- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: HL复习笔记20.1.1 Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
- In nucleophilic substitution reactions involving halogenoalkanes, the halogen atom is replaced by a nucleophile
- The strength of any nucleophile depends on its ability to make its lone pair of electrons available for reaction
- The hydroxide ion, OH-, is a stronger nucleophile than water because it has a full negative charge
- This means that it has a readily available lone pair of electrons
- A water molecule only has partial charges, δ+ and δ-
- This means that its lone pair of electrons is less available than the hydroxide ions
- The lone pairs of electrons in a water molecule are still available to react

Lewis structures of the hydroxide ion and water molecule - illustrating the lone pairs of electrons and charges within their structures
Exam Tip
In general:
- A negatively charged ion will be a stronger nucleophile than a neutral molecule
- A conjugate base will be a stronger nucleophile than its corresponding conjugate acid
- e.g. the hydroxide ion is a stronger nucleophile than water
SN1 Mechanism
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions can occur in two different ways (known as SN2 and SN1 reactions) depending on the structure of the halogenoalkane involved
SN1 reactions
- In tertiary halogenoalkanes, the carbon that is attached to the halogen is also bonded to three alkyl groups
- These halogenoalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution by an SN1 mechanism
- ‘S’ stands for ‘substitution’
- ‘N’ stands for ‘nucleophilic’
- ‘1’ means that the rate of the reaction (which is determined by the slowest step of the reaction) depends on the concentration of only one reagent, the halogenoalkane

- The SN1 mechanism is a two-step reaction
- In the first step, the C-X bond breaks heterolytically and the halogen leaves the halogenoalkane as an X- ion (this is the slow and rate-determining step)
- As the rate-determining step only depends on the concentration of the halogenoalkane, the rate equation for an SN1 reaction is rate = k[halogenoalkane]
- In terms of molecularity, an SN1 reaction is unimolecular
- This forms a tertiary carbocation (which is a tertiary carbon atom with a positive charge)
