- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: HL复习笔记8.2.3 The Solar Constant, Albedo & Emissivity
The Solar Constant
- Since life on Earth is entirely dependant on the Sun’s energy, it is useful to quantify how much of its energy reaches the top of the atmosphere
- This is known as the solar constant
- The solar constant is defined as:
The amount of solar radiation across all wavelengths that is incident in one second on one square metre at the mean distance of the Earth from the Sun
- The value of the solar constant varies year-round because:
- The Earth’s is in an elliptical orbit around the Sun, meaning at certain times of year the Earth is closer to the Sun, and other times of year it is further away
- The Sun’s output varies by about 0.1% during its 11-year sunspot cycle
- Calculations of the solar constant assume that:
- This radiation is incident on a plane perpendicular to the Earth's surface
- The Earth is at its mean distance from the Sun
Worked Example
The Sun emits 4 × 1026 J in one second. The mean distance of the Earth from the Sun is 1.5 × 1011 m.
Using this data, calculate the solar constant.
Step 1: List the known quantities
-
- Power output of Sun, P = 4 × 1026 W
- Distance between the Earth and Sun, r = 1.5 × 1011 m
Step 2: Model the scenario using geometry
-
- As light leaves the surface of the Sun, it begins to spread out uniformly through a spherical shell
- The surface area of a sphere = 4πr2
- The radius r of this sphere is equal to the distance between the Sun and the Earth
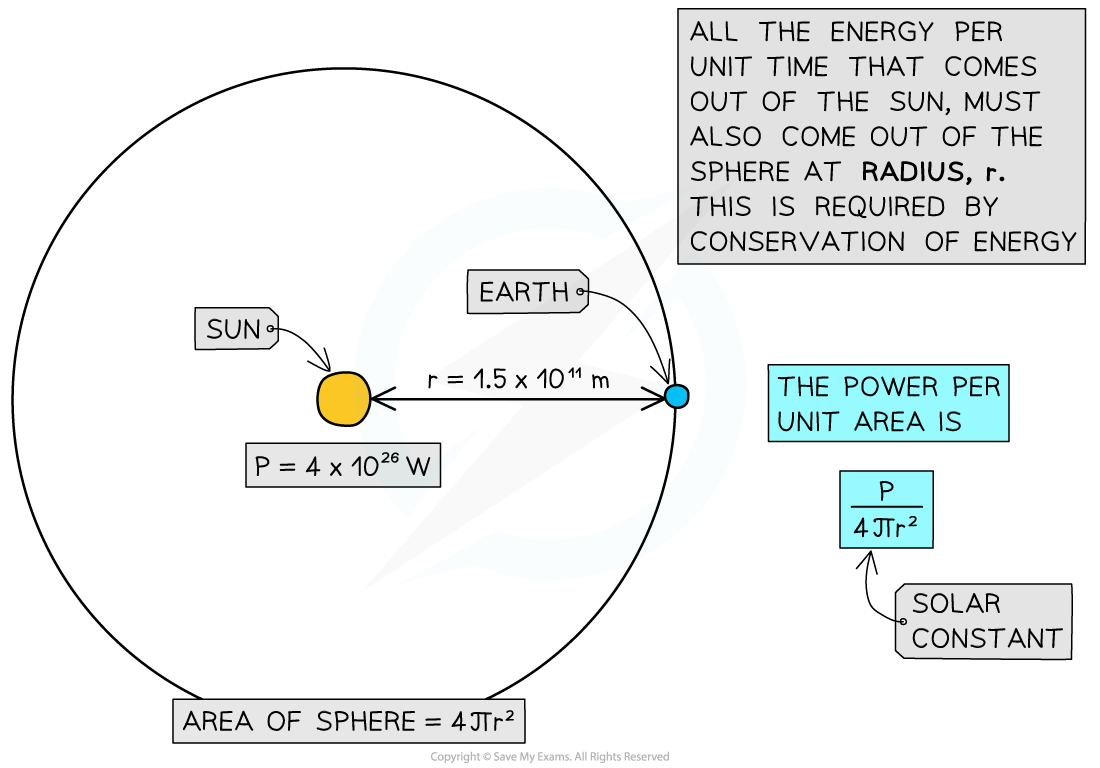
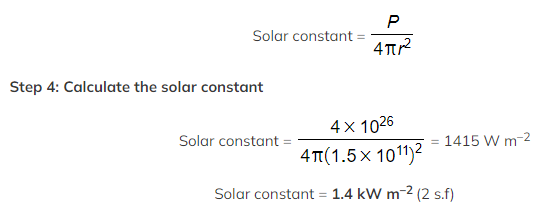
Step 3: Write an equation to calculate the solar constant
 Albedo & Emissivity
Albedo & Emissivity
Albedo
- Albedo, a, is defined as
The proportion of light that is reflected by a given surface
- It can be calculated using the equation
 More specifically, the albedo of a planet is defined as
More specifically, the albedo of a planet is defined as
The ratio between the total scattered, or reflected, radiation and the total incident radiation of that planet
