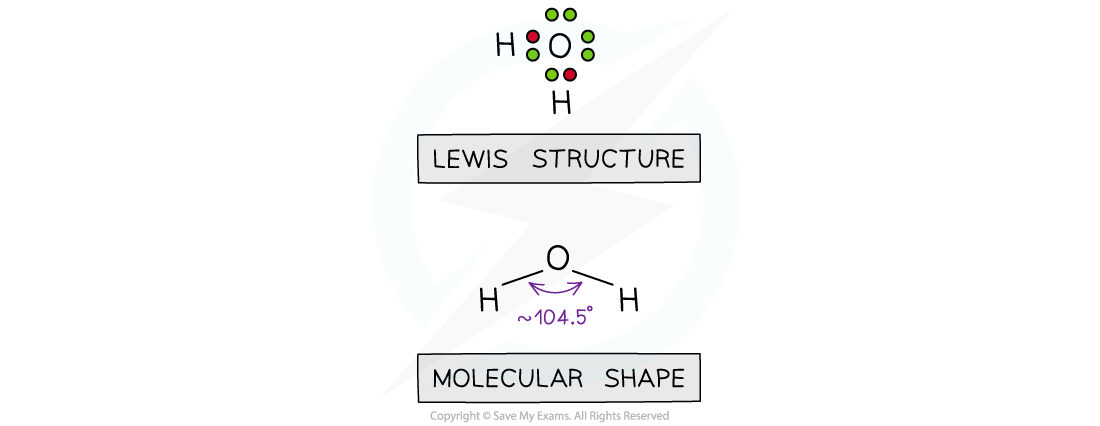
- When an atom forms a covalent bond with another atom, the electrons in the different bonds and the non-bonding electrons in the outer shell all behave as negatively charged clouds and repel each other
- In order to minimise this repulsion, all the outer shell electrons spread out as far apart in space as possible
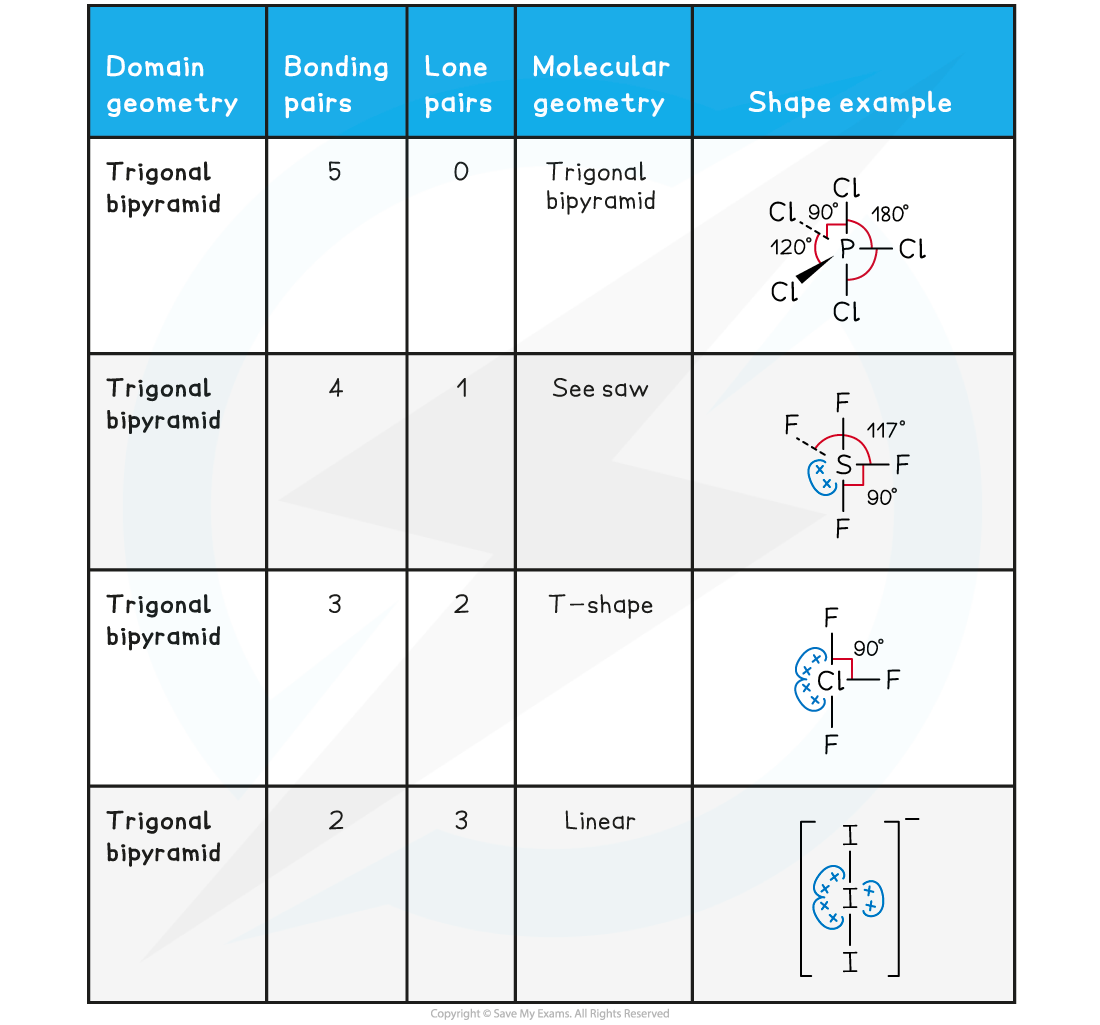
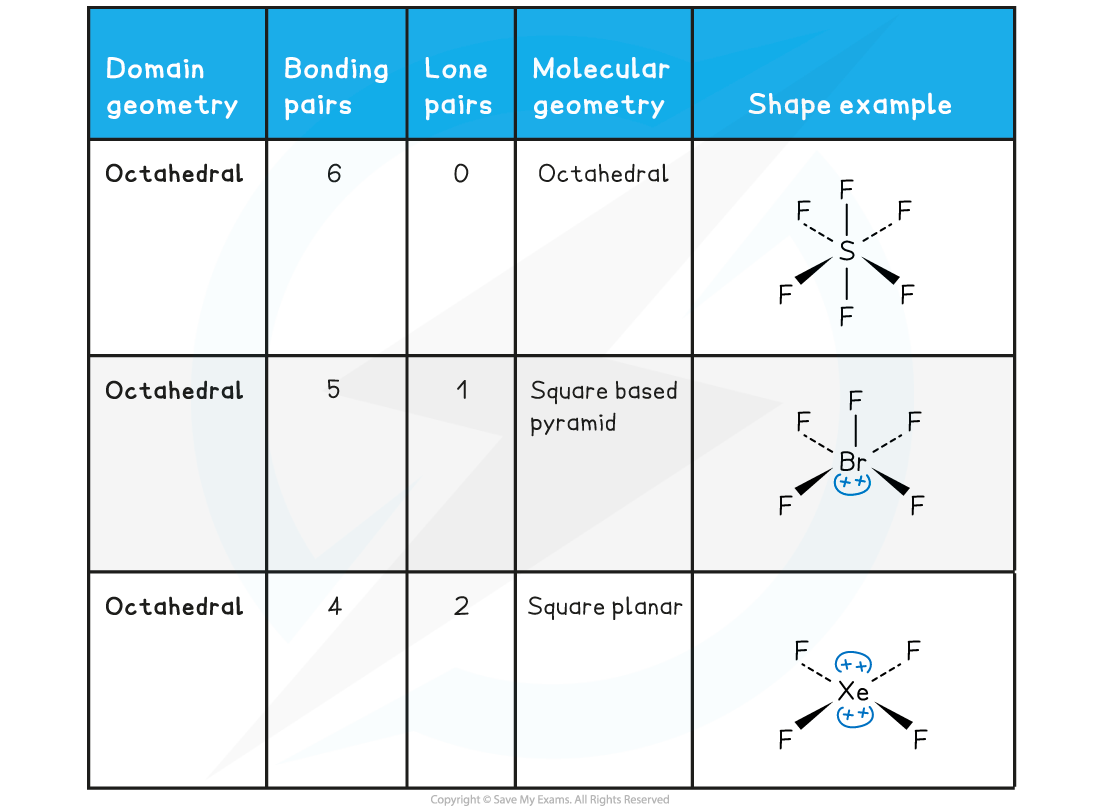
- Molecular shapes and the angles between bonds can be predicted by the valence shell electron pair repulsion theory known by the abbreviation VSEPR theory
- VSEPR theory consists of three basic rules:
-
- All electron pairs and all lone pairs arrange themselves as far apart in space as is possible.
- Lone pairs repel more strongly than bonding pairs
- Multiple bonds behave like single bonds
- These three rules can be used to predict the shape of any covalent molecule or ion, and the angles between the bonds
- The regions of negative cloud charge are known as domains and can have one, two or three pairs electrons