- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: HL复习笔记5.2.1 Hess's Law
Hess's Law
- In 1840, the Russian chemist Germain Hess formulated a law which went on to be known as Hess’s Law
- This went on to form the basis of one of the laws of thermodynamics. The first law of thermodynamics relates to the Law of Conservation of Energy
- It is sometimes expressed in the following form:
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only change form
- This means that in a closed system, the total amount of energy present is always constant
- Hess’s law can be used to calculate the standard enthalpy change of a reaction from known standard enthalpy changes
- Hess’s Law states that:
"The total enthalpy change in a chemical reaction is independent of the route by which the chemical reaction takes place as long as the initial and final conditions are the same."
- This means that whether the reaction takes place in one or two steps, the total enthalpy change of the reaction will still be the same
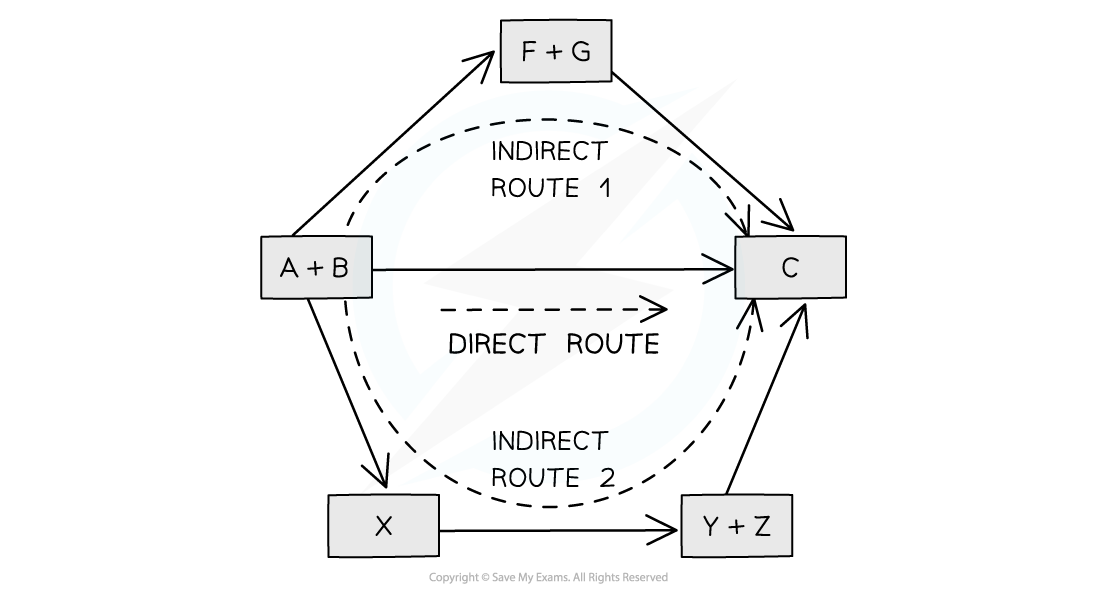
The diagram above illustrates Hess’ Law: the enthalpy change of the direct route, going from reactants (A+B) to product (C) is equal to the enthalpy change of the indirect routes
- Hess’ Law is used to calculate enthalpy changes which can’t be found experimentally using calorimetry, eg:
3C (s) + 4H2 (g) → C3H8(g)
- [popover id="dGQl3oDiqUIQrR1A" label="ΔHf"] , ΔHf (propane) can’t be found experimentally as hydrogen and carbon don’t react under standard conditions
Calculating ΔHr from ΔHf using Hess’s Law energy cycles
- You can see the relationships on the following diagram:
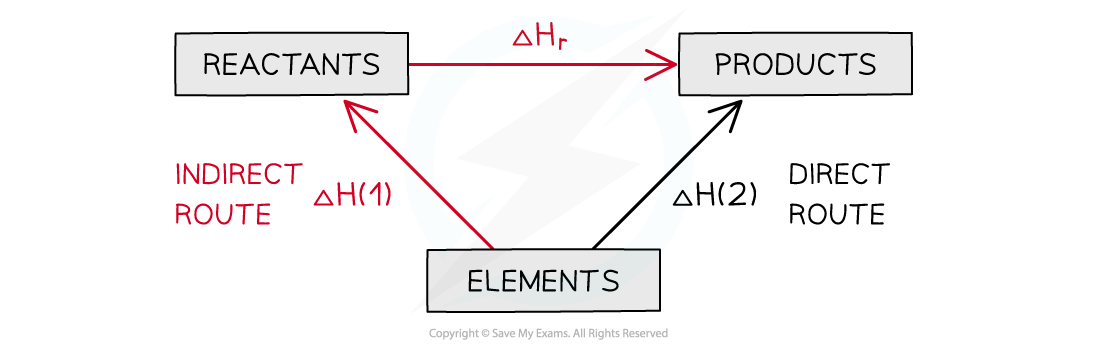
The enthalpy change from elements to products (direct route) is equal to the enthalpy change of elements forming reactants and then products (indirect route)
- The products can be directly formed from the elements = ΔH2
OR
- The products can be indirectly formed from the elements = ΔH1 + ΔHr
- Equation
ΔH2 = ΔH1 + ΔHr
Therefore for energy to be conserved,
ΔHr = ΔH2 – ΔH1
Exam Tip
You do not need to learn Hess's Law word for word as it is not a syllabus requirement, but you do need to understand the principle as it provides the foundation for all the problem solving in Chemical Energetics
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









