- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记8.1.3 Bioinformatics & Metabolism
Bioinformatics: Investigating Metabolism
NOS: Developments in scientific research follow improvements in computing: developments in bioinformatics, such as the interrogation of databases, have facilitated research into metabolic pathways
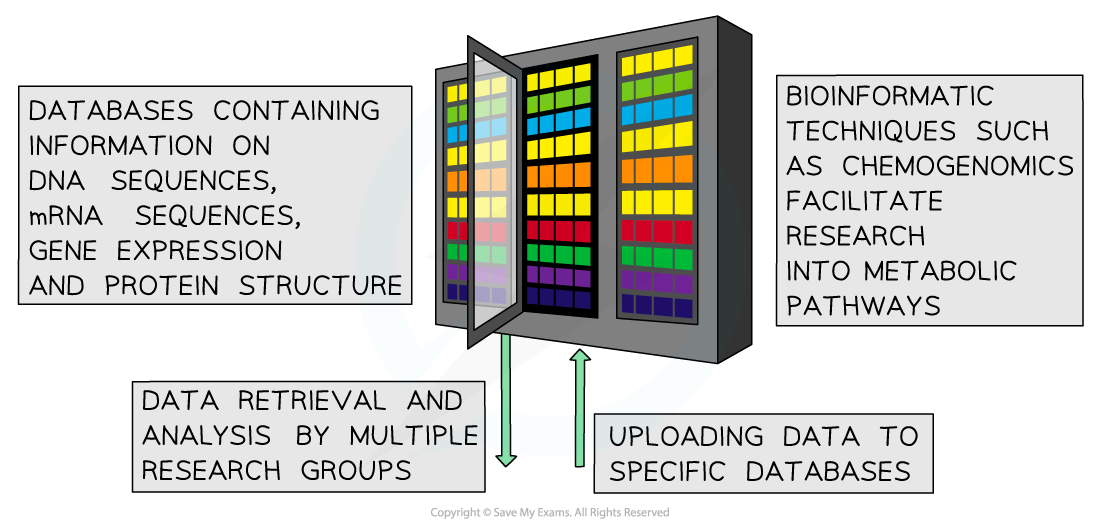
- Bioinformatics is the use of computers to analyse and sequence data in biological research
- It has led to the creation of massive databases of information on molecules such as proteins, genes and DNA sequences
- Bioinformatics involves multiple scientific research groups contributing into central databases; other groups can then analyse the research and raise queries
- There are a number of different applications of bioinformatics
- Testing commercially available drugs on diseases that the drugs have not been originally targeted for
- Theoretical molecular chemicals can be developed to screen databases for new compounds with the potential for targeting specific diseases, such as malaria
- Gene function can be studied using model organisms with similar sequences
- When developing new drugs scientists can test whole libraries of chemicals individually on a range of model organisms
The use of bioinformatics by scientists
- One bioinformatics technique has specifically facilitated research in metabolic pathways and is called chemogenomics
- Chemogenomics focuses on finding chemicals that target enzyme binding sites in order to alter metabolic pathways
Bioinformatics: Identifying Anti-malarial Drugs
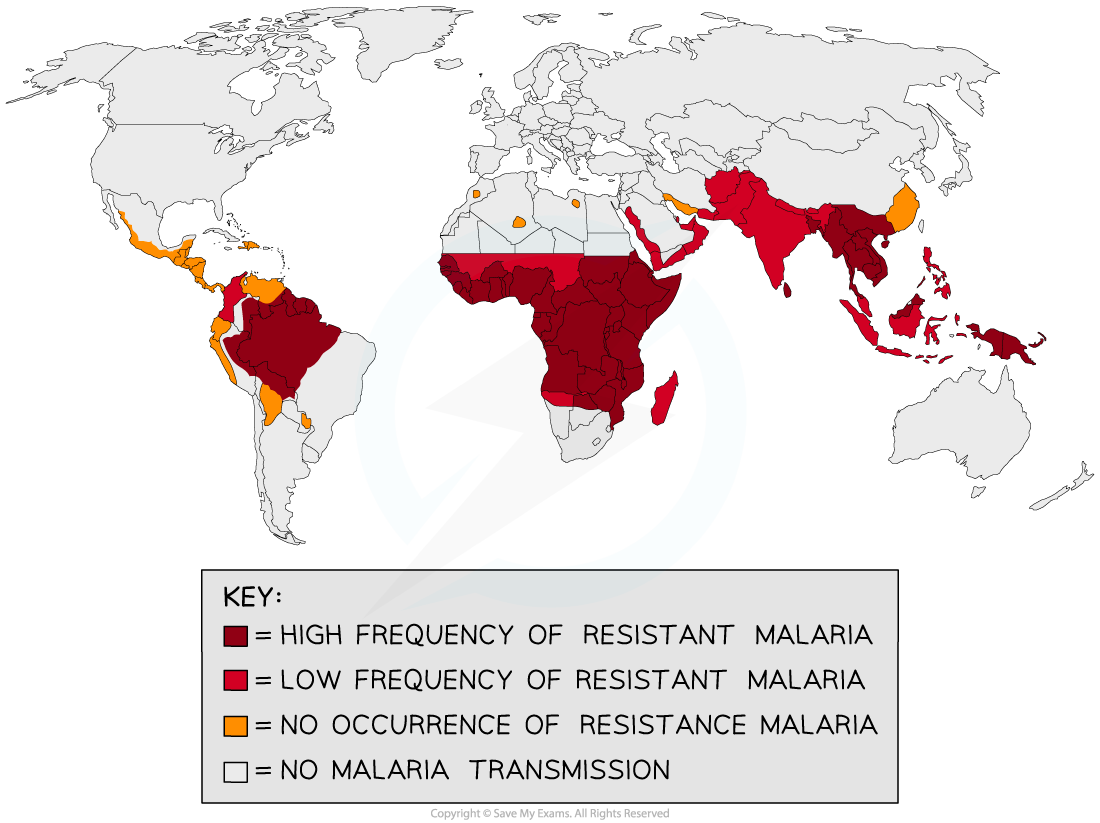
- Malaria is a disease caused by the parasitic protozoans of the genus Plasmodium
- Some Plasmodium protozoa have become resistant to many of the available drugs currently used to treat the disease, such as chloroquine
