- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记11.1.8 Skills: Analysing Epidemiological Data
Analysing Epidemiological Data
- Epidemiology is the study of the distribution and incidence of diseases in the population and the associated or contributory risk factors
- It has contributed to our understanding of many diseases including lung cancer and coronary heart disease
- Monitoring diseases in populations is important in understanding the seriousness of the disease and the mechanisms behind the spreading of the disease in order to develop contingencies to minimise the damage done
- Data collected can be used to devise vaccination programs, such as that used to eradicate polio in the 1980's
- It also allows more specific targeting of the spread of disease in smaller geographical regions and populations where outbreaks are documented
- Analysis of epidemiological data highlights trends in the success of vaccination programs and also highlights the failures e.g. When outbreaks occur due to lack of vaccination uptake
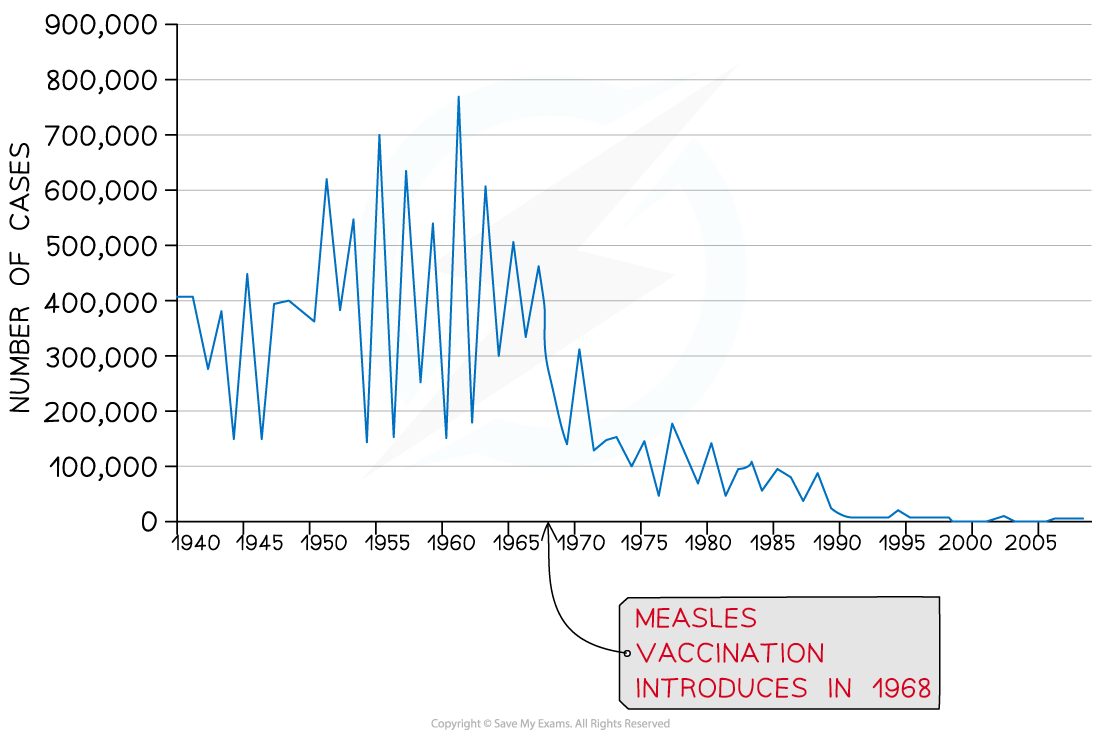
Epidemiological studies show the impact of a vaccination program on the incidence of measles
Important factors affecting epidemiological analysisThere are some factors that contribute to the analysis of disease that need to be considered:
-
- Populations generally increase year on year which can contribute to an increase in outbreaks of disease
- Improvements in health care, sanitation, and medical advances can influence data on disease
- Climate, disease presence and survival, mean diseases exist at different levels of exposure in different regions
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