- In the second step, the tertiary carbocation is attacked by the nucleophile
- For example, the nucleophilic substitution of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane by hydroxide ions to form 2-methyl-2-propanol
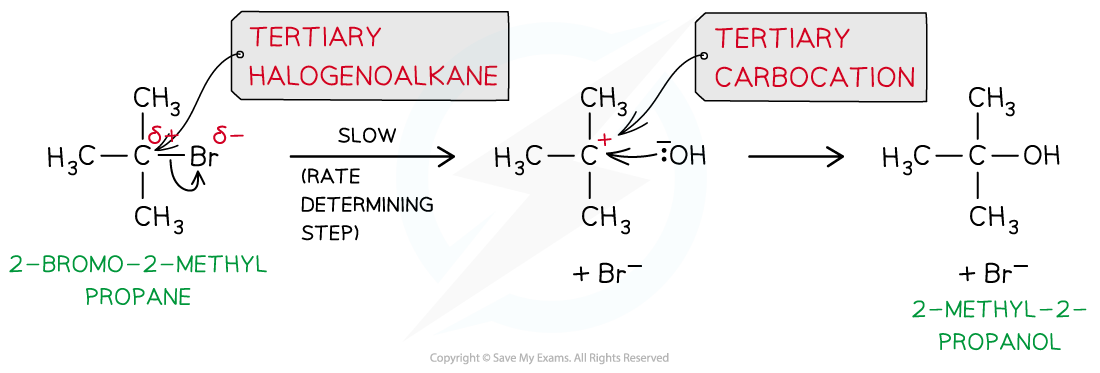
The mechanism of nucleophilic substitution in 2-bromo-2-methylpropane which is a tertiary halogenoalkane
Exam Tip
You are expected to know the difference between the heterolytic fission that features in SN1 reactions and homolytic fission in other reactions:
- Heterolytic fission forms anions and cations and uses double headed arrows to show the movement of both electrons from the covalent bond
- Homolytic fission forms free radicals and uses single headed arrows, sometimes called fish hooks, to show the movement of a single electron as the covalent bond breaks
SN2 Mechanism
SN2 reactions
- In primary halogenoalkanes, the carbon that is attached to the halogen is bonded to one alkyl group
- These halogenoalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution by an SN2 mechanism
- ‘S’ stands for ‘substitution’
- ‘N’ stands for ‘nucleophilic’
- ‘2’ means that the rate of the reaction (which is determined by the slowest step of the reaction) depends on the concentration of both the halogenoalkane and the nucleophile ions

- The SN2 mechanism is a one-step reaction
- The nucleophile donates a pair of electrons to the δ+ carbon atom of the halogenoalkane to form a new bond
- As this is a one-step reaction, the rate-determining step depends on the concentrations of the halogenoalkane and nucleophile, the rate equation for an SN2 reaction is rate = k[halogenoalkane][nucleophile]
- In terms of molecularity, an SN2 reaction is bimolecular
- At the same time, the C-X bond is breaking and the halogen (X) takes both electrons in the bond (heterolytic fission)
- The halogen leaves the halogenoalkane as an X- ion
- The nucleophile donates a pair of electrons to the δ+ carbon atom of the halogenoalkane to form a new bond
- For example, the nucleophilic substitution of bromoethane by hydroxide ions to form ethanol
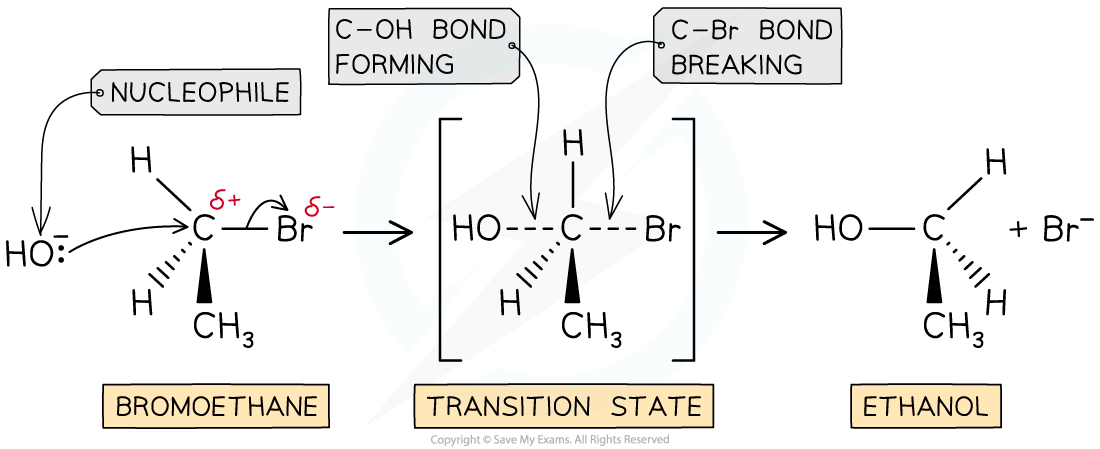
The SN2 mechanism of bromoethane with hydroxide causing an inversion of configuration
