- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记7.2.3 Transcription
Nucleosomes Regulate Transcription
- Nucleosomes are the structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes that facilitate supercoiling
- Within a nucleosome, DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones
- The tails of histones can be chemically modified which can influence whether a gene will be expressed or not
- An acetyl group, methyl group or a phosphate group can be added
- Chemical modifications can either activate or deactivate genes by making the gene more or less accessible to transcription factors
- Methyl groups can also be directly added to DNA to change the activity of a gene
Acetylation and methylation of histone tails
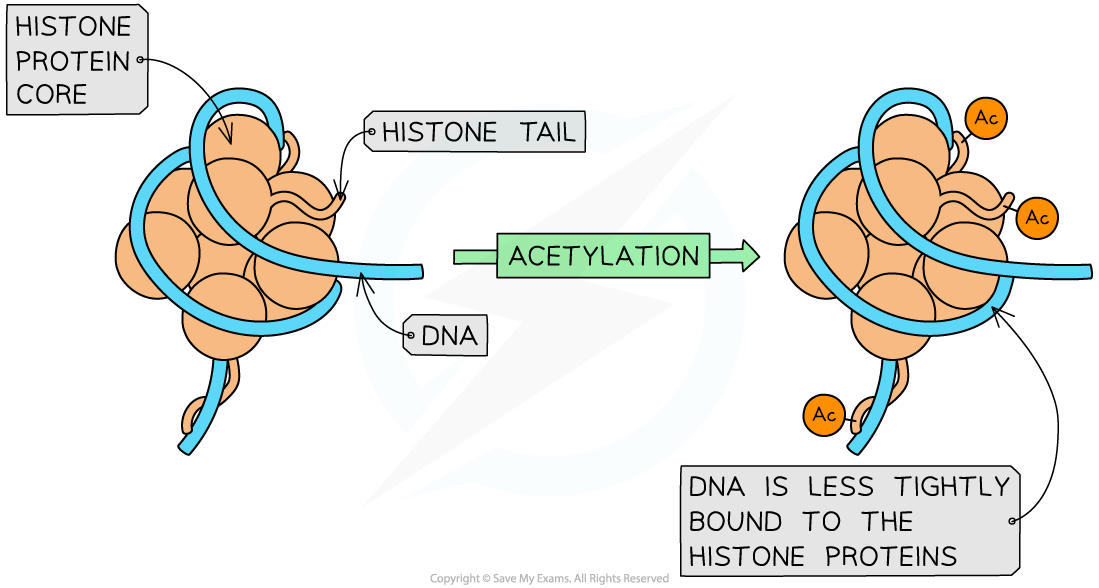
- Positively charged lysine (an amino acid) in histone tails binds to negatively charged DNA
- This helps DNA to coil tightly around the histone protein core
- Adding an acetyl group (acetylation) to lysine neutralises the charge, causing the DNA to be less tightly wrapped
- RNA polymerase and transcription factors can more easily access the DNA so gene expression is stimulated
- Adding a methyl group (methylation) to lysine maintains the positive charge causing the DNA to be more tightly wrapped and therefore inhibits transcription/expression
Acetylation of the Nucleosome
Methylation of DNA
- DNA methylation commonly involves the direct addition of a methyl group (-CH3) to cytosine bases which can influence gene expression
- Methylation of DNA suppresses the transcription of the affected gene by inhibiting the binding of transcription factors
- Cells use this mechanism to lock genes in the ‘off’ position
- DNA methylation can be affected by many environmental, lifestyle or age-related factors
Direction of Transcription
- The synthesis of mRNA occurs in three stages:
- Initiation
- Elongation
- Termination
- During initiation, RNA polymerase binds near the promoter, causing the DNA strands to separate to form an open complex
- During elongation, RNA polymerase moves along the antisense strand
- RNA polymerase adds the 5‘ end of the free RNA nucleotide to the 3’ end of the growing mRNA molecule
- Elongation occurs in a 5’ to 3’ direction, synthesising a single strand of RNA
- Termination occurs when RNA polymerase reaches a terminator sequence
- Which triggers the detachment of the polymerase enzyme and mRNA strand
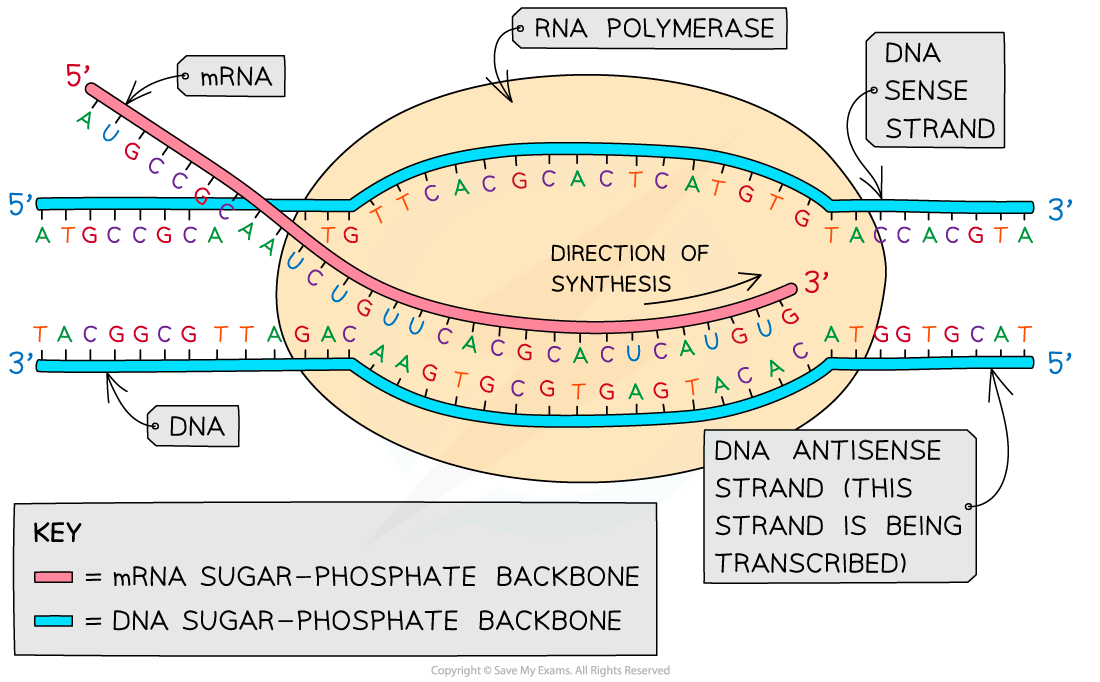
The antisense strand of the DNA molecule is the one that is transcribed
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2025. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









