- Successive ionisation data can be used to:
- Predict or confirm the simple electronic configuration of elements
- Confirm the number of electrons in the outer shell of an element
- Deduce the group an element belongs to in the Periodic Table
- By analysing where the large jumps appear and the number of electrons removed when these large jumps occur, the electron configuration of an atom can be determined
- Na, Mg and Al will be used as examples to deduce the electronic configuration and positions of elements in the Periodic Table using their successive ionisation energies
- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: HL复习笔记12.1.2 Ionisation Energy Trends
Trends Across a Period
- Ionisation energies show periodicity – a trend across a period of the Periodic Table
- As could be expected from their electron configuration, the group 1 metals have a relatively low ionisation energy, whereas the noble gases have very high ionisation energies
- The size of the first ionisation energy is affected by four factors:
- Size of the nuclear charge
- Distance of outer electrons from the nucleus
- Shielding effect of inner electrons
- Spin-pair repulsion
- First ionisation energy increases across a period and decreases down a group

A graph showing the ionisation energies of the elements hydrogen to sodium
Ionisation energy across a period
- The ionisation energy across a period generally increases due to the following factors:
- Across a period the nuclear charge increases
- This causes the atomic radius of the atoms to decrease, as the outer shell is pulled closer to the nucleus, so the distance between the nucleus and the outer electrons decreases
- The shielding by inner shell electrons remain reasonably constant as electrons are being added to the same shell
- It becomes harder to remove an electron as you move across a period; more energy is needed
- So, the ionisation energy increases
Dips in the trend
- There is a slight decrease in IE1 between beryllium and boron as the fifth electron in boron is in the 2p subshell, which is further away from the nucleus than the 2s subshell of beryllium
- Beryllium has a first ionisation energy of 900 kJ mol-1 as its electron configuration is 1s2 2s2
- Boron has a first ionisation energy of 800 kJ mol-1 as its electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2px1