- The bromine atom of the bromoethane molecule causes steric hindrance
- This means that the hydroxide ion nucleophile can only attack from the opposite side of the C-Br bond
- Attack from the same side as the bromine atom is sometimes called frontal attack
- While attack from the opposite side is sometimes called backside or rear-side attack
- As the C-OH bond forms, the C-Br bond breaks causing the bromine atom to leave as a bromide ion
- As a result of this, the molecule has undergone an inversion of configuration
- The common comparison for this is an umbrella turning inside out in the wind

Inversion of configuration - umbrella analogy
Exam Tip
If you are asked to explain reaction mechanisms where there is an inversion of configuration, you will be expected to:
- Use partial charges, δ+ and δ-, to help explain why the nucleophile attacks and the halogen leaves
- Use dotted, wedge and tapered bonds to show the change in configuration of the atoms / functional groups around the carbon that is being attacked
- Draw the transition state with the nucleophile attached to the carbon with a dotted bond and the halogen still attached to the carbon, also, with a dotted bond
- Be aware that the compound you draw is a transition state and not an intermediate
Factors Affecting Nucleophilic Substitution
Factors affecting nucleophilic substitution
- Various factors affect the rate of nucleophilic substitution, regardless of SN1 or SN2, involving a halogenoalkane:
- The nature of the nucleophile
- The halogen involved (leaving group)
- The structure (class) of the halogenoalkane
- Protic & aprotic solvents
1. The nature of the nucleophile
- The most effective nucleophiles are neutral or negatively charged species that have a lone pair of electrons available to donate to the δ+ carbon in the halogenoalkane
- The greater the electron density on the nucleophile ion or molecule; the stronger the nucleophile
- Consequently, negative anions tend to be more reactive than their corresponding neutral species, e.g. hydroxide ions and water molecules (as previously discussed)
- When nucleophiles have the same charge, the electronegativity of the atom carrying the lone pair becomes the deciding factor
- The less electronegative the atom carrying the lone pair; the stronger the nucleophile