- The development and life cycle of the parasite is governed by specific enzymes and metabolic pathways
- A global research effort is in place to determine new methods of treatment for malaria
- The use of bioinformatics has a crucial place in this research by targeting the enzymes and metabolites within the parasite
Map showing the occurrence of resistant malaria parasites across the globe
The use of bioinformatics in identifying malarial inhibitors
- Scientists have sequenced the proteome of the parasitic Plasmodium falciparum
- Consequently the enzymes involved in the parasite's metabolism have been identified and can be targeted for inhibition
- Targeting these enzymes and metabolic pathways by inhibition can facilitate the development of new anti-malarial drugs and medications
- Bioinformatics can be used to screen the parasite's enzymes against a database of chemicals to identify potential enzyme inhibitors
- Molecular models of the target enzymes can be tested against computer designed models of inhibitors
- So far over 300,000 chemicals have been screened against resistant malaria strains to identify 19 new chemicals that can inhibit the parasite's enzymes
The use of bioinformatics in finding treatments for malaria
- Aside from targeting malarial inhibitors, bioinformatics has also played a key role developing other new treatments for malaria, including
- Chemical modification of current anti-malarial drugs to create hybrid drugs
- Screening databases for new compounds with potential anti-malarial activity
- 15 new chemicals have been identified that bind to 61 malarial proteins creating new lines of investigation for scientists to follow in the search for anti-malarials
转载自savemyexams

早鸟钜惠!翰林2025暑期班课上线

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1








