- 翰林提供学术活动、国际课程、科研项目一站式留学背景提升服务!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Biology: HL复习笔记3.2.2 Stages of Meiosis
DNA Replication before Meiosis
- Before meiosis occurs, all of the DNA inside the nucleus of the 'parent' cell is replicated
- This occurs during a period of the cell cycle known as interphase
Once this has occurred, each chromosome now consists of two genetically identical sister chromatids, which are joined together by a centromere
- The sister chromatids are genetically identical because DNA replication is a very accurate process and only a very small number of mistakes occur when DNA is being copied
The two DNA molecules formed by DNA replication prior to meiosis are considered to be sister chromatids until the splitting of the centromere at the start of anaphase (a stage during meiosis II, during which the sister chromatids are pulled apart)
- After this, they are once again considered as individual chromosomes
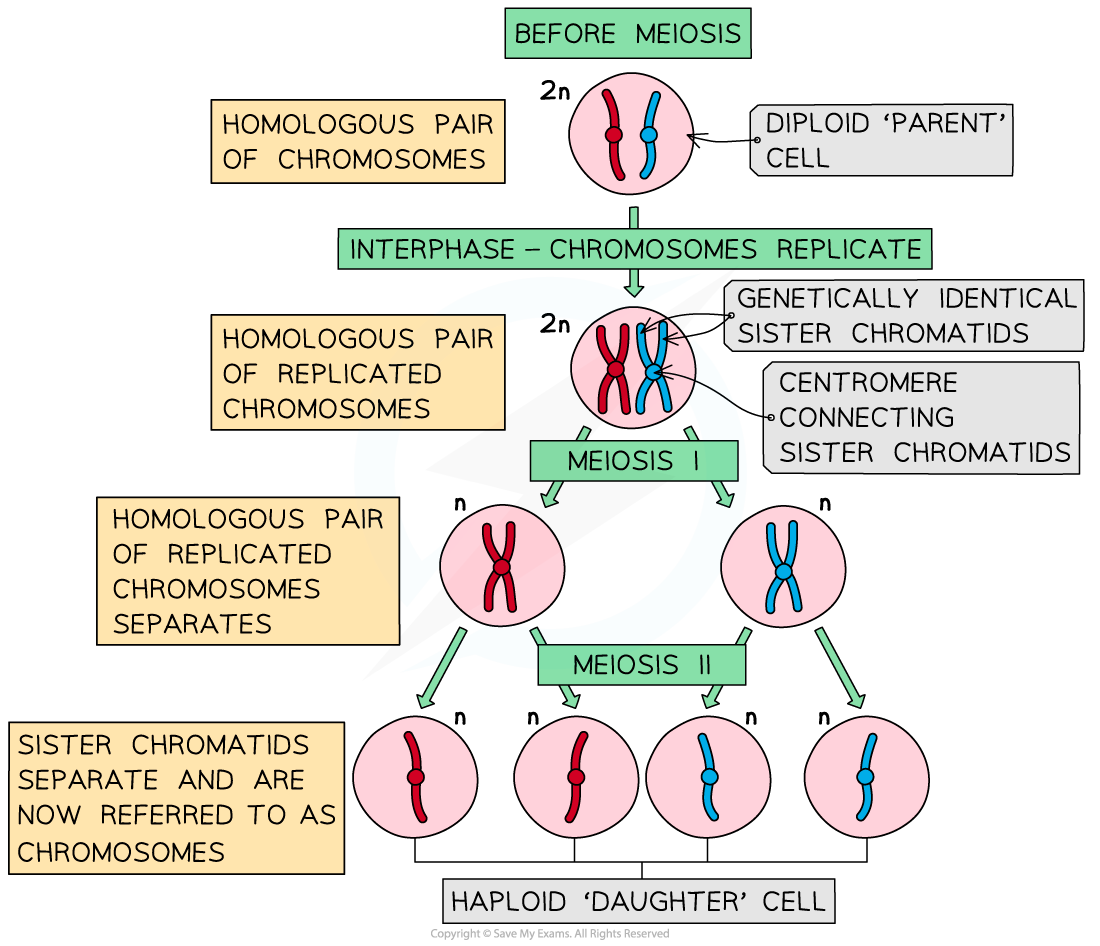
DNA replication before meiosis
Exam Tip
Understanding the difference between chromosomes and chromatids can be difficult. We count chromosomes by the number of centromeres present. So when the 46 chromosomes duplicate during interphase and the amount of DNA in the cell doubles there are still only 46 chromosomes present because there are still only 46 centromeres present. However, there are now 92 chromatids, which are strands of replicated chromosomes.