- For example:
- Ammonia is a stronger electrophile than water because the nitrogen atom in ammonia is less electronegative than the oxygen atom in water
- This is because a less electronegative atom has a weaker grip on its lone pair of electrons, which means that they are more available for reaction
- The effectiveness of nucleophiles is as follows:
Strongest CN- > OH- > NH3 > H2O Weakest
2. The halogen involved (leaving group)
- The halogenoalkanes have different rates of substitution reactions
- Since substitution reactions involve breaking the carbon-halogen bond, the bond energies can be used to explain their different reactivities
Approximate Halogenoalkane Bond Energy Table

- The table above shows that the C-I bond requires the least energy to break, and is therefore the weakest carbon-halogen bond
- During substitution reactions, the C-I bond will breaks heterolytically as follows:
R3C-I + OH- → R3C-OH + I-
- The C-F bond, on the other hand, requires the most energy to break and is, therefore, the strongest carbon-halogen bond
- Fluoroalkanes will therefore be less likely to undergo substitution reactions
- This idea can be confirmed by reacting the product formed by nucleophilic substitution of the halogenoalkane with aqueous silver nitrate solution
- As a halide ion is released, this results in the formation of a precipitate
- The rate of formation of these precipitates can also be used to determine the reactivity of the halogenoalkanes
Halogenoalkane Precipitates Table
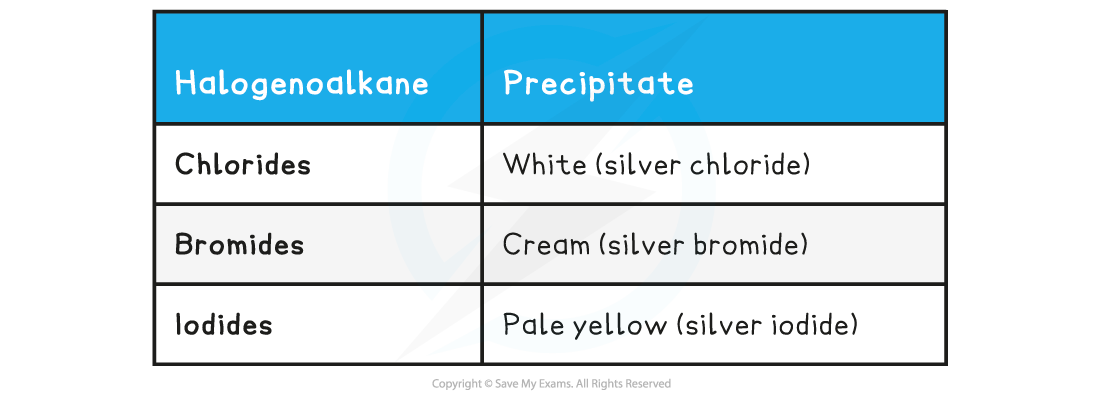
- The formation of the pale yellow silver iodide is the fastest (fastest nucleophilic substitution reaction) whereas the formation of the silver fluoride is the slowest (slowest nucleophilic substitution reaction)
- This confirms that fluoroalkanes are the least reactive and iodoalkanes are the most reactive halogenoalkanes
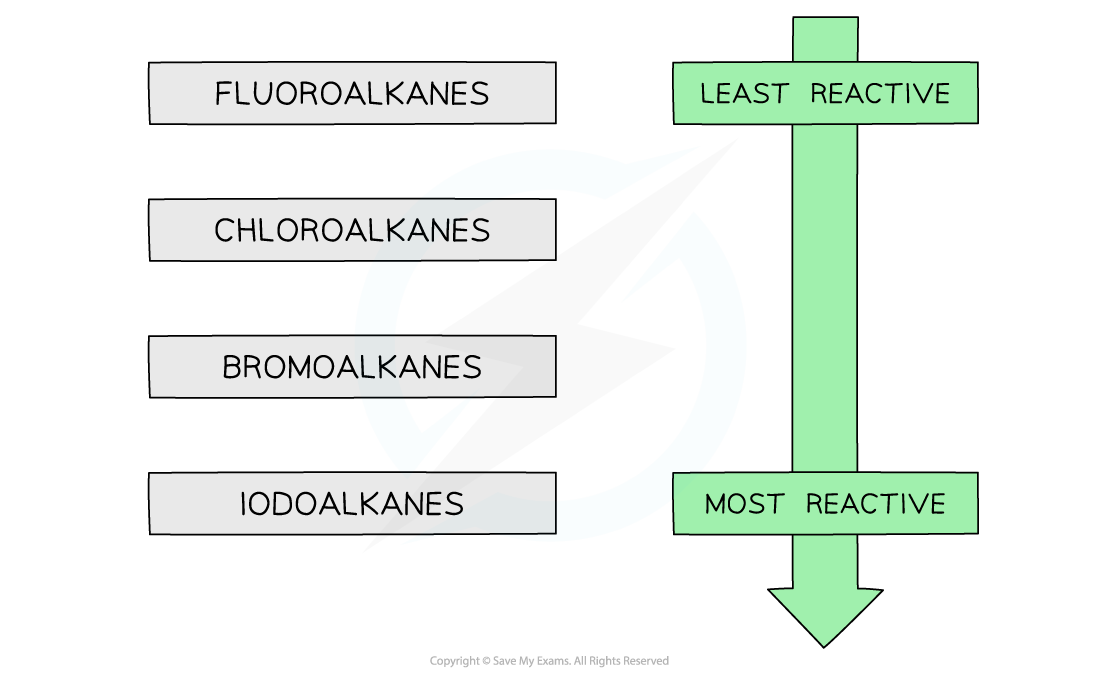
The trend in reactivity of halogenoalkanes
3. The structure (class) of the halogenoalkane
- Tertiary halogenoalkanes undergo SN1 reactions, forming stable tertiary carbocations
- Secondary halogenoalkanes undergo a mixture of both SN1 and SN2 reactions depending on their structure
- Primary halogenoalkanes undergo SN2 reactions, forming the less stable primary carbocations
