- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: HL复习笔记3.1.6 Phase Change
Phase Change
- A phase change happens whenever matter changes its state
- During a phase change, thermal energy is transferred to or from a substance
- This energy transfer does not change the temperature of the substance undergoing the phase change
- This means:
- The thermal energy provided (or removed) does not affect the kinetic energy of the molecules within the substance
- Only the potential energy (i.e. the spacing between the atoms or molecules) is affected
- The four main phase changes are:
- Melting - i.e. when a substance changes from solid to liquid as it absorbs thermal energy
- Freezing - i.e. when a substance changes from liquid to solid as it releases thermal energy
- Vaporisation (or boiling) - i.e. when a substance changes from liquid to gas as it absorbs thermal energy
- Condensation - i.e. when a substance changes from gas to liquid as it releases thermal energy
Water
- Each substance has its own melting (or freezing) and boiling points
- For example, the freezing point of water is 0°C and its boiling point is 100°C
- Possible phase changes of water include:
- Solid ice melting into liquid water at 0°C
- Liquid water boiling and changing into gaseous water vapour at 100°C
- Both these changes happen when thermal energy is absorbed
- If thermal energy is released from water vapour at 100°C, it condenses back into water
- If water continues to release thermal energy, it cools down until it reaches 0°C and freezes into ice
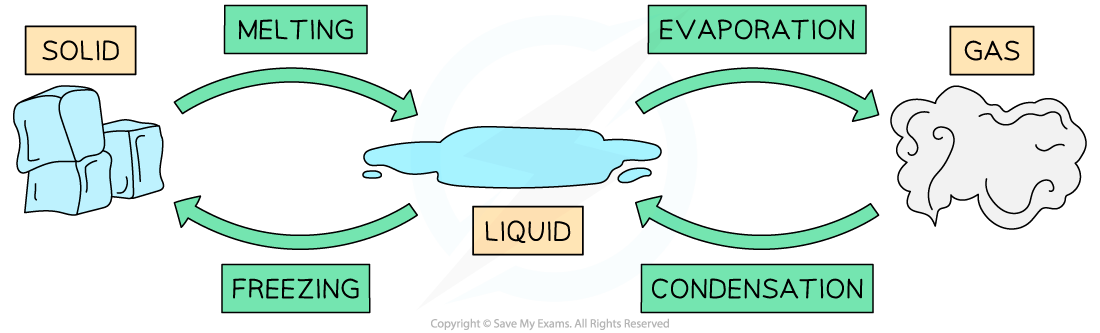 Phase changes for water
Phase changes for water
- Melting and freezing happen at the melting / freezing point of a substance
- Vaporisation and condensation happen at the boiling point of a substance
Phase Change Graphs
- A heating or cooling curve shows how the temperature of a substance changes with time
- The 'flat' sections of the graph indicate that there is no change in temperature over time, hence the substance is undergoing a phase change
- The thermal energy supplied to or removed from the substance only affects the potential energy of the particles
- The regions of the graph that are not flat indicate that the substance is being heated or cooled down
- The thermal energy supplied to or removed from the substance changes the average kinetic energy of the particles, hence resulting in an overall change in temperature of the substance
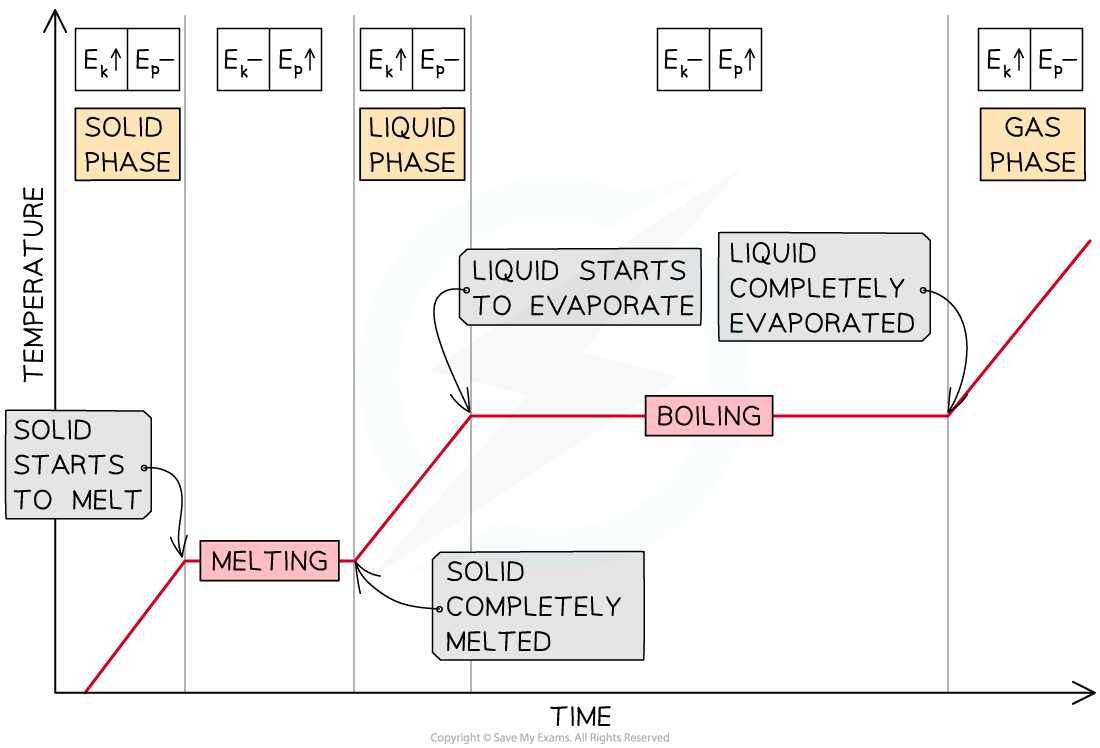
Heating Curves
- As energy is being supplied to a solid substance, its temperature increases until it reaches its melting point
- The temperature remains constant until the substance has melted completely
- If energy continues to be supplied, the liquid substance warms up until the boiling point is reached, and the substance vaporises
- Then, the temperature of the gas increases
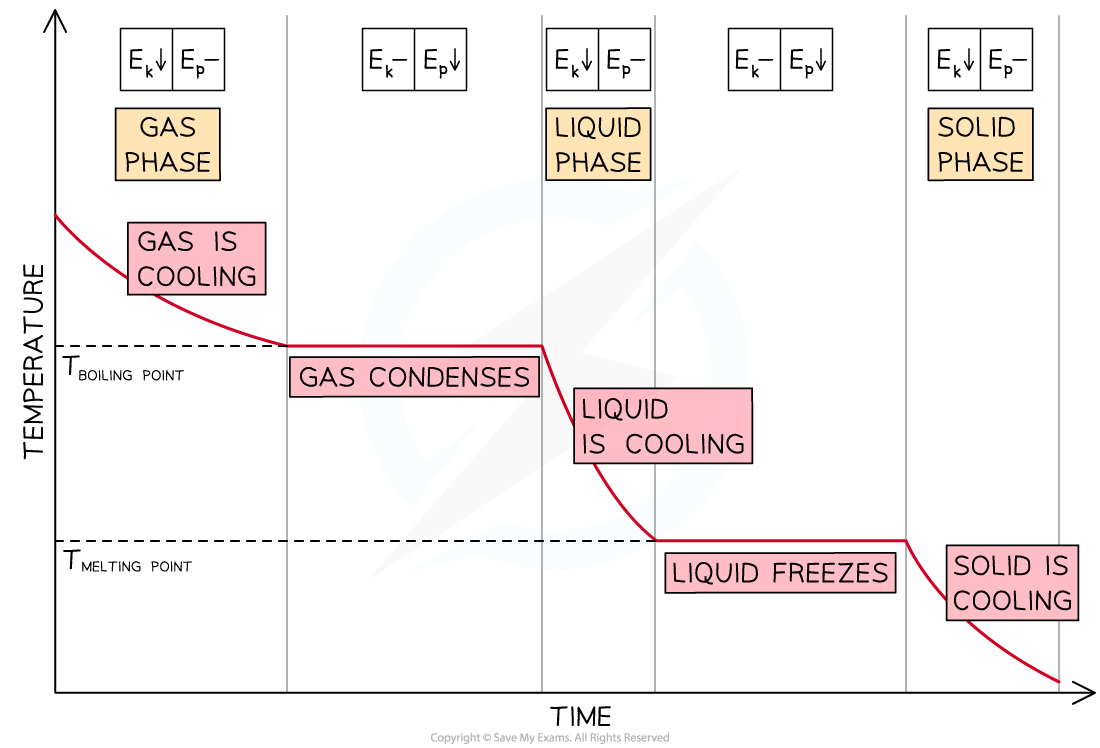
Cooling Curves
- As energy is being removed from a gaseous substance, its temperature decreases until the boiling point is reached
- The temperature remains constant until the substance has condensed completely
- If energy continues to be removed, the liquid substance cools down until its freezing point and changes into a solid
- Then, the temperature of the solid decreases
- Heating or cooling curves can also display how the temperature of a substance changes with energy
