- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: HL复习笔记7.1.4 The Reaction Quotient
The Reaction Quotient
- The reaction quotient, Q, is the ratio of products and reactants for a reaction that has NOT yet reached equilibrium
- The expression for Q is very similar to Kc:

- It is a useful concept because the size of Q can tell us how far a reaction is from equilibrium and in which direction the reaction proceeds
- For Example,
- If Q = Kc then the reaction is at equilibrium, no net reaction occurs
- If Q < Kc the reaction proceeds to the right in favour of the products
- If Q > Kc the reaction proceeds to the left in favour of the reactants
- Using values of the concentrations of the substances present we can work out if a reaction is at equilibrium or not, as the following example shows:
Worked Example
The equilibrium constant for the following reaction:
COI2 (g) ⇌ CO (g) + I2 (g)
is 5.1 x 10-2 at 298 K
Deduce whether the following reaction mixture concentrations represent a reaction at equilibrium and for those not at equilibrium indicate the direction is proceeding: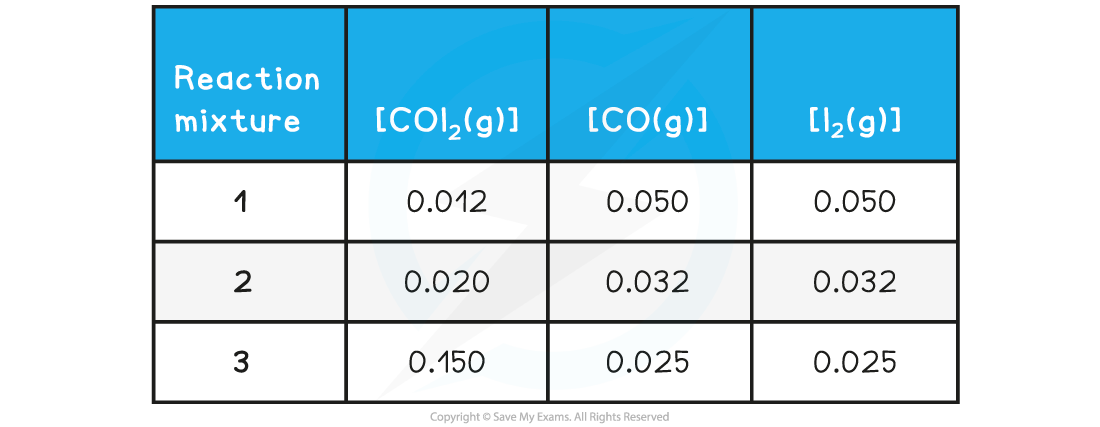
Answer:
The reaction quotient expression is
 Reaction mixture 1:
Reaction mixture 1:
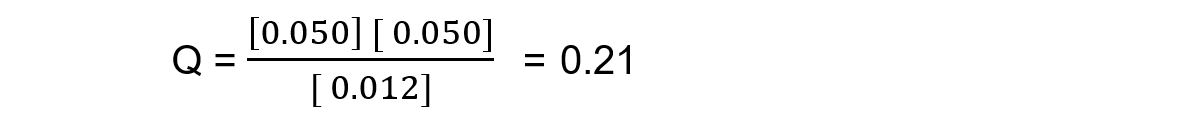 In this mixture Q >> Kc, so Q has to decrease to reach Kc. This means the reaction must be moving to the left, in order to reach equilibrium, so the reactants are favoured
In this mixture Q >> Kc, so Q has to decrease to reach Kc. This means the reaction must be moving to the left, in order to reach equilibrium, so the reactants are favoured
Reaction mixture 2: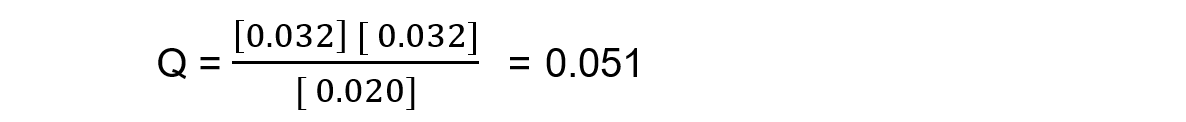
In this mixture, the value of Q = Kc, so the reaction is at equilibrium
Reaction mixture 3:
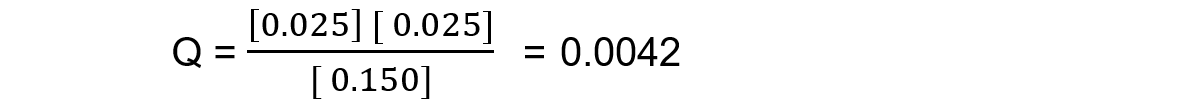 In this mixture Q < Kc, so Q has to increase to reach Kc. This means the reaction must be moving to the right, in order to reach equilibrium, so the products are favoured
In this mixture Q < Kc, so Q has to increase to reach Kc. This means the reaction must be moving to the right, in order to reach equilibrium, so the products are favoured
Exam Tip
The calculation of Q is not explicitly part of the SL course, just as calculating Kc values only comes in HL chemistry. However, a comparison of Q and Kc is relevant and the worked example is included only to illustrate how Q is determined from experimental data.
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