- This has to do with the positive inductive effect of the alkyl groups attached to the carbon which is bonded to the halogen atom
- The alkyl groups push electron density towards the positively charged carbon, reducing the charge density
- In tertiary carbocations, there are three alkyl groups stabilising the carbocation
- In primary carbocations, there is only one alkyl group
- This is why tertiary carbocations are much more stable than primary ones
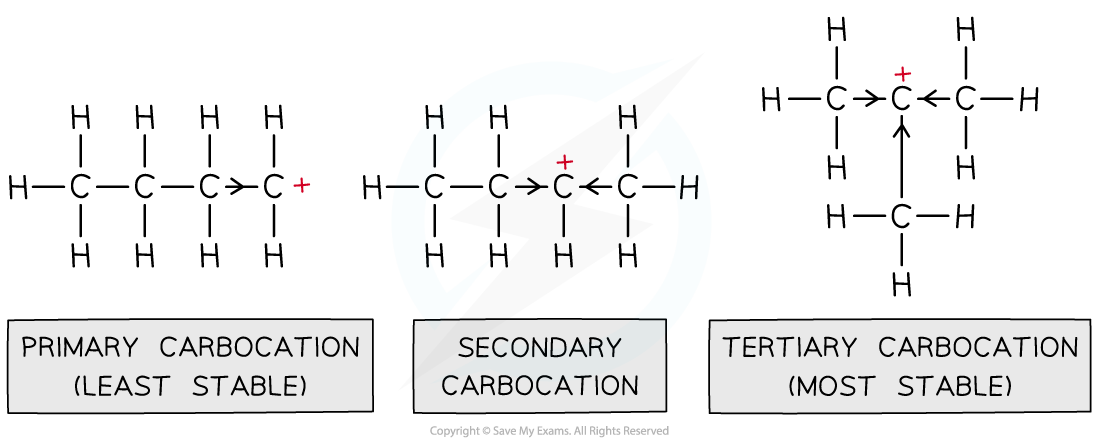
The diagram shows the trend in stability of primary, secondary and tertiary carbocations
- Overall, the structure (class) has a direct effect on the formation of the carbocation and, therefore, the rate-determining step
- Consequently, this affects the overall rate of the nucleophilic substitution reaction
Protic & Aprotic Solvents
4. Protic & Aprotic Solvents
Hydrogen bonding
- Protic, polar solvents contain a hydrogen atom bonded to a very electronegative nitrogen or oxygen atom
- This means that they are capable of hydrogen bonding
- Examples of protic solvents include ammonia, carboxylic acids, ethanol and water
- Aprotic, polar solvents contain hydrogen atoms but they are not bonded to an electronegative atom
- This means that they cannot participate in hydrogen bonding
- Examples of aprotic solvents include ethanenitrile, ethyl ethanoate and propanone
Solvation
- Solvation is where solvent molecules surround a dissolved ion
- In SN1 reactions, the rate-determining step is not the attack of the nucleophile
- The rate-determining step is the formation of the carbocation intermediates and halide ion
- Both ions could be stabilised by the use of a protic solvent, as shown in the following example:
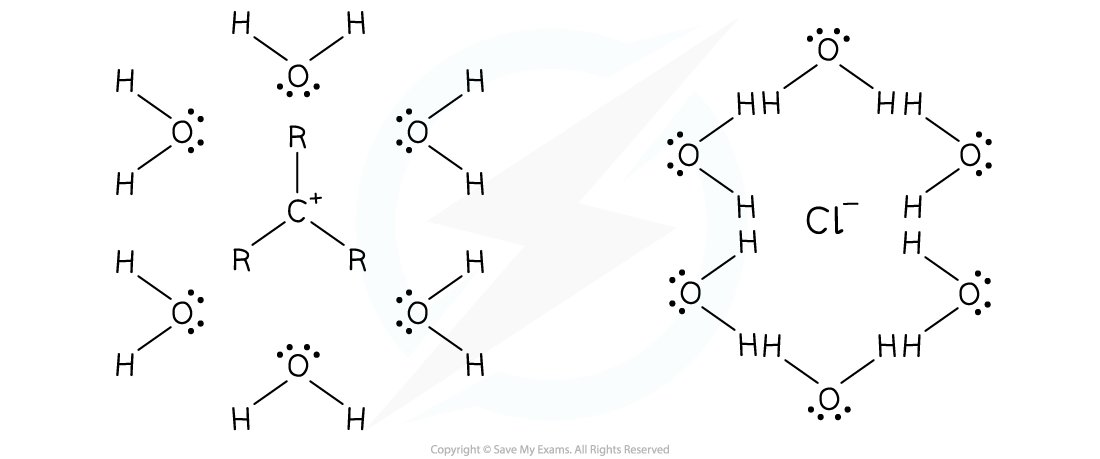
Protic polar solvent stabilising carbocation intermediates and halide ions
-
- In SN2 reactions, the rate-determining step is the attack of the nucleophile
- The use of aprotic solvents does not solvate the nucleophile
- This means that the nucleophile is more able to react and form the transition state
- SN1 reactions are best conducted using protic, polar solvents
- SN2 reactions are best conducted using aprotic, non-polar solvents
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