- Earth’s albedo is generally taken to be 0.3, which means 30% of the Sun’s rays that reach the ground are reflected, or scattered, back into the atmosphere
- Earth’s albedo varies daily and depends on:
- Cloud formations and season – the thicker the cloud cover, the higher the degree of reflection
- Latitude
- Terrain – different materials reflect light to different degrees
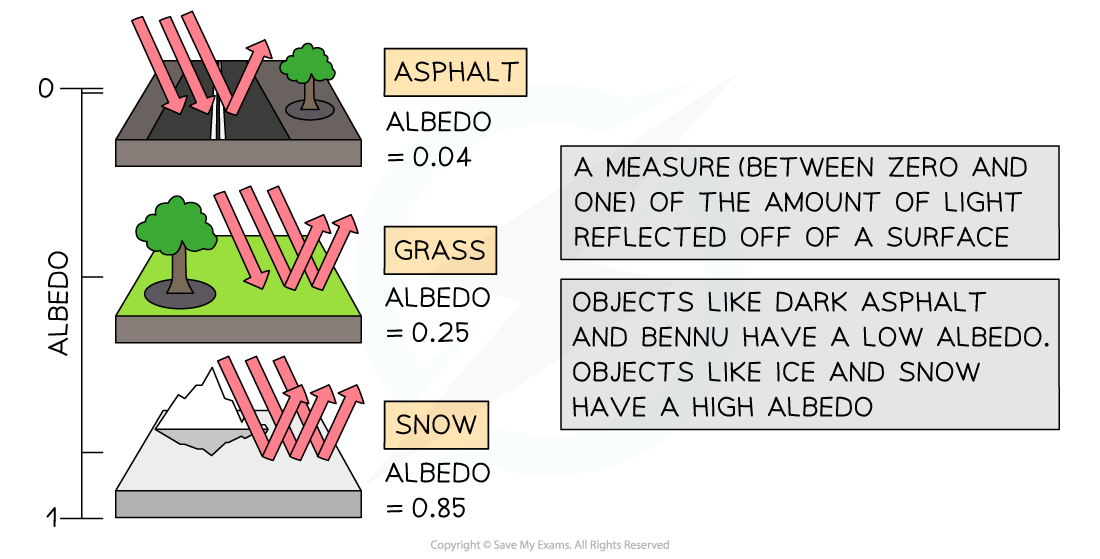
- It is useful to know the albedo of common materials:
- Fresh asphalt = 0.04
- Bare soil = 0.17
- Green grass = 0.25
- Desert sand = 0.40
- New concrete = 0.55
- Ocean ice = 0.50 - 0.70
- Fresh snow = 0.85
- Albedo has no units because it is a ratio (or fraction) of power
Emissivity
- Stars are good approximations to a black body, whereas planets are not
- This can be quantified using the emissivity
- Emissivity, e, is defined as
The power radiated by a surface divided by the power radiated from a black body of the same surface area and temperature
- It can be calculated using the equation
 Calculations of the emissivity assume that the black body:
Calculations of the emissivity assume that the black body:
- Is at the same temperature as the object
- Has the same dimensions as the object
- For a perfect black body, emissivity is equal to 1
- When using the Stefan-Boltzmann law for an object which is not a black body, the equation becomes:
P = eσAT4
- Where:
- P = total power emitted by the object (W)
- e = emissivity of the object
- σ = the Stefan-Boltzmann constant
- A = total surface area of the object black body (m2)
- T = absolute temperature of the body (K)
Worked Example Step 1: Define albedo
Step 1: Define albedo
-
- Albedo = the proportion of radiation that is reflected
- Therefore, the energy reflected by fresh snow = 0.85
-
- If 85% of the radiation is reflected, we can assume that 15% is absorbed
- Therefore, the energy absorbed by fresh snow = 1 – 0.85 = 0.15
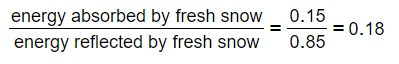
Exam Tip
You will be expected to remember that a perfect black body has an emissivity of 1 - this information is not included in the data booklet!
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








