- A buffer solution is a solution which resists changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added
- A buffer solution is used to keep the pH almost constant
- A buffer can consist of weak acid – conjugate base or weak base – conjugate acid
- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: HL复习笔记18.1.4 Buffers
Buffers
Ethanoic acid & sodium ethanoate as a buffer
- A common buffer solution is an aqueous mixture of ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate
- Ethanoic acid is a weak acid and partially ionises in solution to form a relatively low concentration of ethanoate ions
CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq)
ethanoic acid ⇌ ethanoate
high conc ⇌ low conc
- Sodium ethanoate is a salt which fully ionises in solution
CH3COONa + aq → Na+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq)
sodium ethanoate → ethanoate ion
low conc. → high conc.
- There are reserve supplies of the acid (CH3COOH) and its conjugate base (CH3COO–)
- The buffer solution contains relatively high concentrations of CH3COOH (due to the partial ionisation of ethanoic acid) and CH3COO– (due to the full ionisation of sodium ethanoate)
- In the buffer solution, the ethanoic acid is in equilibrium with hydrogen and ethanoate ions
CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq)
high conc. high conc.
- The equilibrium position shifts to the left as H+ ions react with CH3COO– ions to form more CH3COOH until equilibrium is re-established
- As there is a large reserve supply of CH3COO–, the concentration of CH3COO– in solution doesn’t change much as it reacts with the added H+ ions
- As there is a large reserve supply of CH3COOH, the concentration of CH3COOH in solution doesn’t change much as CH3COOH is formed from the reaction of CH3COO– with H+
- As a result, the pH remains reasonably constant

When hydrogen ions are added to the solution the pH of the solution would decrease. However, the ethanoate ions in the buffer solution react with the hydrogen ions to prevent this and keep the pH constant
- The OH– reacts with H+ to form water
OH– (aq) + H+ (aq) → H2O (l)
- The H+ concentration decreases
- The equilibrium position shifts to the right and more CH3COOH molecules ionise to form more H+ and CH3COO– until equilibrium is re-established
CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + CH3COO– (aq)
