- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: HL复习笔记20.3.3 Optical Isomers
Optical Isomers
Optical isomers
- A carbon atom that has four different atoms or groups of atoms attached to it is called a chiral carbon or chiral centre
- Chira comes from a Greek word meaning hand, so we talk about these molecules having a handedness
- The carbon atom is described as being asymmetric, i.e. there is no plane of symmetry in the molecule
- Compounds with one chiral centre (chiral molecules) exist as two optical isomers, also known as enantiomers
- Just like the left hand cannot be superimposed on the right hand, enantiomers are non-superimposable
- Enantiomers are mirror images of each other
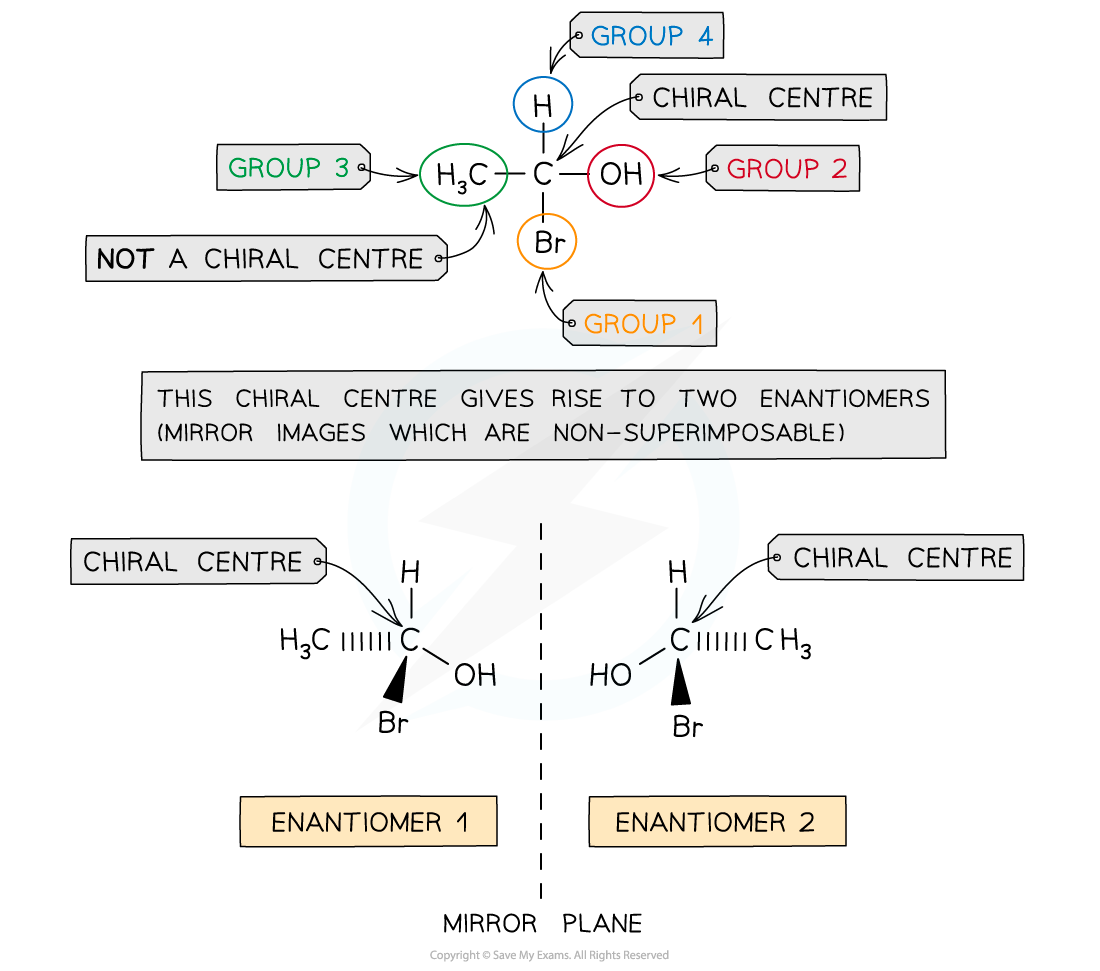
A molecule has a chiral centre when the carbon atom is bonded to four different atoms or group of atoms; this gives rises to enantiomers
Exam Tip
When drawing optical isomers, always draw mirror images including wedge and dashed bonds 

Diastereomers
- Diastereomers are compounds that contain more than one chiral centre
