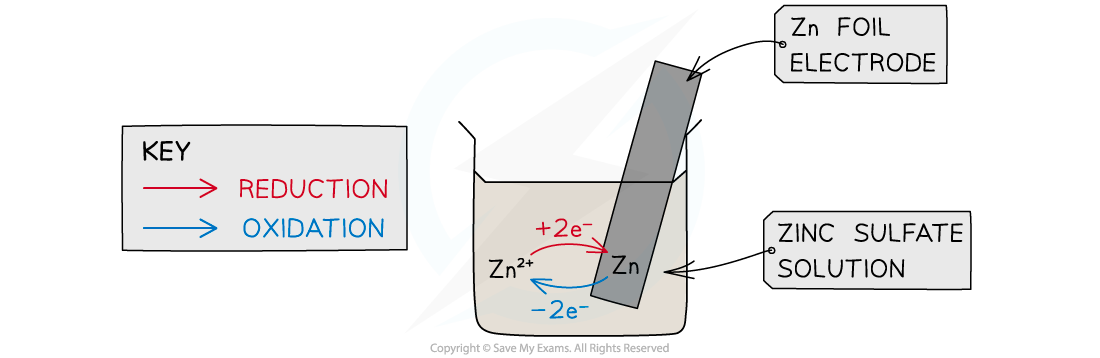
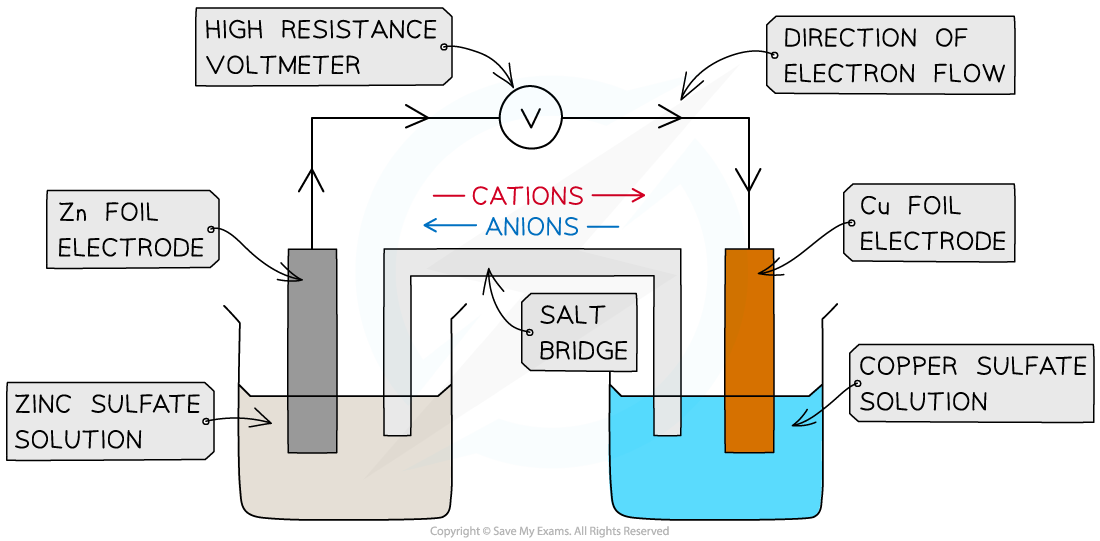
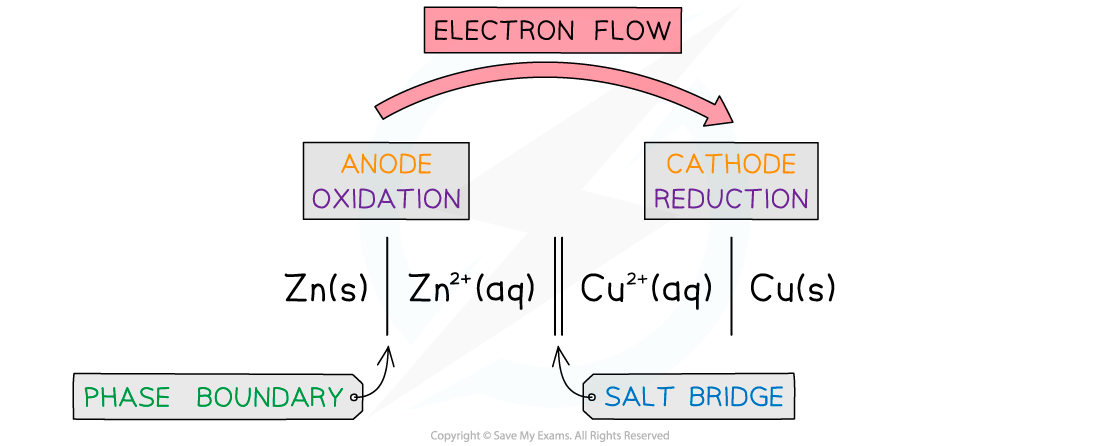
- This is a half cell and the strip of metal is an electrode
- The position of the equilibrium determines the potential difference between the metal strip and the solution of metal
- The Zn atoms on the rod can deposit two electrons on the rod and move into solution as Zn2+ ions:
Zn(s) ⇌ Zn2+(aq) + 2e–
-
- This process would result in an accumulation of negative charge on the zinc rod
- Alternatively, the Zn2+ ions in solution could accept two electrons from the rod and move onto the rod to become Zn atoms:
Zn2+(aq) + 2e– ⇌ Zn(s)
-
- This process would result in an accumulation of positive charge on the zinc rod
- In both cases, a potential difference is set up between the rod and the solution
- This is known as an electrode potential
- A similar electrode potential is set up if a copper rod is immersed in a solution containing copper ions (eg CuSO4), due to the following processes: