- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Maths: Pure复习笔记2.9.1 Translations
Translations
What are graph transformations?
- When you alter a function in certain ways, the effects on the graph of the function can be described by geometrical transformations
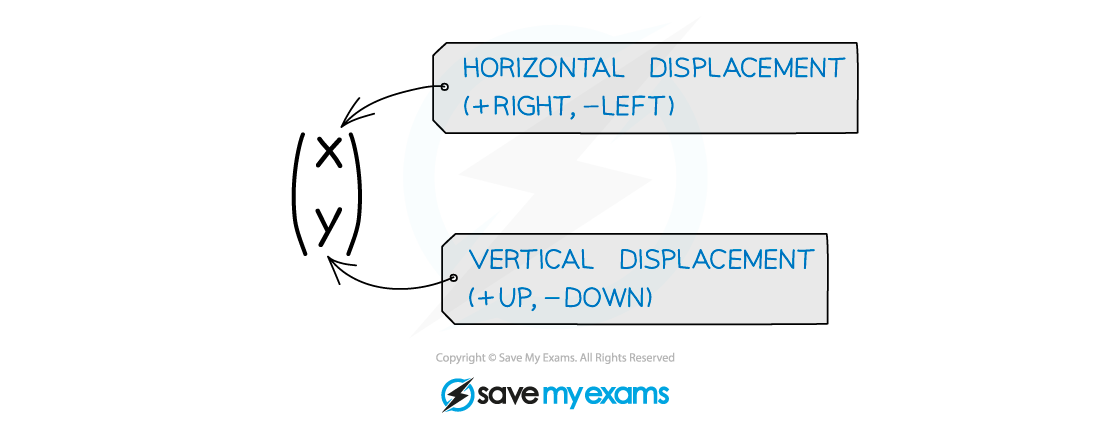
- With a translation the shape, size, and orientation of the graph remain unchanged – the graph is merely shifted (up or down, left or right) in the xy plane

- A particular translation (how far left/right, how far up/down) is specified by a translation vector:
What do I need to know about graph translations?
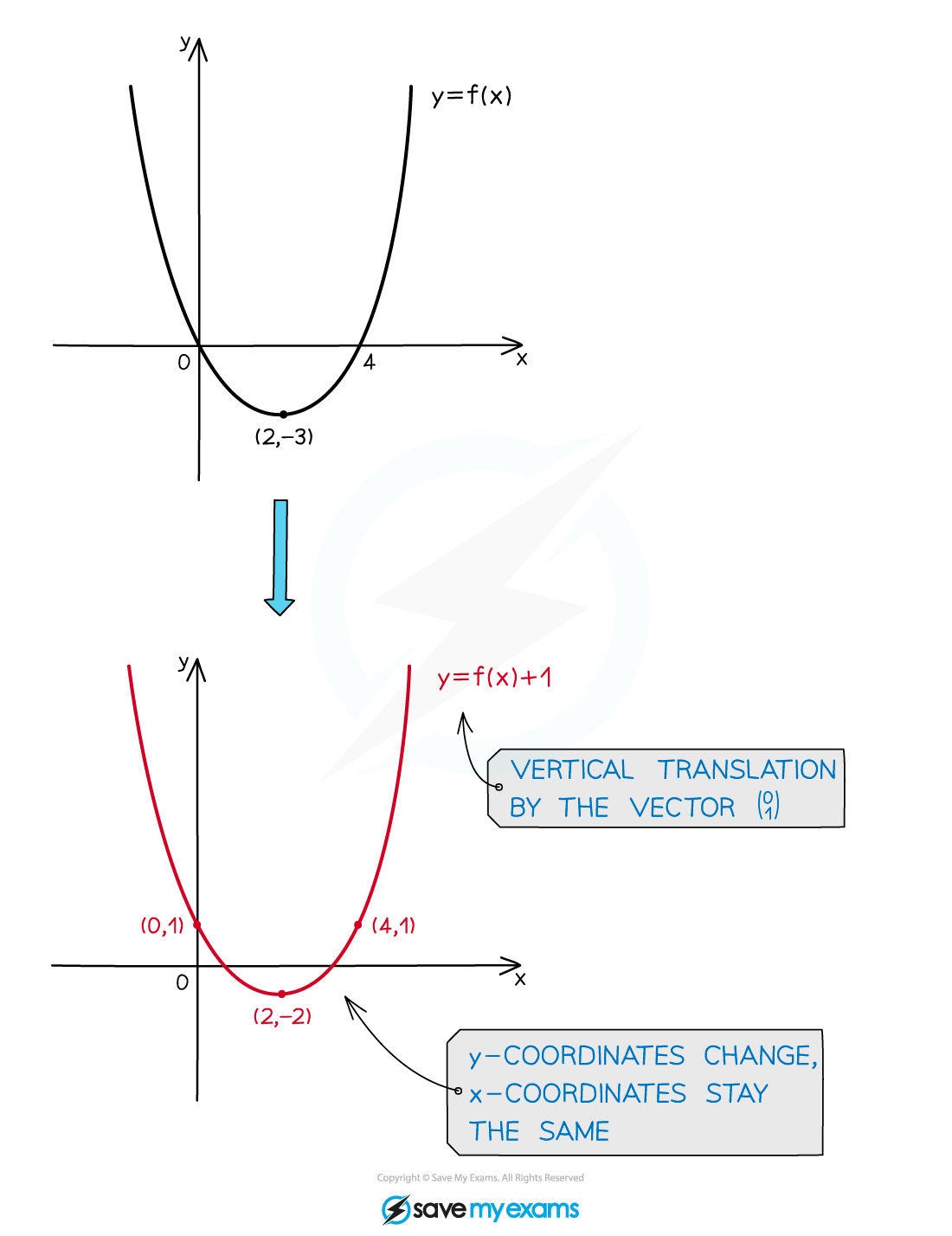
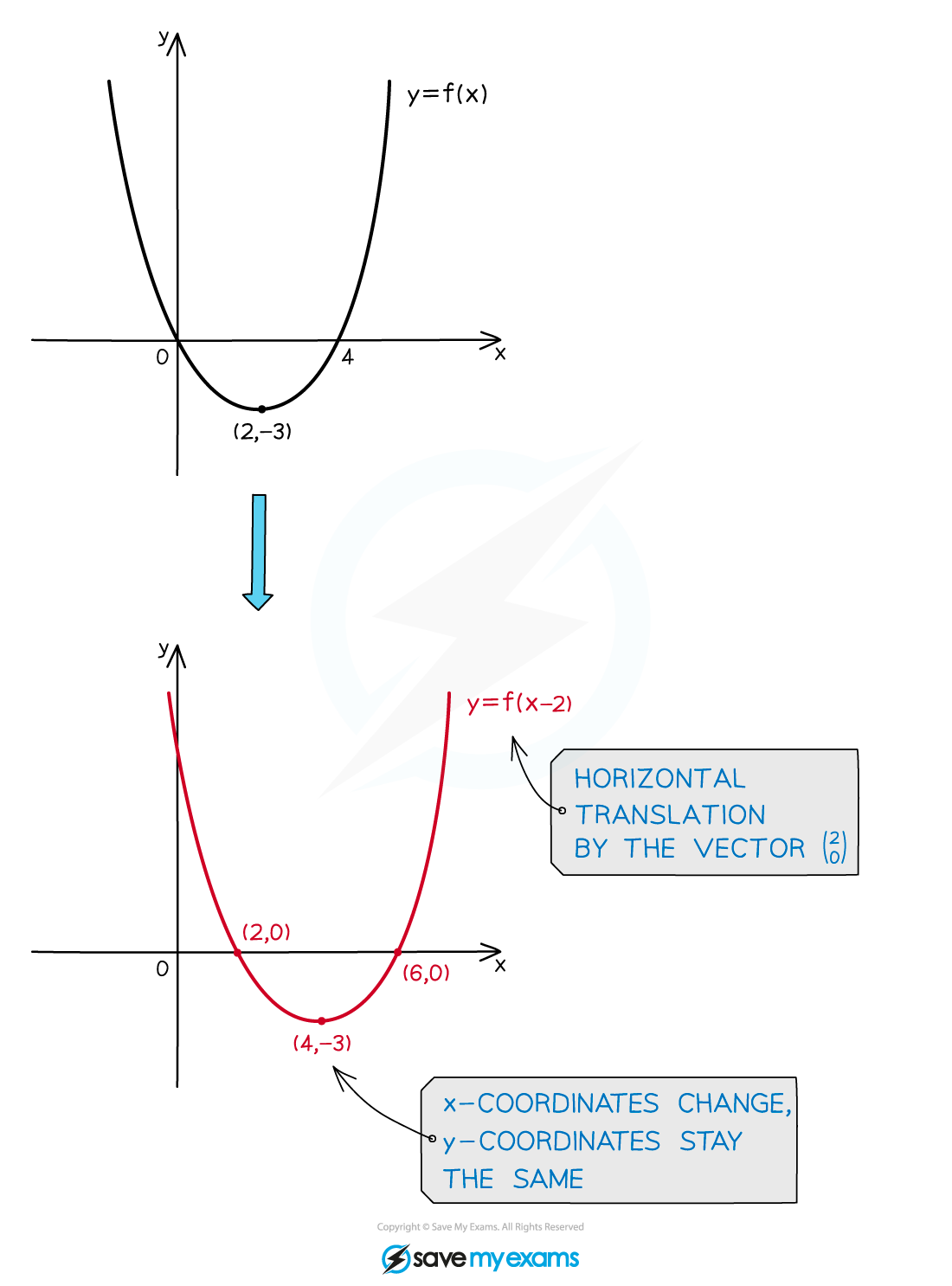
- The graph of
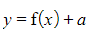 is a vertical translation of the graph
is a vertical translation of the graph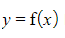 by the vector