- There is a slight decrease in IE1 between nitrogen and oxygen due to spin-pair repulsion in the 2px orbital of oxygen
- Nitrogen has a first ionisation energy of 1400 kJ mol-1 as its electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2px1 2py1 2pz1
- Oxygen has a first ionisation energy of 1310 kJ mol-1 as its electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py1 2pz1
- In oxygen, there are 2 electrons in the 2px orbital, so the repulsion between those electrons makes it slightly easier for one of those electrons to be removed
From one period to the next
- There is a large decrease in ionisation energy between the last element in one period, and the first element in the next period
- This is because:
- There is increased distance between the nucleus and the outer electrons as you have added a new shell
- There is increased shielding by inner electrons because of the added shell
- These two factors outweigh the increased nuclear charge
Successive Ionisation Energies
Successive ionisation energies of an element
- The successive ionisation energies of an element increase
- This is because once you have removed the outer electron from an atom, you have formed a positive ion
- Removing an electron from a positive ion is more difficult than from a neutral atom
- As more electrons are removed, the attractive forces increase due to decreasing shielding and an increase in the proton to electron ratio
- The increase in ionisation energy, however, is not constant and is dependent on the atom’s electronic configuration
- Taking calcium as an example:
Ionisation Energies of Calcium Table
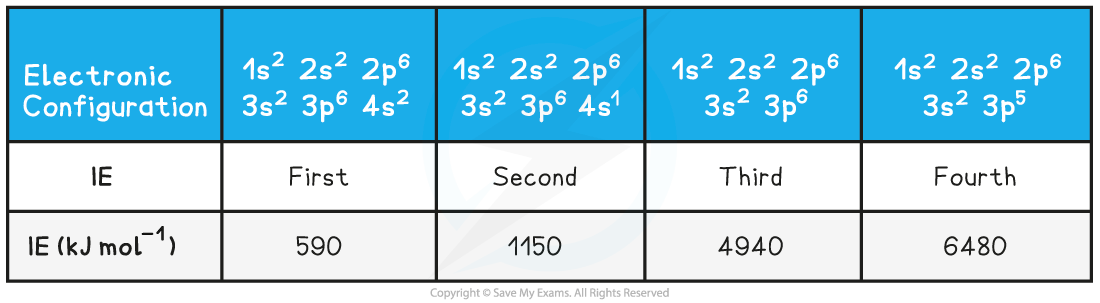
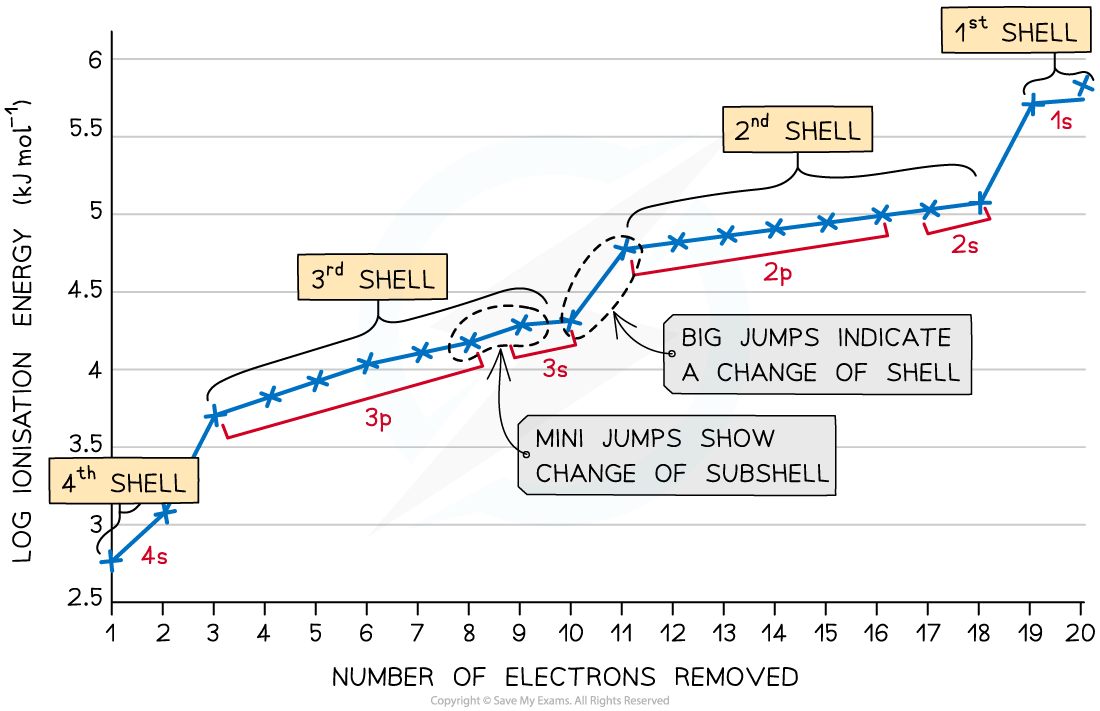
Successive ionisation energies for the element calcium
- The first electron removed has a low IE1 as it is easily removed from the atom due to the spin-pair repulsion of the electrons in the 4s orbital
- The second electron is more difficult to remove than the first electron as there is no spin-pair repulsion
- The third electron is much more difficult to remove than the second one corresponding to the fact that the third electron is in a principal quantum shell which is closer to the nucleus (3p)
- Removal of the fourth electron is more difficult as the orbital is no longer full, and there is less spin-pair repulsion
- The graph shows there is a large increase in successive ionisation energy as the electrons are being removed from an increasingly positive ion