Formation of Bivalents & Crossing Over
- At the start of meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up with each other
- As DNA replication has already occurred, each chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids
- This means that a pair of homologous chromosomes is made up of four DNA molecules
A pair of homologous chromosomes is known as a bivalent
- The pairing process resulting in the formation of a bivalent is known as synapsis
- After synapsis has occurred, a process known as crossing over may occur
- During crossing over, two non-sister chromatids (i.e. one chromatid from each of the homologous chromosomes) form a junction
- At this junction, the two chromatids break and rejoin with each other
- As these crossover events occur at exactly the same position on the two non-sister chromatids, this allows genes to exchange between the chromatids
- Non-sister chromatids are homologous but are not genetically identical and this means that some of the alleles of the exchanged genes will be different
- This process, therefore, produces chromatids with completely new combinations of alleles (that were not previously present in the DNA of the 'parent' cell)
- As these chromatids will eventually be split up into different gametes, crossing over is of great importance because it is a significant source of genetic variation between gametes
- This ensures there is genetic variation in populations of sexually-reproducing species, which is key to a species' ability to evolve and adapt to changes in its environment over time
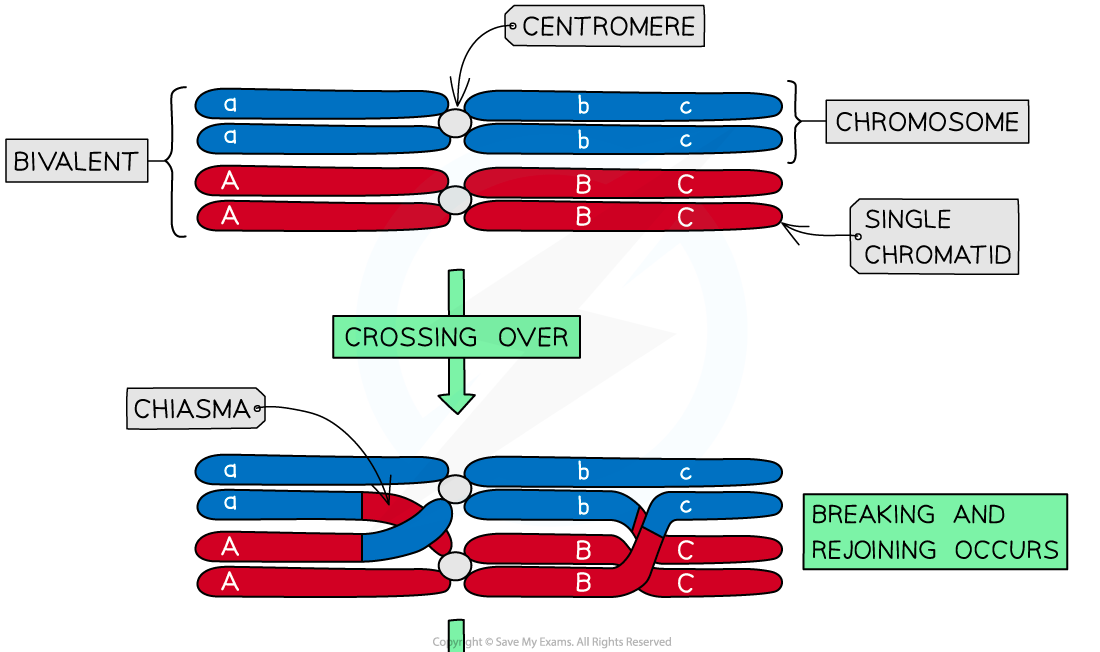
