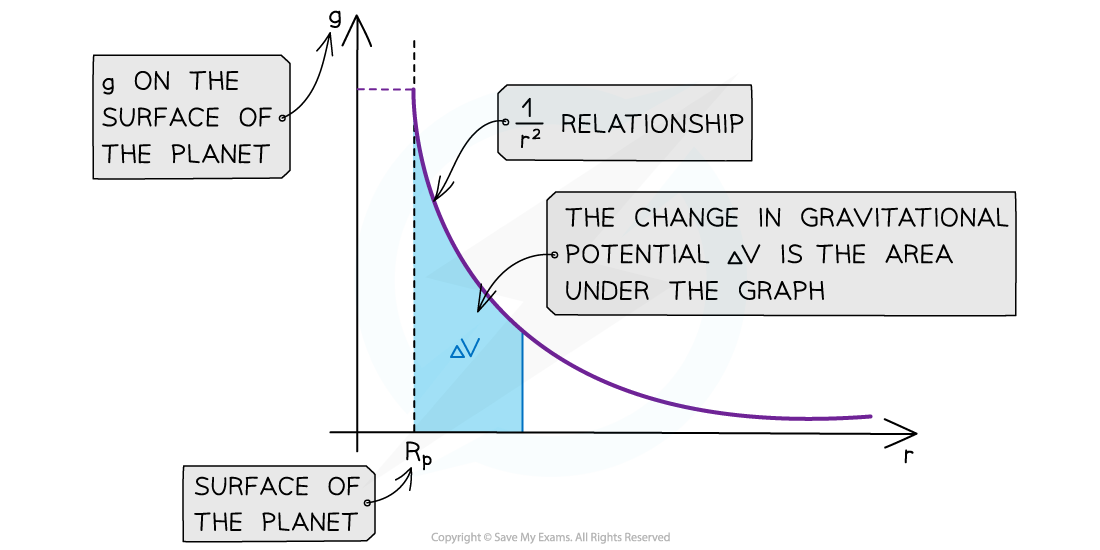
- The key features of this graph are:
- The values for g are all positive
- As r increases, g against r follows a 1/r2 relation (inverse square law)
- The area under this graph is the change in gravitational potential ΔV
- The graph has a steep decline as r increases
- The area under the graph can be estimated by counting squares, if it is plotted on squared paper, or by splitting it into trapeziums and summing the area of each trapezium
- The inverse square law relation means that as the distance r doubles, the value of g decreases by a factor of four
- This is a graphical representation of the equation:
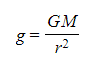 Where G and M are constant
Where G and M are constant
Worked Example
Sketch a graph on the axes below to indicate how the gravitational potential varies with distance along a line outwards from the surface of planet A which is 80 times the mass of planet B.


- Graph increases from a large negative value for V at the surface of A as distance increases
- Up to a value close to, but below 0 near the surface of planet B
- The graph then falls near the surface of planet B
- From a point much closer to planet B than A
Electric Potential
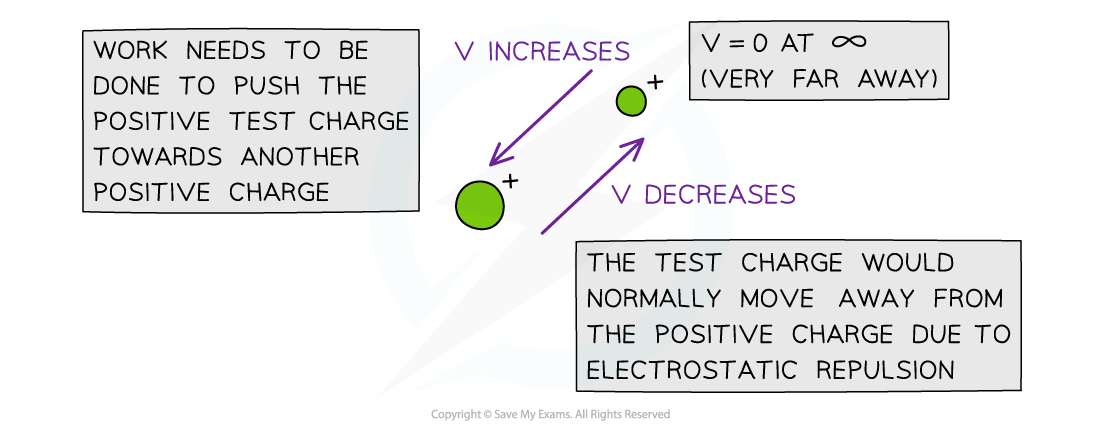
- In order to move a positive charge closer to another positive charge, work must be done to overcome the force of repulsion between them
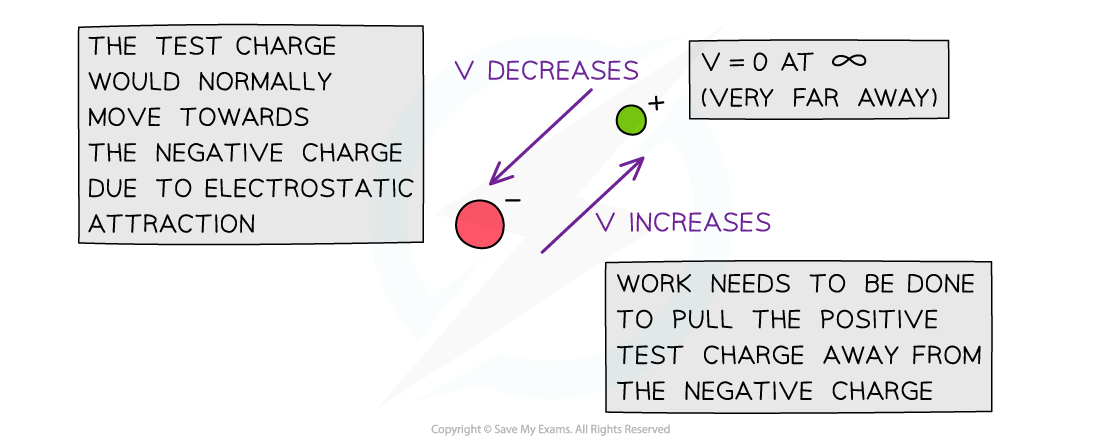
- Similarly, to move a positive charge away from a negative charge, work must be done to overcome the force of attraction between them
- Energy is therefore transferred to the charge that is being pushed upon
- This means its potential energy increases
- If the positive charge is free to move, it will start to move away from the repelling charge
- As a result, its potential energy decreases back to 0
- This is analogous to the gravitational potential energy of a mass increasing as it is being lifted upwards and decreasing as it falls
- The electric potential at a point is defined as:
The work done per unit positive charge in bringing a point test charge from infinity to a defined point
- Electric potential is a scalar quantity
- This means it doesn’t have a direction
- However, electric potential can have a positive or negative sign, this is because it is:
- Positive around an isolated positive charge
- Negative around an isolated negative charge
- Zero at infinity