- Diastereomers are not mirror images of each other because each chiral carbon has two isomers
- This also means that they have different physical and chemical properties
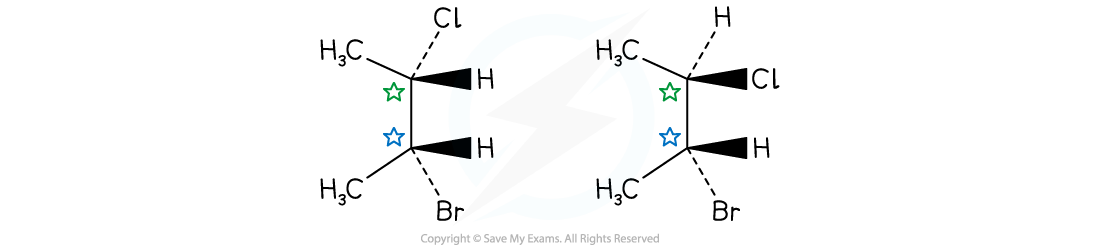
2-bromo-3-chlorobutane exists as a diastereomer due to 2 chiral centres
Polarimetry
Properties of optical isomers
- The chemical properties of optical isomers are generally identical, with one exception
- Optical isomers interact with biological sensors in different ways
- For example, one enantiomer of carvone smells of spearmint, while the other smells of caraway

- For example, one enantiomer of carvone smells of spearmint, while the other smells of caraway
- Optical isomers interact with biological sensors in different ways
Carvone optical isomers have distinctive smells
- Optical isomers have identical physical properties, with one exception
- Isomers differ in their ability to rotate the plane of polarised light
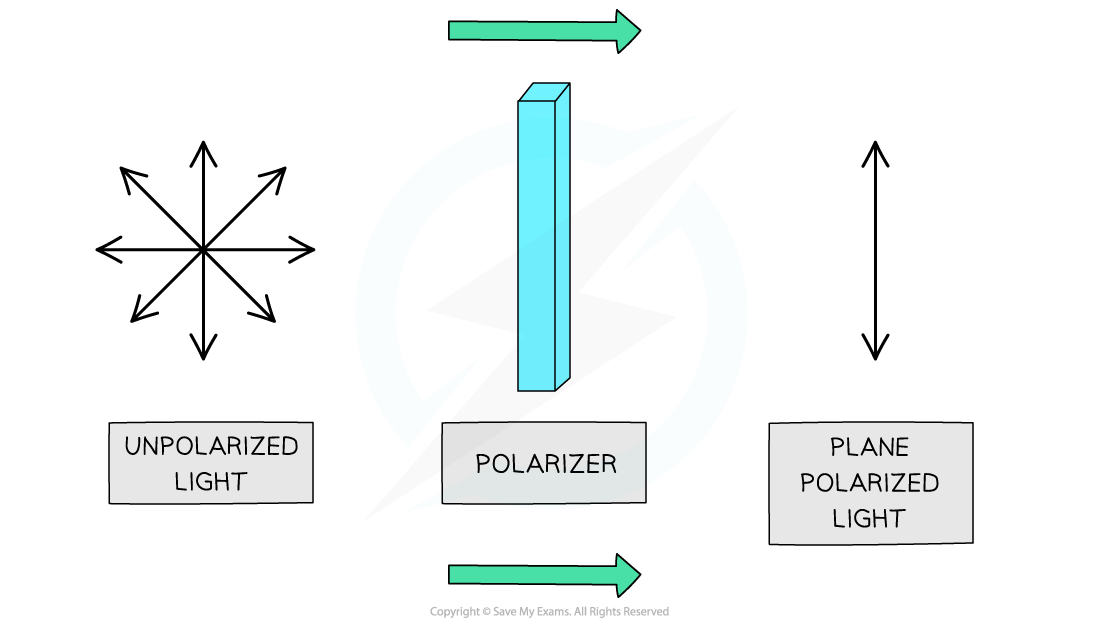
When unpolarised light is passed through a polariser, the light becomes polarised as the waves will vibrate in one plane only