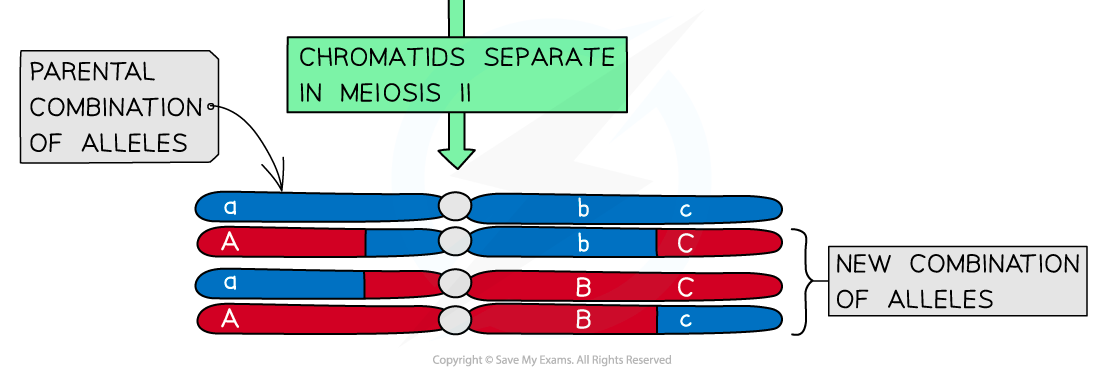
Crossing over of non-sister chromatids leading to the exchange of genetic material
Random Orientation
- At metaphase, during meiosis I, homologous chromosomes line up at the cell equator as they prepare to separate
- Spindle microtubules grow out from the poles of the cell and attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes
- Each of the two homologous chromosomes in a bivalent is attached to a different pole
- The orientation of the bivalents when they line up at the cell equator determines which pole each chromosome gets attached to (and eventually pulled towards)
- The orientation of the bivalents is completely random
- In addition, the bivalents also assort independently of one another (i.e. the orientation of one bivalent never affects the orientation of another)
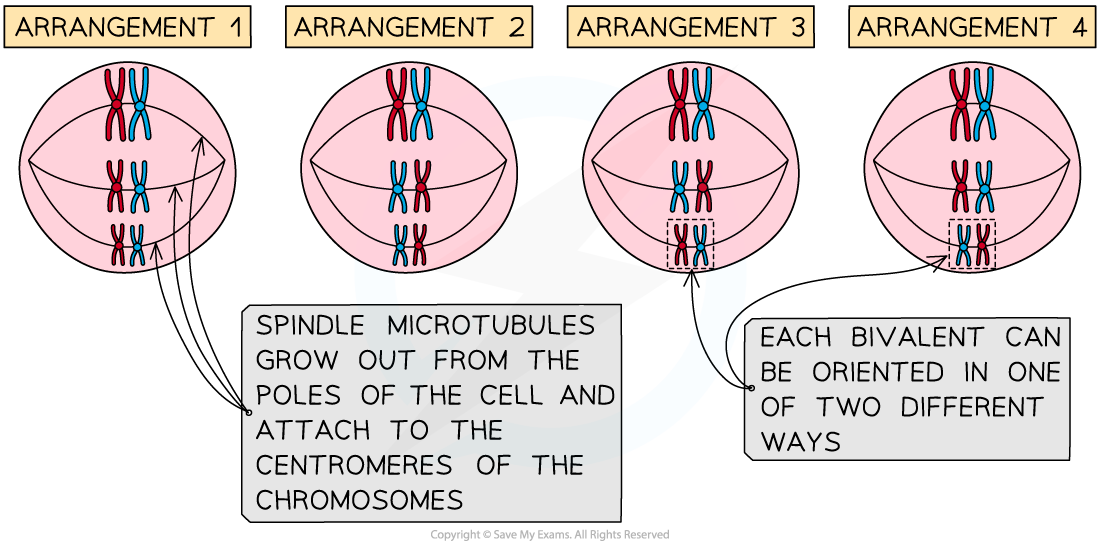
The orientation of bivalents lining up at the cell equator is random
Reduction Division
- During meiosis, the homologous chromosomes forming a bivalent separate in a process known as disjunction
- The homologous chromosomes then move to opposite poles of the cell
- As one chromosome of each type moves to each pole, the two separate nuclei formed by the first division of meiosis (meiosis I) now only contain one of each type of chromosome, making the two new cells haploid
- Essentially, the chromosome number of the cells has been halved
This is why the first division of meiosis is known as a reduction division
- The chromosome number has been reduced (halved) from diploid to haploid
转载自savemyexams

最新发布
© 2026. All Rights Reserved. 沪ICP备2023009024号-1