- In the following worked example, energy (in J) is plotted on the x-axis instead of time
Worked Example
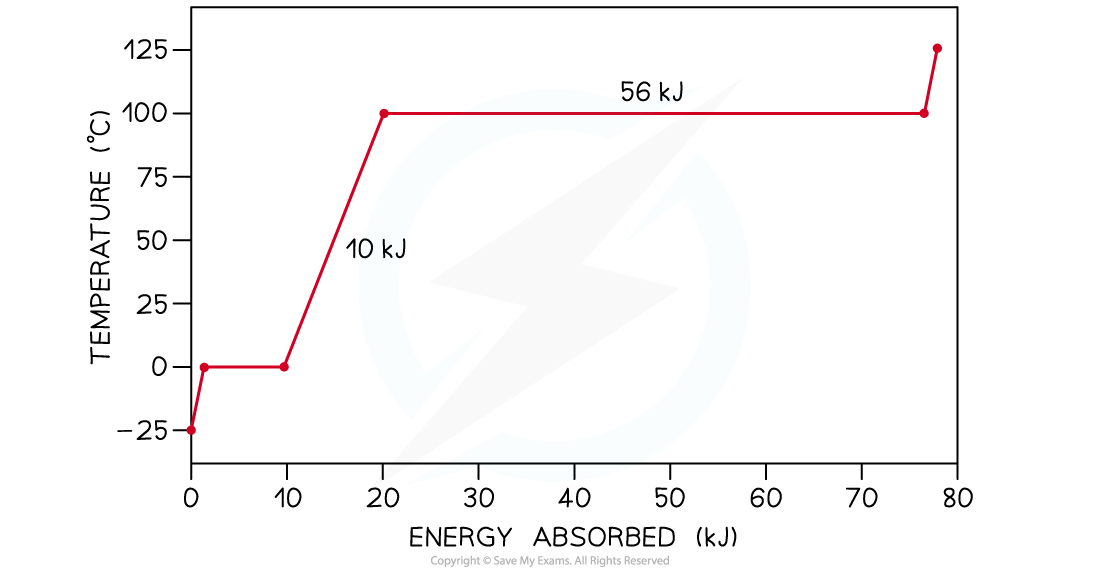
The graph below is the heating curve for a 25 g cube of ice being heated at a constant rate. Calculate:
- The specific heat capacity of water in its liquid phase
- The specific latent heat of vaporisation
Step 1: Write down the mass m of ice in kilograms (kg)
m = 25 g = 0.025 kg
Step 2: Read from the graph the amount of energy E1 being supplied to the water in its liquid phase as it warms up
-
- The first flat section of the graph indicates the change of phase of ice into water
- The non-flat region that follows is the one relating to water in its liquid phase being heated up
E1 = 20 kJ – 10 kJ = 10 kJ
Step 3: Convert this energy from kilojoules into joules
E1 = 10 kJ = 10000 J
Step 4: Read from the graph the change in temperature ΔT1 of the water as it warms up
ΔT1 = 100°C – 0°C = 100°C
Step 5: Write down the equation linking thermal energy E1 to mass m, specific heat capacity c and change in temperature ΔT1
E1 = mcΔT1
Step 6: Solve for the specific heat capacity c
![]()

c = 4000 J kg–1 °C–1
Step 7: Read from the graph the amount of energy E2 being supplied to the water as it changes into a gas at 100°C
-
- The second flat section of the graph indicates the change of phase of water into water vapour
- This energy must be converted from kilojoules (kJ) into joules (J)
E2= 56 kJ = 56000 J
Step 8: Write down the equation linking thermal energy E2 to mass m and specific latent heat of vaporisation Lv
E2 = mLv
Step 9: Solve for the specific latent heat of fusion Lv
![]()
![]()
Lv = 2.2 × 106 J kg–1
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









