- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: HL复习笔记9.1.8 The Winkler Method
The Winkler Method
- The Winkler Method is a technique used to measure dissolved oxygen in freshwater systems
- Dissolved oxygen is used as an indicator of the health of a water body, where higher dissolved oxygen concentrations correlate with high productivity and little pollution
- The biological oxygen demand (BOD) is the amount of oxygen used to decompose the organic matter in a sample of water over a specified time period, usually 5 days, at a specified temperature
- A high BOD indicates a greater quantity of organic waste in the water, which means a lower level of dissolved oxygen
Chemical analysis
- In the first step, manganese(II) sulfate is added to a water sample and then the solution is made alkaline with NaOH
- In the alkaline solution, dissolved oxygen will oxidize manganese(II) ions to manganese(IV)
2Mn2+(aq) + 4OH- (aq) + O2 (aq) → 2MnO2 (s) + 2H2O (l)
- The manganese(IV) oxide, MnO2, appears as a brown precipitate
- In the second part, acidified potassium iodide, KI, is added to the solution
- The precipitate will dissolve back into solution, so Mn(IV) is reduced back to Mn(II) liberating iodine in the process
MnO2 (s) + 2I−(aq) + 4H+ (aq) → Mn2+(aq) + I2(aq) + 2H2O(l)
- Thiosulfate is used, with a starch indicator, to titrate the iodine liberated
2S2O32−(aq) + I2 (aq) → S4O62−(aq) + 2I−(aq)
- From the above stoichiometric equations, we can see that:
1 mole of O2 → 2 moles of MnO2 → 2 moles of I2 → 4 moles of S2O32−
- Therefore, after determining the number of moles of iodine produced, we can work out the number of moles of oxygen molecules present in the original water sample
- The oxygen content is usually presented as mg/dm3 or ppm
Winkler Method Calculation
- The following calculation shows how the data from a Winkler analysis is carried out:
Worked Example
A sample of lake water was analysed using the Winkler Method. The size of the sample was 600 cm3 and the following table shows the results of a titration of the liberated iodine against 0.0500 mol dm-3 sodium thiosulfate solution in the final step of the analysis: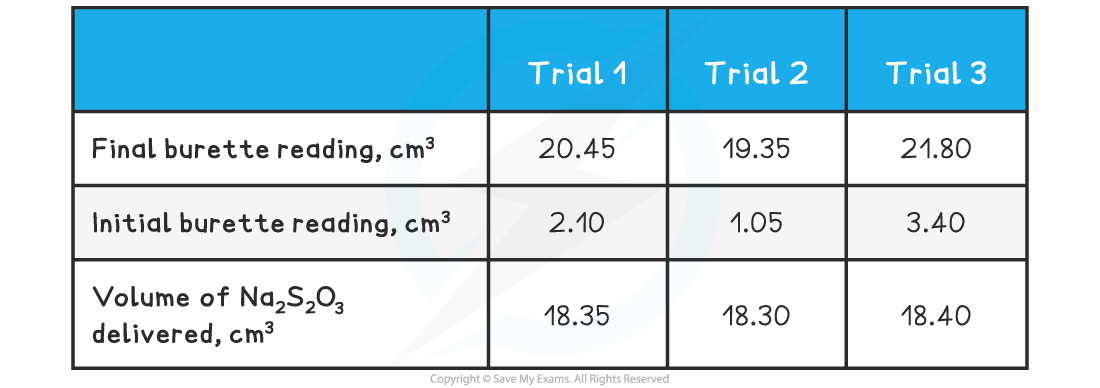 Determine the dissolved oxygen content of the water sample in g dm-3
Determine the dissolved oxygen content of the water sample in g dm-3
Answer:
Step 1: Determine the average volume of delivered
Average volume Na2S2O3 = (18.35 + 18.30 + 18.40) ÷ 3
Average volume Na2S2O3 = 18.35 cm3
Step 2: Determine the number of moles of sodium thiosulfate reacted
Moles of Na2S2O3 = volume in dm3 x concentration = 0.01835 dm3 x 0.0500 mol dm-3= 9.175 x 10-4 mol
Step 3: Determine the moles of oxygen reacted
1 mol of O2 is equivalent to 4 mol of Na2S2O3
Therefore, amount of oxygen in the sample is = (9.175 x 10-4) ÷ 4 = 2.294 x 10-4 mol
Step 4: Calculate the concentration of the dissolved oxygen
Concentration = mol ÷ volume in dm3 = (2.294 x 10-4 mol) ÷ 0.600 dm3= 3.823 x 10-4 mol dm-3
Convert to g dm-3 = 3.823 x 10-4 mol dm-3 x 32.00 g mol-1 = 0.01223 g dm-3
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