by the vector 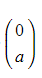
- The graph moves up for positive values of a and down for negative values of a
- The x-coordinates stay the same
- The graph of
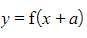 is a horizontal translation of the graph
is a horizontal translation of the graph 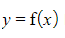 by the vector
by the vector 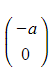
- The graph moves left for positive values of a and right for negative values of a
- The y-coordinates stay the same
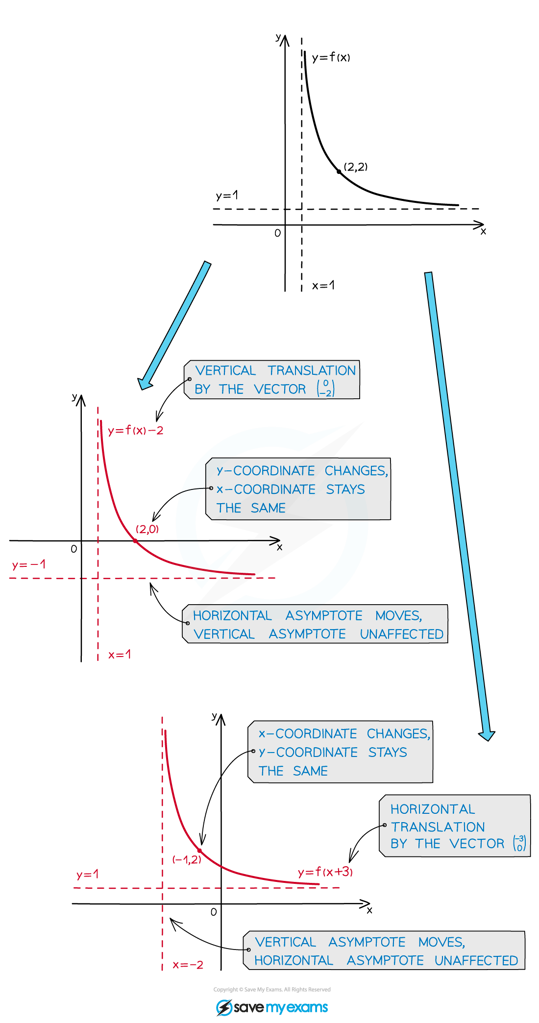
- Any asymptotes of f(x) are also translated. If an asymptote is parallel to the direction of translation, however, it will not be affected
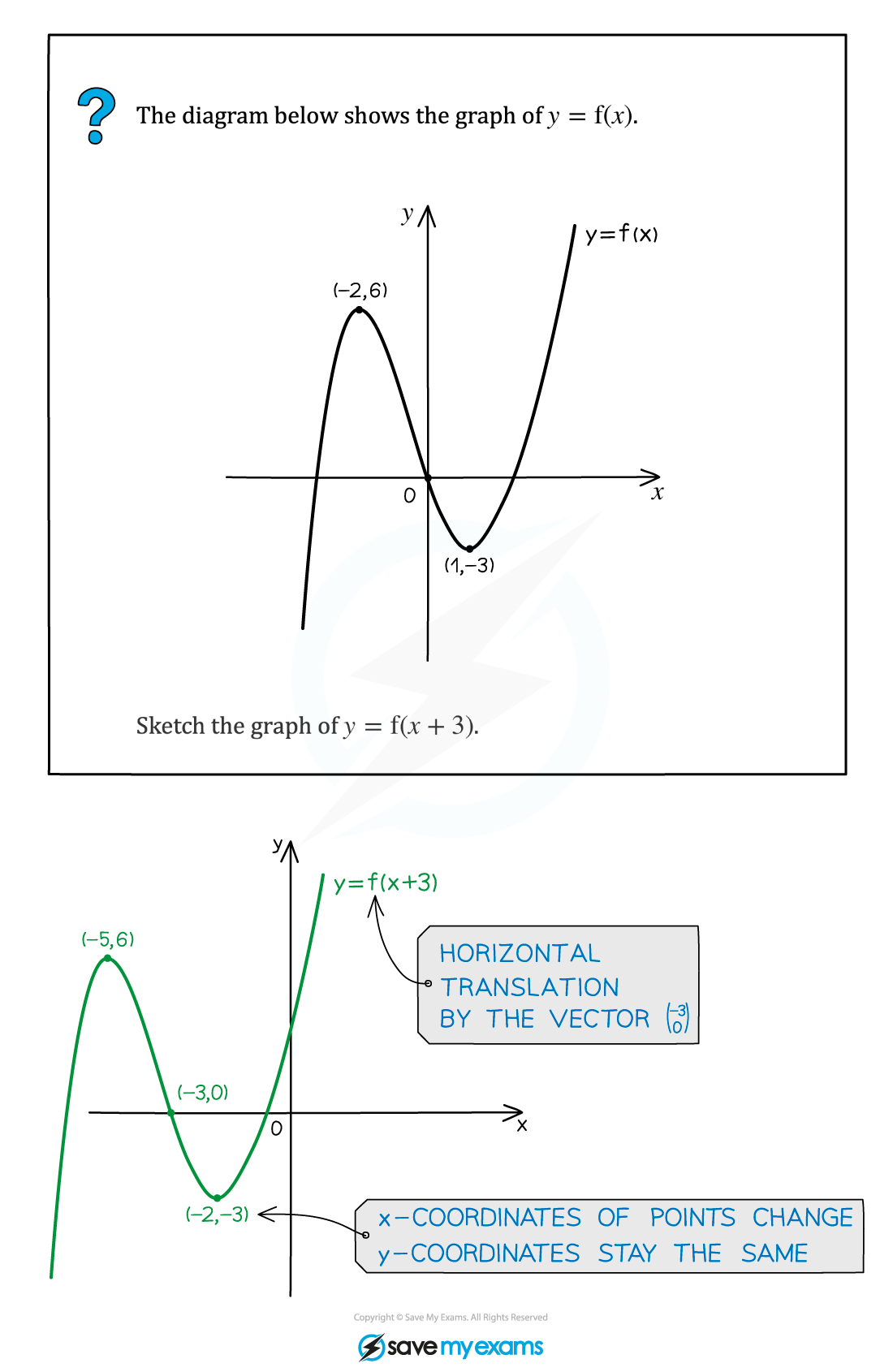
Worked Example
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