- The major difference between the two enantiomers is:
- One enantiomer rotates plane polarised light in a clockwise manner and the other in an anticlockwise fashion
- A common way to differentiate the isomers is to use (+) and (-), but there are other systems using d and l, D and L, or R and S
- The rotation of plane polarised light can be used to determine the identity of an optical isomer of a single substance
- For example, pass plane polarised light through a sample containing one of the two optical isomers of a single substance
- Depending on which isomer the sample contains, the plane of polarised light will be rotated either clockwise or anti-clockwise by a fixed number of degrees
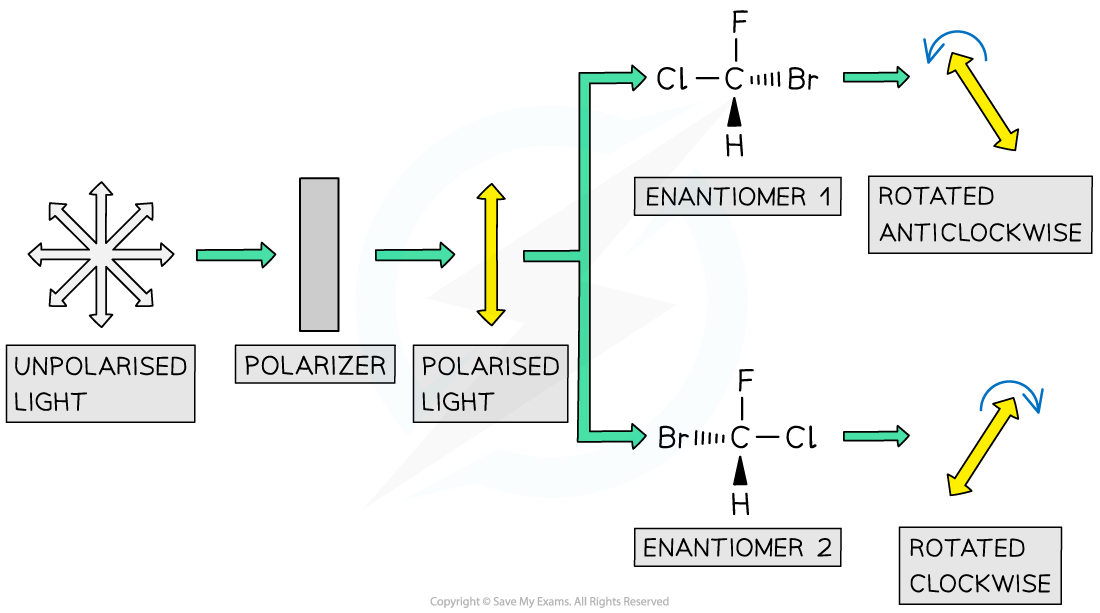
Each enantiomer rotates the plane of polarised light in a different direction
Racemic Mixtures
- A racemic mixture (or racemate) is a mixture containing equal amounts of each enantiomer
- One enantiomer rotates light clockwise, the other rotates light anticlockwise
- A racemic mixture is optically inactive as the enantiomers will cancel out each others effect
- This means that the plane of polarised light will not change
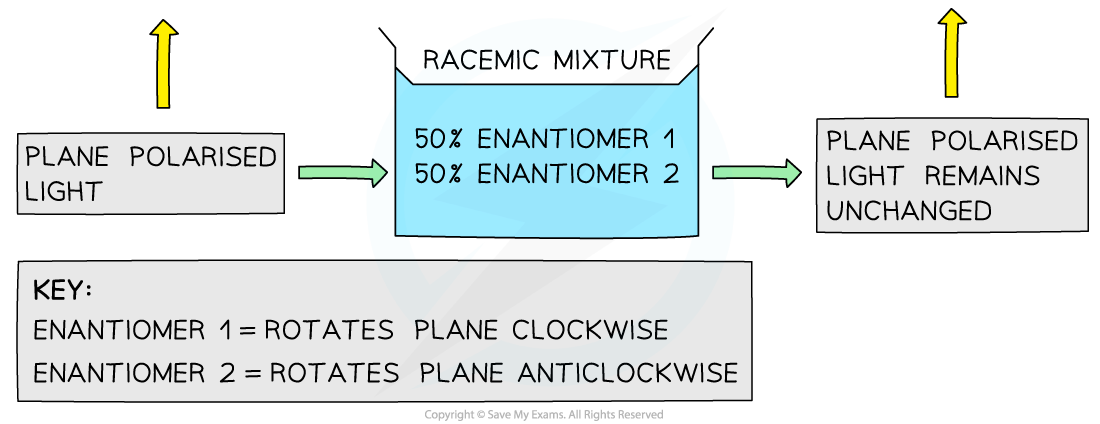
- This means that the plane of polarised light will not change
Racemic mixtures are optically inactive
Racemic mixtures and drugs
- In the pharmaceutical industry, it is much easier to produce synthetic drugs that are racemic mixtures than producing one enantiomer of the drug
- Around 56% of all drugs in use are chiral and of those 88% are sold as racemic mixtures
- Separating the enantiomers gives a compound that is described as enantiopure, it contains only one enantiomer
- This separation process is very expensive and time consuming, so for many drugs it is not worthwhile, even though only half the of the drug is pharmacologically active
- For example, the pain reliever ibuprofen is sold as a racemic mixture
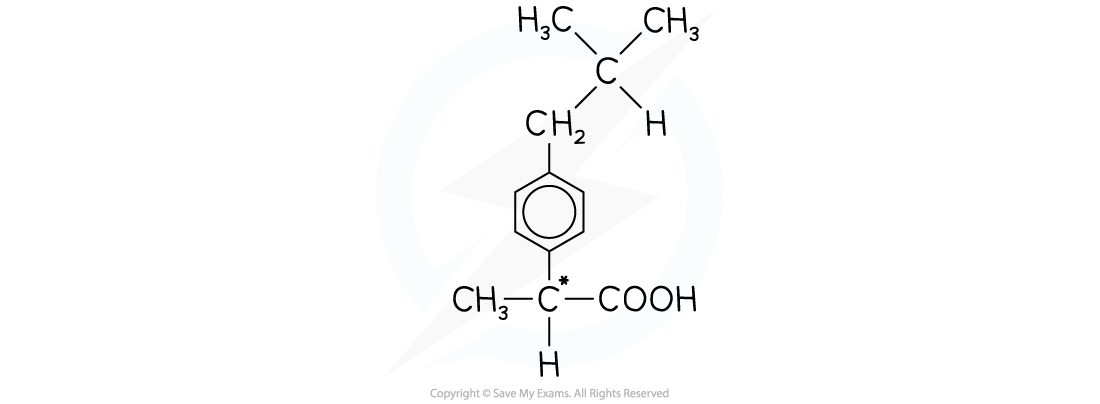
The structure of ibuprofen showing the chiral carbon that is responsible for the racemic mixture produced in the synthesis of the drug
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