- As there is a large reserve supply of CH3COOH, the concentration of CH3COOH in solution doesn’t change much when CH3COOH dissociates to form more H+ ions
- As there is a large reserve supply of CH3COO–, the concentration of CH3COO– in solution doesn’t change much
- As a result, the pH remains reasonably constant

When hydroxide ions are added to the solution, the hydrogen ions react with them to form water; The decrease in hydrogen ions would mean that the pH would increase however the equilibrium moves to the right to replace the removed hydrogen ions and keep the pH constant
Exam Tip
Remember that buffer solutions cannot cope with excessive addition of acids or alkalis as their pH will change significantly.The pH will only remain relatively constant if small amounts of acids or alkalis are added.
The Buffer Region
- These are seen on a pH curve and represent the region where small additions in acid or base result in little change in the overall pH of the solution
- For a weak acid - strong base titration between sodium hydroxide, NaOH (aq) , and ethanoic acid, CH3COOH (aq)
NaOH (aq) + CH3COOH (aq) → CH3COONa (aq) + H2O (l)
- The initial rise in pH is steep as the neutralisation of the weak acid by the strong base is rapid
- Sodium ethanoate is then formed which creates a buffer that will resist changes in pH so the pH rises gradually
- A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate salt
- This section of the curve is known as the buffer region
- Only small increases in pH are seen when the strong base is added in this part of the titration curve
- At this point, the acid is in equilibrium with the salt ion
- CH3COOH (aq) + H2O (l) ⇌ CH3COO- + H3O+ (aq)
- Continuing to add the strong base will 'use up' all of the acid so the forward reaction will then be favoured
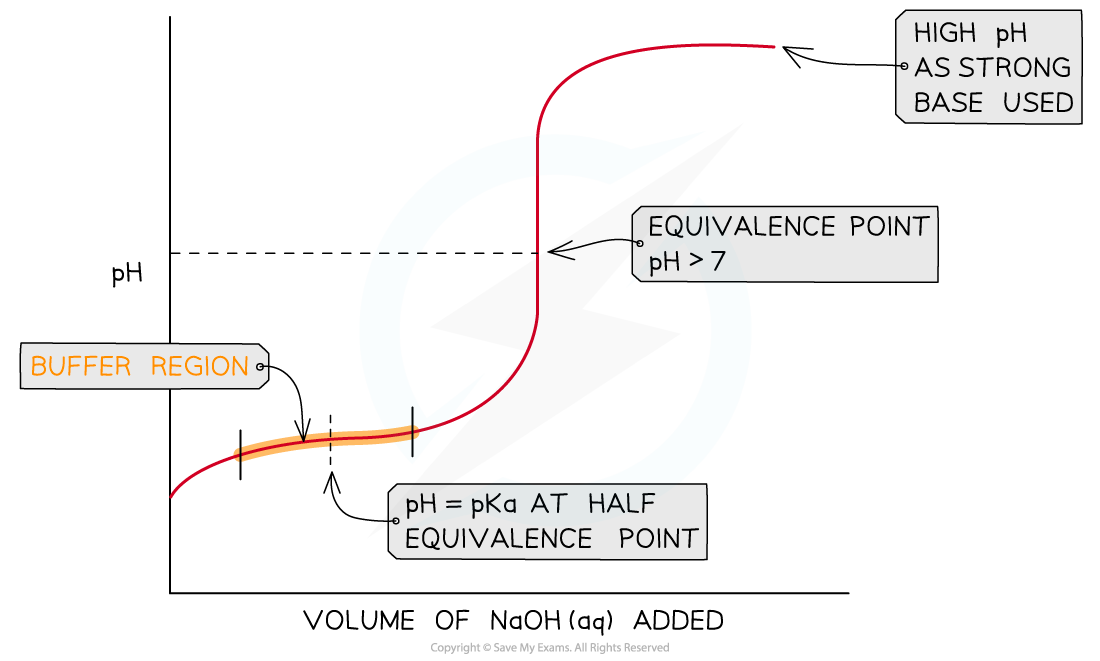
Buffer region shown is a weak acid - strong base titration curve
- A buffer region is also observed during a weak base - strong acid titration
- Ammonia, NH3 (aq), and hydrochloric acid, HCl (aq), is a common example
NH3 (aq) + HCl (aq) → NH4Cl (aq)
- The starting pH of the weak base will fall as it begins to be neutralised and the conjugate acid, NH4+ (aq), will be produced
- This results in a buffer that resists change in pH
- Due to this, the pH will only fall gradually
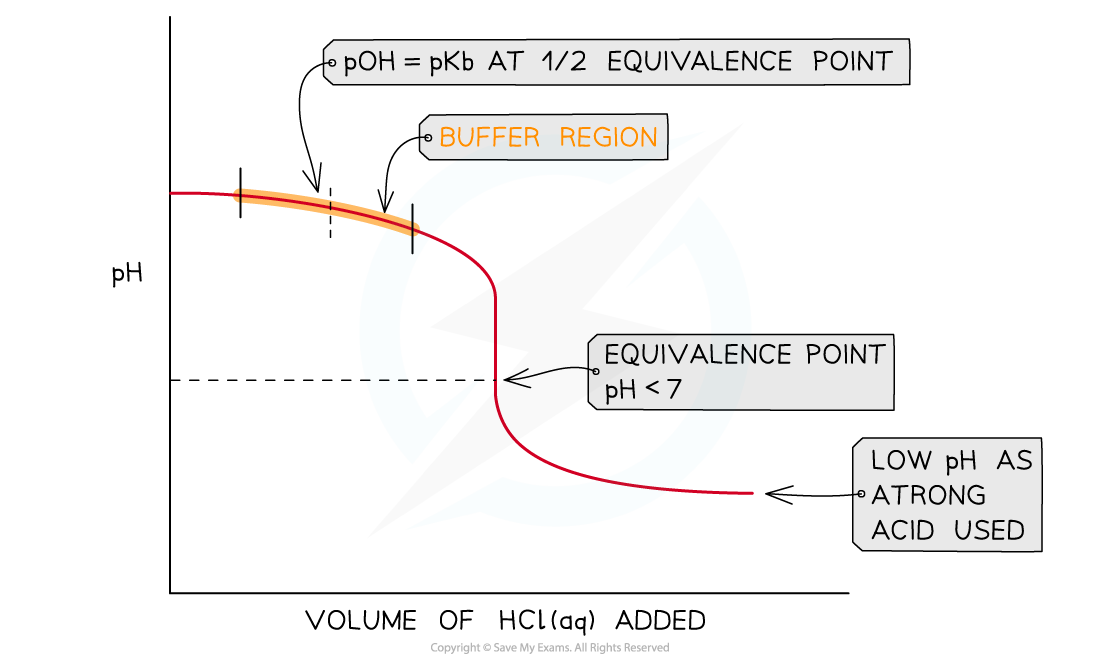
Buffer region shown is a weak base - strong acid titration curve
转载自ssavemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









