- The following general reaction will be used as an example to study the rate of reaction
D (aq) → E (aq) + F (g)
- The rate of reaction at different concentrations of D is measured and tabulated
D (aq) → E (aq) + F (g)
Rate of reactions table
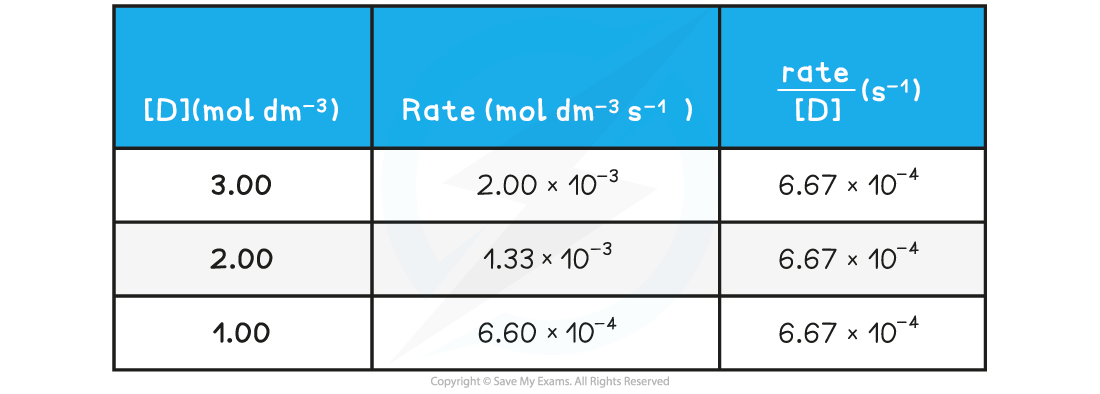
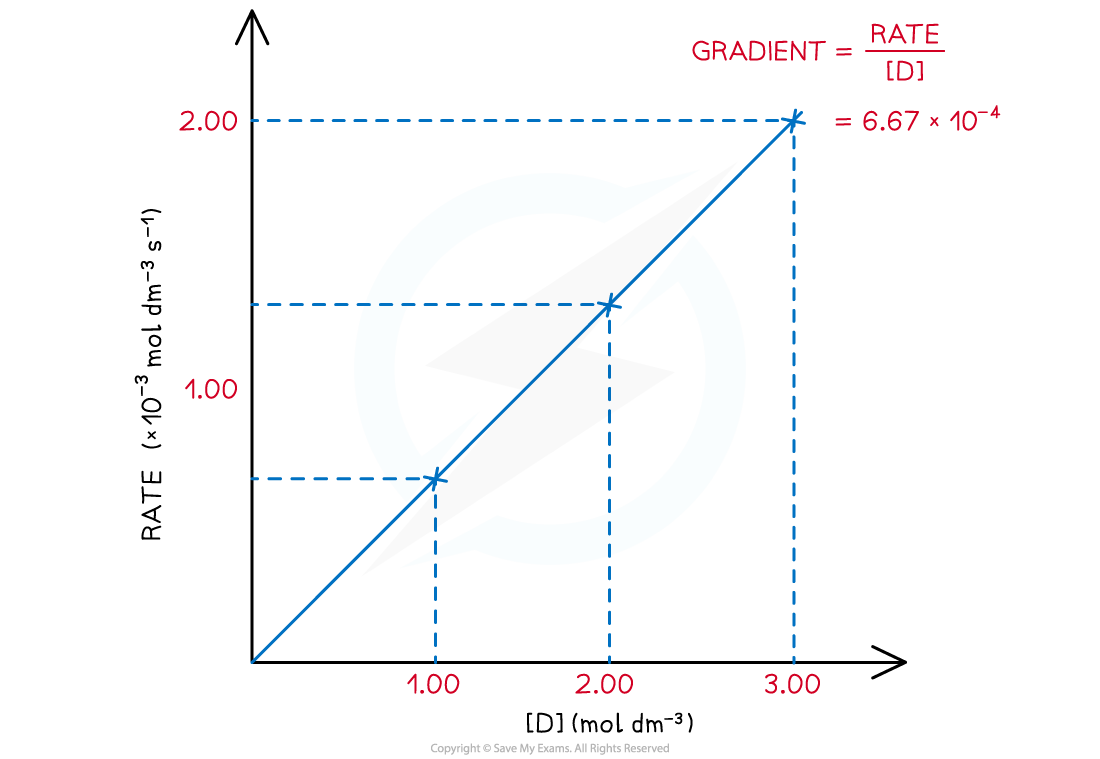
Rate of reaction over various concentrations of D
Rate ∝ [D] or Rate = k[D]
A (aq) + B (aq) → C (aq) + D (g)
Rate of reaction = k [A]m [B]n
The chemical equation for the thermal decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide is:
2N2O5 (g) → 4NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
The rate equation for this reaction is:
Rate = k[N2O5 (g)]
Answers
Answer 1:
Answer 2:
The following equation represents the oxidation of bromide ions in acidic solution
BrO3- (aq) + 5Br- (aq) + 6H+ (aq) → 3Br2 (l) + 3H2O (l)
The rate equation for this reaction is:
Rate = k[BrO3- (aq)][Br- (aq)][H+ (aq)]
Answers
Answer 1:
Answer 2:
(CH3)3CBr + OH- → (CH3)3COH + Br-
Table to show the experimental data of the above reaction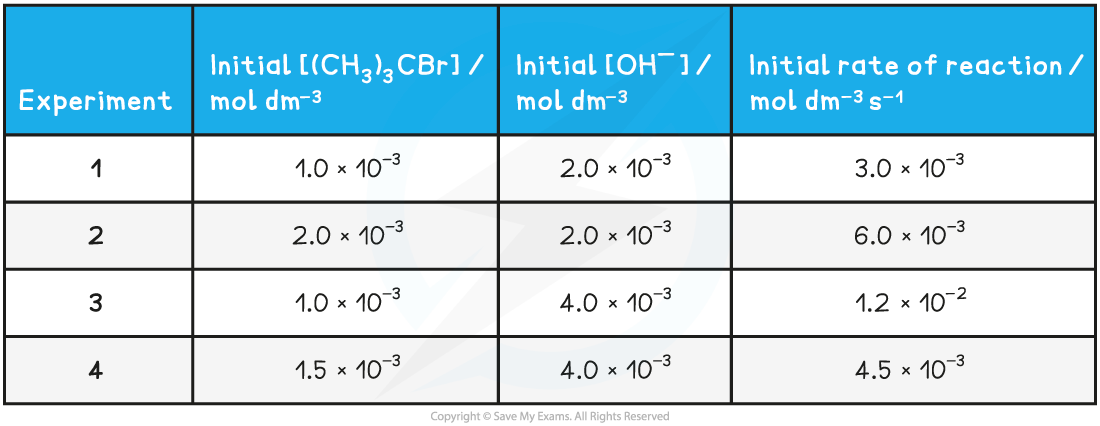
Rate = k [(CH3)3CBr] [OH-]2
Exam Tip
Examiners will often give concentration and rate data in standard form to test your mathematical skills!Take your time because it is easy to make a mistake - the most common one is failing to notice a factor of ten, e.g. one rate value is x10-4 while the rest are x10-3
转载自savemyexams

翰林课程体验,退费流程快速投诉邮箱: yuxi@linstitute.net 沪ICP备2023009024号-1