- Positive work is done by the mass from infinity to a point around a positive charge and negative work is done around a negative charge. This means:
- When a positive test charge moves closer to a negative charge, its electric potential decreases
- When a positive test charge moves closer to a positive charge, its electric potential increases
- To find the potential at a point caused by multiple charges, the total potential is the sum of the potential from each charge
Electric Potential Difference
- Two points at different distances from a charge will have different electric potentials
- This is because the electric potential increases with distance from a negative charge and decreases with distance from a positive charge
- Therefore, there will be an electric potential difference between the two points
- This is represented by the symbol ΔV
- ΔV is normally given as the equation
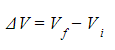
- Where:
- Vf = final electric potential (J C-1)
- Vi = initial electric potential (J C-1)
- A difference in electric potential will give a difference in electric potential energy, which can also be calculated
Graphical Representation of Electric Potential
- Electric field strength, E and the electric potential, V can be graphically represented against the distance from the centre of a charge, r
- E, V and r are related by the equation:
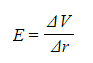 Where:
Where:
- E = electric field strength (V m-1)
- ΔV = change in potential (V)
- Δr = displacement in the direction of the field (m)
- An electric field can be defined in terms of the variation of electric potential at different points in the field:
The electric field at a particular point is equal to the gradient of a potential-distance graph at that point
- The potential gradient in an electric field is defined as:
The rate of change of electric potential with respect to displacement in the direction of the field
- The graph of potential V against distance r for a negative or positive charge is:
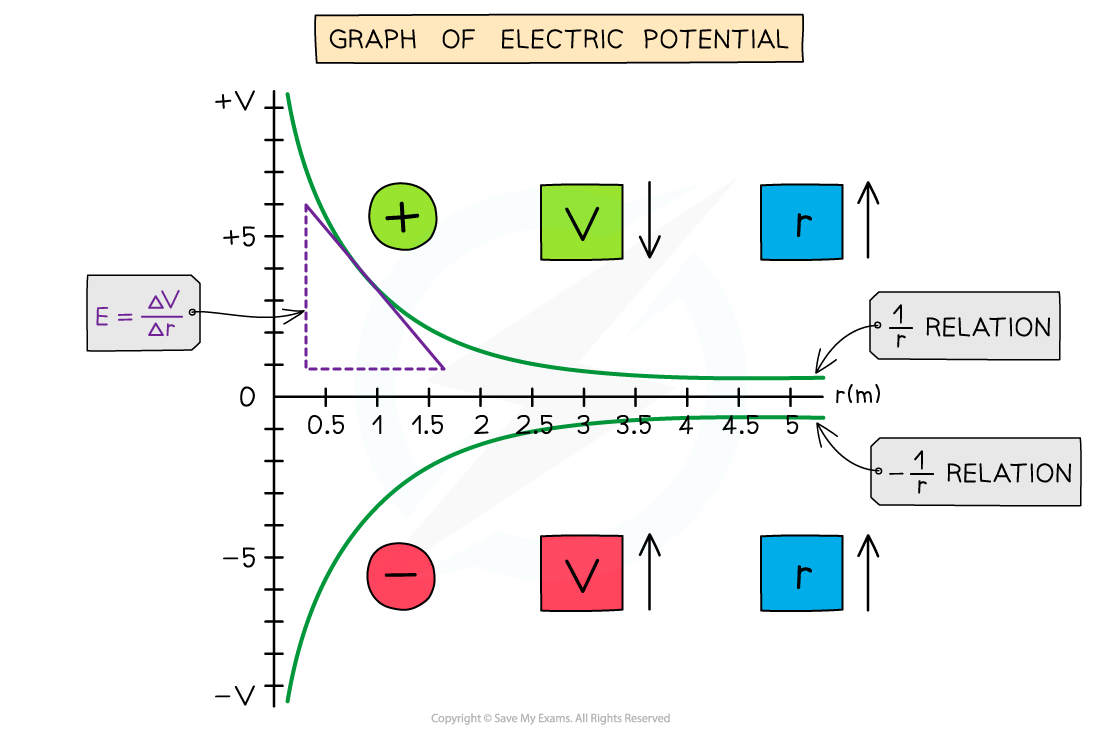
The electric potential around a positive charge decreases with distance and increases with distance around a negative charge
- The key features of this graph are:
- The values for V are all negative for a negative charge
- The values for V are all positive for a positive charge
- As r increases, V against r follows a 1/r relation for a positive charge and -1/r relation for a negative charge
- The gradient of the graph at any particular point is the value of E at that point
- The graph has a shallow increase (or decrease) as r increases
- The electric potential changes according to the charge creating the potential as the distance r increases from the centre:
- If the charge is positive, the potential decreases with distance
- If the charge is negative, the potential increases with distance
- To calculate E, draw a tangent to the graph at that point and calculate the gradient of the tangent
- This is a graphical representation of the equation:
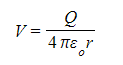 Where Q and 4πε0 are constants
Where Q and 4πε0 are constants
- The graph of E against r for a charge is:
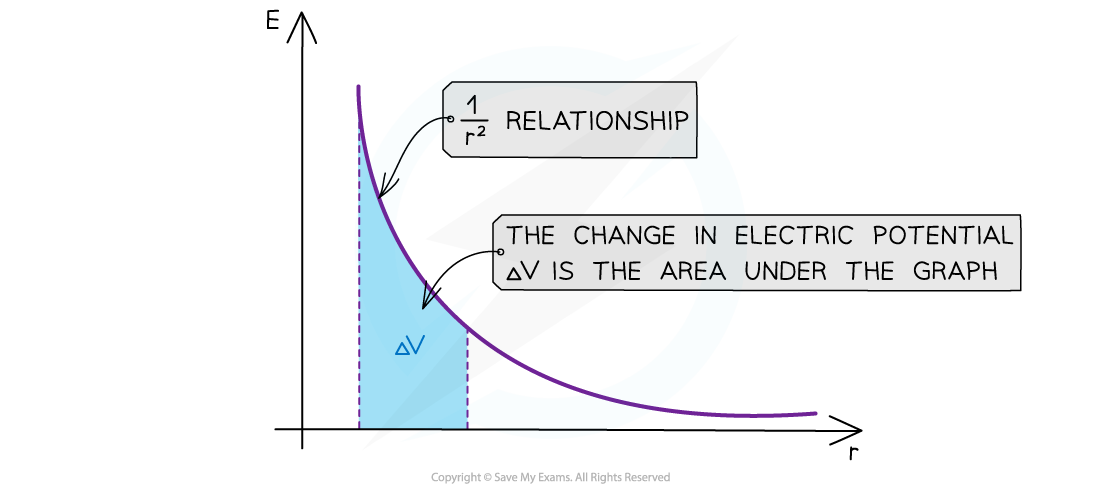
The electric field strength E has a 1/r2 relationship
- The key features of this graph are:
- The values for E are all positive
- As r increases, E against r follows a 1/r2 relation (inverse square law)
- The area under this graph is the change in electric potential ΔV
- The graph has a steep decline as r increases
- The area under the graph can be estimated by counting squares, if it is plotted on squared paper, or by splitting it into trapeziums and summing the area of each trapezium
- The inverse square law relation means that as the distance r doubles, E decreases by a factor of 4
- This is a graphical representation of the equation:
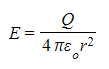 Where Q and 4πε0 are constants
Where Q and 4πε0 are constants
Exam Tip
Drawing, interpreting or calculating from inverse square law graphs are common exam questions - there are lots of similarities between gravitational and electric field graphs:
Graphs of field strength against distance should start off steeper and decrease rapidly compared to that of potential graphs against distance, to distinguish it as an inverse square law (1/r2) relation instead of just an inverse relation (1/r)
There are plenty of differences too:
For example, gravitational potential always increases with respect to distance whereas electric potential can increase or decrease
One way to remember whether the electric potential increases or decreases with respect to the distance from the charge is by the direction of the electric field lines - the potential always decreases in the same direction as the field lines and vice versa.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