- The big jumps on the graph show the change of shell and the small jumps are the change of subshell
Deducing the Group
Successive Ionisation Energies Table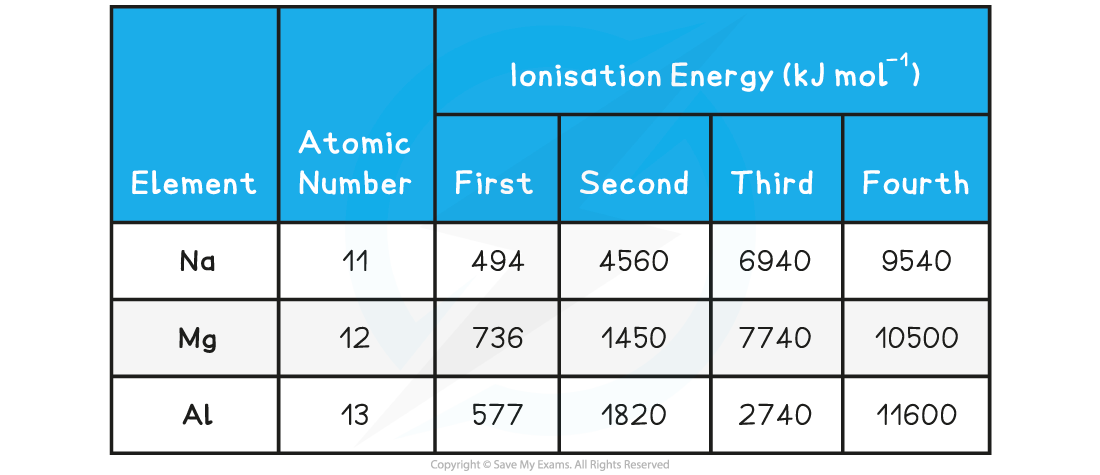
Sodium
- For sodium, there is a huge jump from the first to the second ionisation energy, indicating that it is much easier to remove the first electron than the second
- Therefore, the first electron to be removed must be the last electron in the valence shell thus Na belongs to group I
- The large jump corresponds to moving from the 3s to the full 2p subshell
- Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
Magnesium
- There is a huge increase from the second to the third ionisation energy, indicating that it is far easier to remove the first two electrons than the third
- Therefore the valence shell must contain only two electrons indicating that magnesium belongs to group II
- The large jump corresponds to moving from the 3s to the full 2p subshellMg 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
Aluminium
- There is a huge increase from the third to the fourth ionisation energy, indicating that it is far easier to remove the first three electrons than the fourth
- The 3p electron and 3s electrons are relatively easy to remove compared with the 2p electrons which are located closer to the nucleus and experience greater nuclear charge
- The large jump corresponds to moving from the third shell to the second shell
- Al 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1
Worked Example
Values for the successive IEs of an unknown element are:IE1 = 899 kJ mol-1, IE2 = 1757 kJ mol-1, IE3 = 14850 kJ mol-1, IE4 = 21005 kJ mol-1Deduce which group of the periodic table of elements you would expect to find the unknown element.
Answer:
The largest jump is betweenIE2 andIE3which will correspond to a change in energy level. Therefore the unknown element must be in group 2.
Worked Example
The table shows successive ionisation energies for element X in period 2.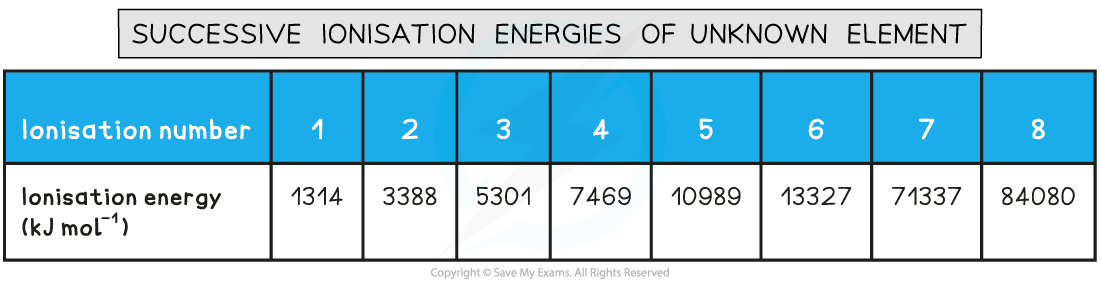
Identify element X.
Answer:
-
- The largest jump in ionisation energy is between IE6 and IE7 meaning that the 7th electron is being removed from an energy level closer to the nucleus
- Therefore element X must be group 6
- If element X is in group 6 and in period 2 it must be oxygen
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








