- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记11.1.7 Monoclonal Antibodies
Creating Hybridoma Cells
Introduction
- Monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) are artificially produced antibodies produced from a single B cell clone
- The hybridoma method is used to make monoclonal antibodies
- The method enables large quantities of identical antibodies to be produced
- The hybridoma method solved the problem of having B cells that could divide by mitosis but not produce antibodies and plasma cells that could produce antibodies but not divide
- This method was established in the 1970s
- Monoclonal antibodies bind antigens, in the same way naturally produced antibodies
Creating Hybridoma cells
- Hybridoma cells are created by combining specific antibody producing B cells with myeloma (tumour) cells
- Plasma cells producing the required antibodies are created by injecting mice with the target antigen to trigger an immune response
- This results in plasma cells producing the required antibodies to complement the target antigen
- These plasma cells are removed from the spleen of the mouse before being fused with immortal myeloma cells cultured in the lab to make hybridoma cells
- Hybridoma cells producing the required monoclonal antibody can then be isolated and used in large scale monoclonal antibody production
Producing Monoclonal Antibodies
- The hybrid cells produced using the hybridoma method above, are grown in a selective growth medium
- A mix of hybridoma cells producing several different types of antibody can then be screened to identify and isolate the hybridoma producing the desired antibody
- A culture of these hybridoma cells can then be encouraged to divide by mitosis in optimum conditions in a fermenter to produce identical clones all producing identical antibodies - monoclonal antibodies
- Monoclonal antibodies are complementary to the original antigen injected into the mouse initially
- Monoclonal antibodies have multiple applications to include the diagnosis of many different diseases such as HIV, malaria, COVID-19, or even the treatment of diseases such as rabies
- Additionally, they may be used in food safety testing and pregnancy testing
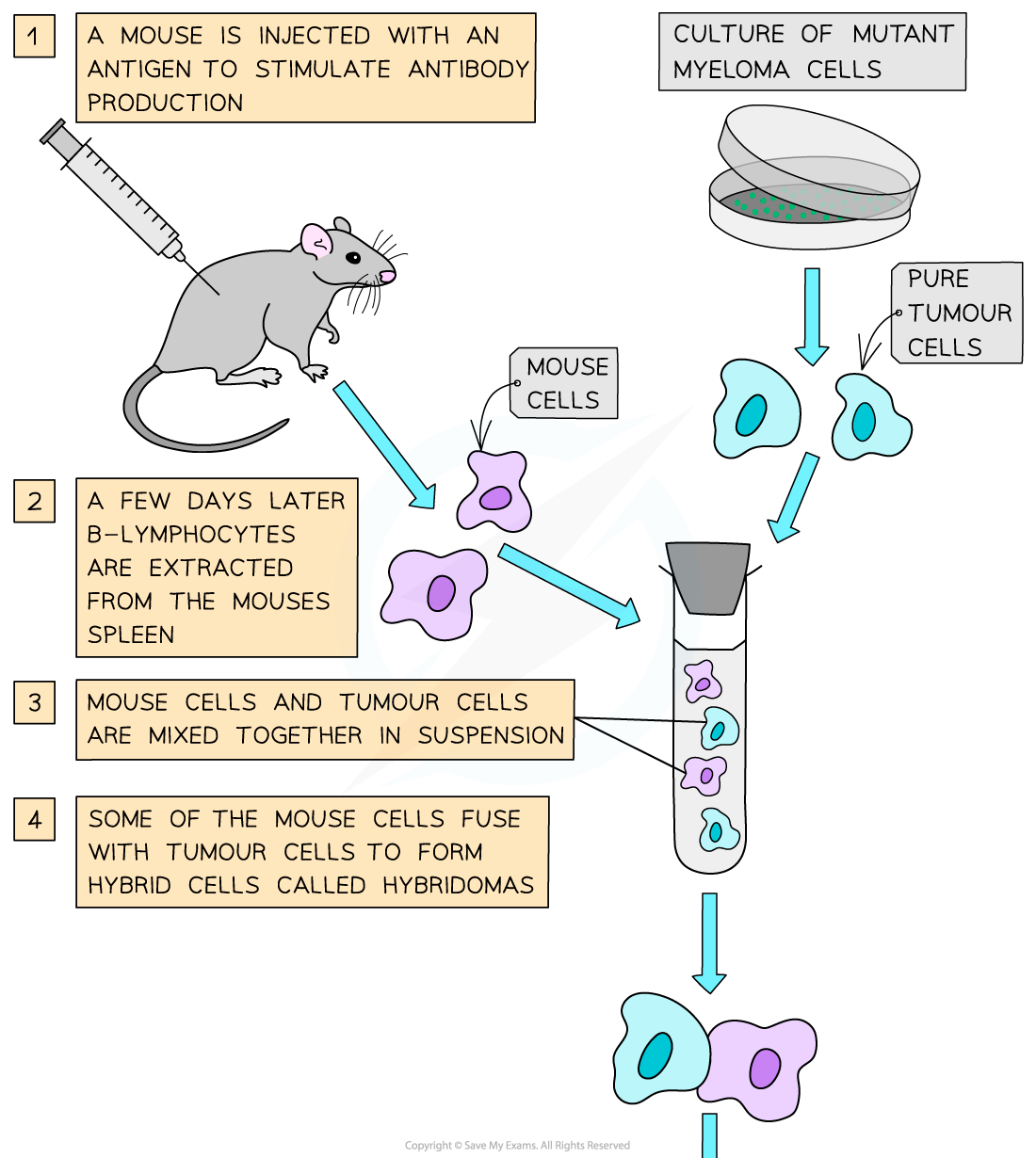
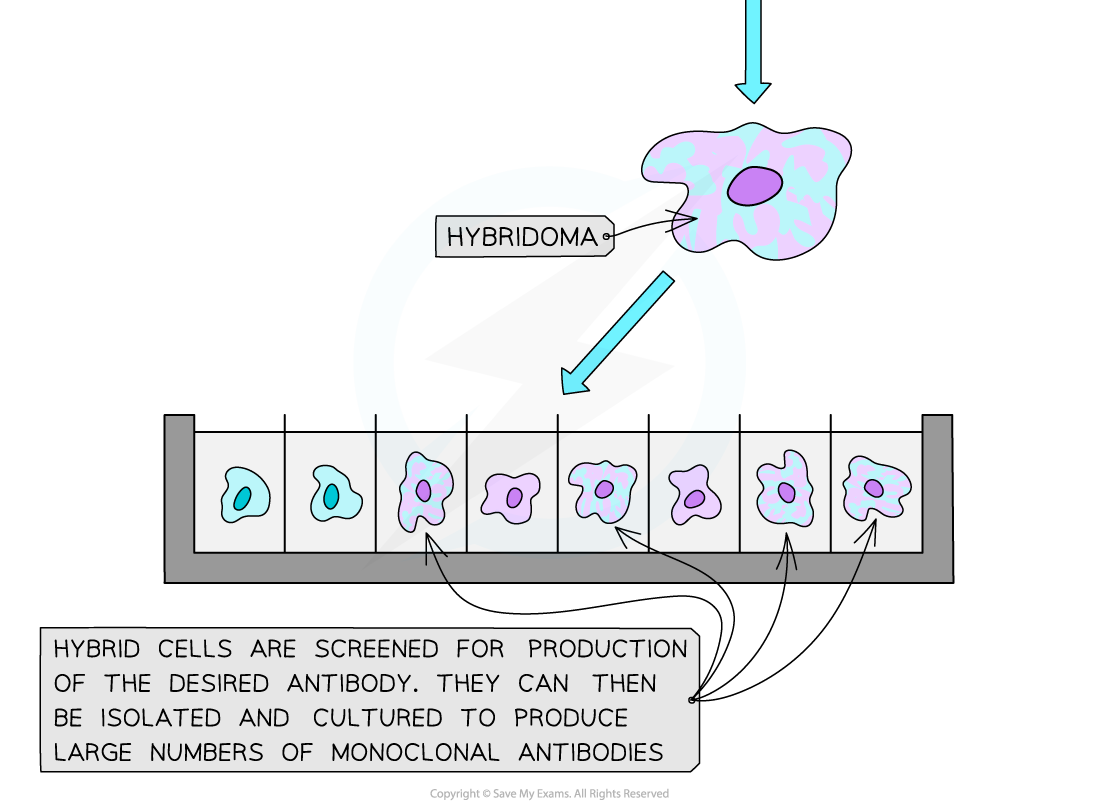
The hybridoma method is used to produce monoclonal antibodies
Pregnancy Test Kits
- Urine samples can be used in pregnancy testing
- Pregnancy testing sticks contain monoclonal antibody molecules that are specific to a hormone produced during pregnancy (that therefore becomes present in the mother's urine)
- This hormone is human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), which is secreted by the early embryo after it has implanted in the uterus
- The antibodies in the testing sticks all originate from a single clone of B lymphocyte cells that all produce the same antibody specific to hCG
- This minimises the chances of false test results
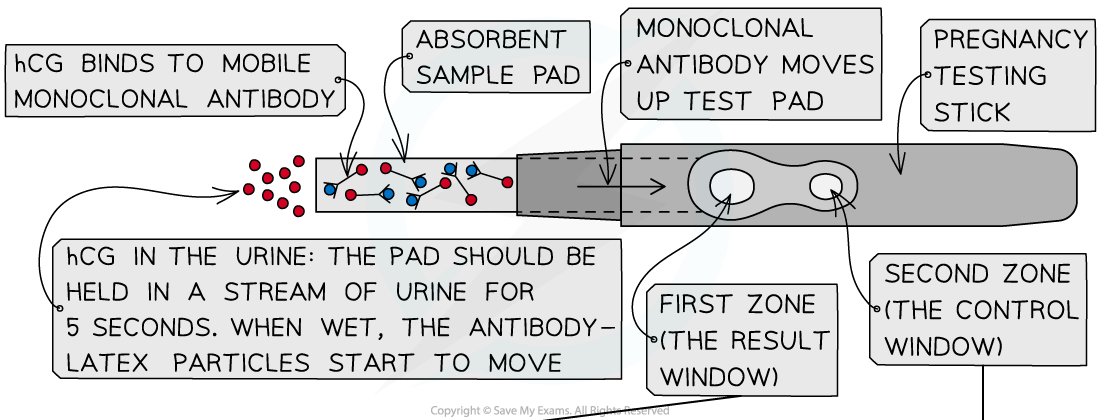
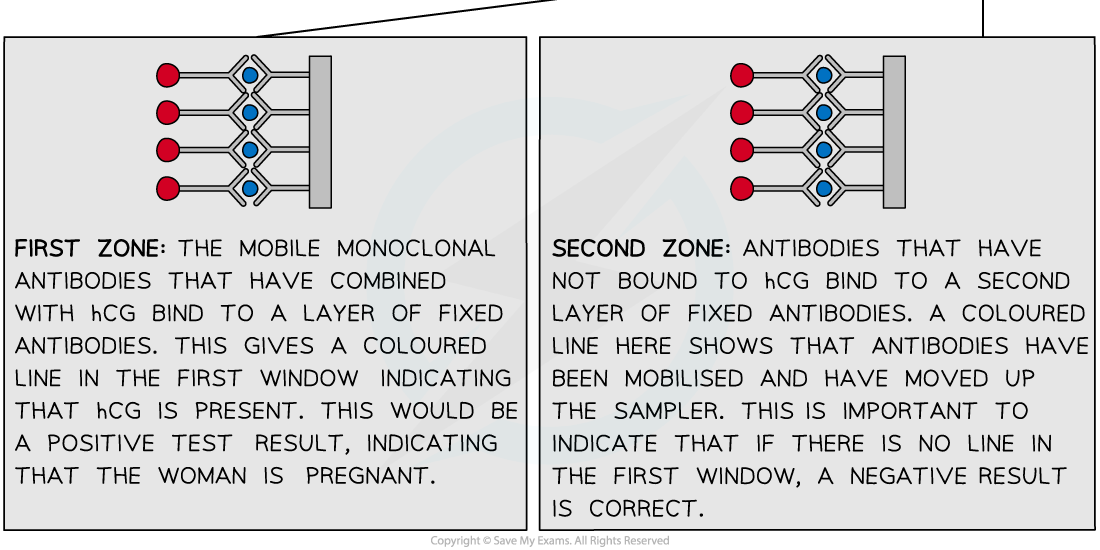
Monoclonal antibodies are used to detect the presence of the hormone hCG in the urine of pregnant women.
Exam Tip
Remember monoclonal antibodies are produced from a hybridoma cell - a cell formed by the fusion of plasma cells and tumour (cancer) cells, which divide continuously therefore producing large quantities of a wanted antibody.
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








